This document presents a case study on scrum methodology, focusing on its implementation, measurement metrics, and evaluation from both business and developer perspectives. It outlines specific goals such as assessing defect density, estimating project costs, and evaluating team effectiveness with scrum practices. The conclusion emphasizes the need for an in-depth understanding of scrum usage in organizations and improving processes through appropriate metrics.







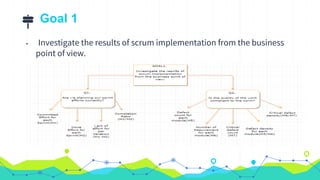
![Measurement Construct
MC #:
Related IRF #:
Information Need Calculating defect density for each module in scrum project
Measurable Concept Project defect density
Applied Levels [ ] Organization [ X ] Project
Relevent Entities 1. Found defects for each module
2. Requirements of each module
Attributes 1. Module defects
2. Module requirements
Base Measures M5: Defect count for each module
M6: Number of requirements for each module
Measurement Method 1. Count found defects for each module
2. Count requirements for each module
Type of Measurement Method 1. Objective
2. Objective
Scale 1. Integers from zero to infinity
2. Integers from zero to infinity
Type of Scale 1. Ratio
2. Ratio
Unit of Measurement 1. Defects
2. Requirements
Derived Measure Defect density for each module
Measurement Function Divide Total Defect Count of Each Module to Total Requirement Count of Each Module
Indicator Module defect density relative to requirement size of a module
Model Compute defect density by dividing number of requirements over defect count for each module
Decision Criteria Defect count of a module should be less than half of the requirement count of a module](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmp782-projectpresentation-180324144712/85/A-Case-Study-Measuring-Scrum-Implementation-9-320.jpg)

![Measurement Construct
MC #:
Related IRF #:
Information Need Estimation of the project cost that use scrum methodology.
Measurable Concept Project cost – Rework density
Applied Levels [ ] Organization [ X ] Project
Relevent Entities 1. PBI values that produced by team
2. Rework PBI values that produced by team
Attributes 1. Product Backlog Item (PBI)
2. PBI Phase Number
Base Measures M20: Total PBI Count
M21: Rework PBI Count
Measurement Method 1. Count PBI for all sprints
2. Count PBI phases for all PBI’s for all sprints
Type of Measurement Method 1. Objective
2. Objective
Scale 1. Integers from zero to infinity
2. Integers from zero to infinity
Type of Scale 1. Ratio
2. Ratio
Unit of Measurement 1. PBI
2. PBI
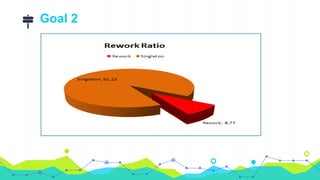
Derived Measure PBI Rework Ratio
Measurement Function Divide Total PBI Count by Rework PBI Count
Indicator Rework Ratio of Scrum
Model Compute each distinct PBI and repeated PBI (PBI Phases)
Decision Criteria Resulting ratio should less than 0.10 to carry on more effective scrum and to reduce cost of the project](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmp782-projectpresentation-180324144712/85/A-Case-Study-Measuring-Scrum-Implementation-12-320.jpg)