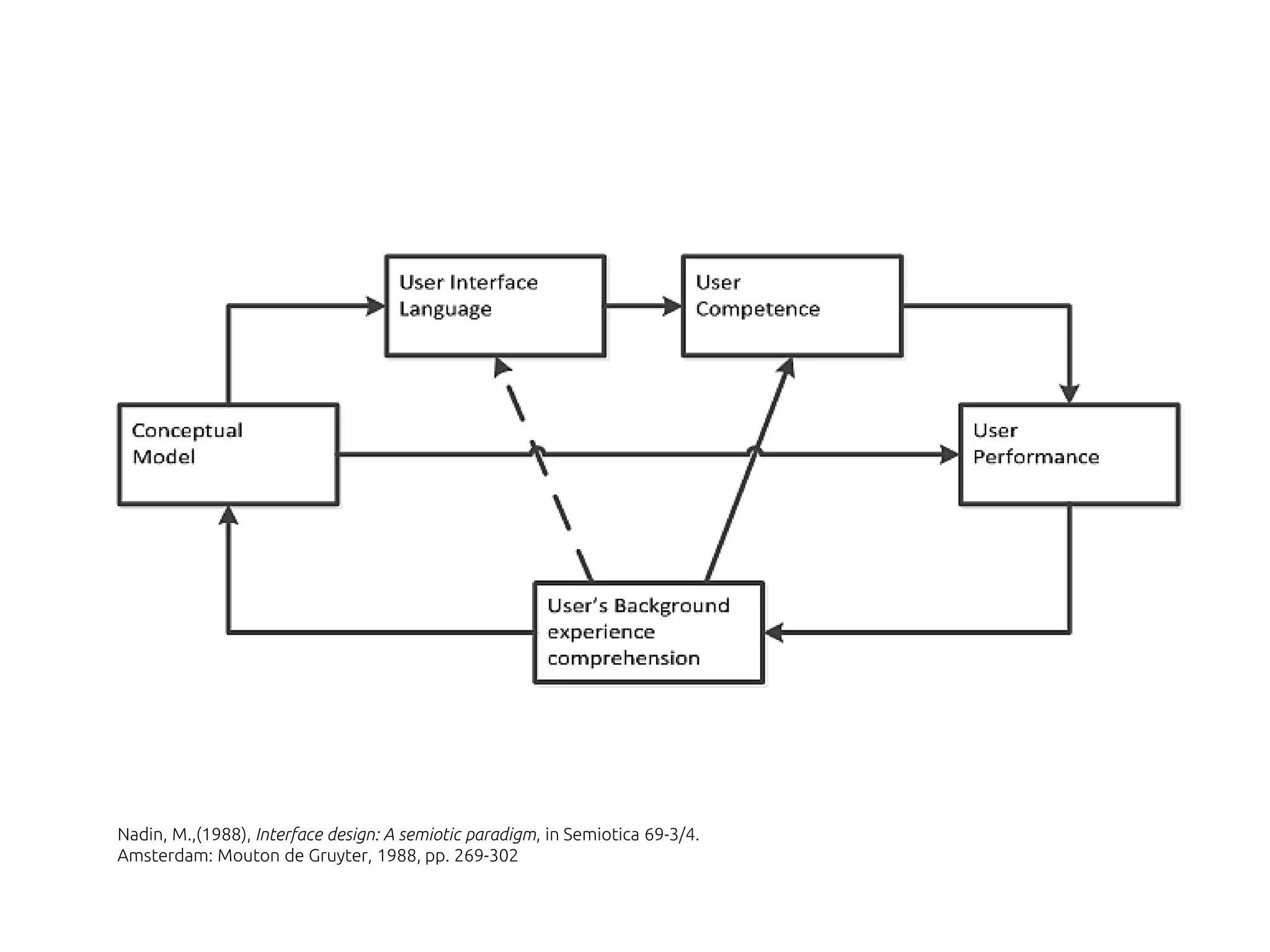
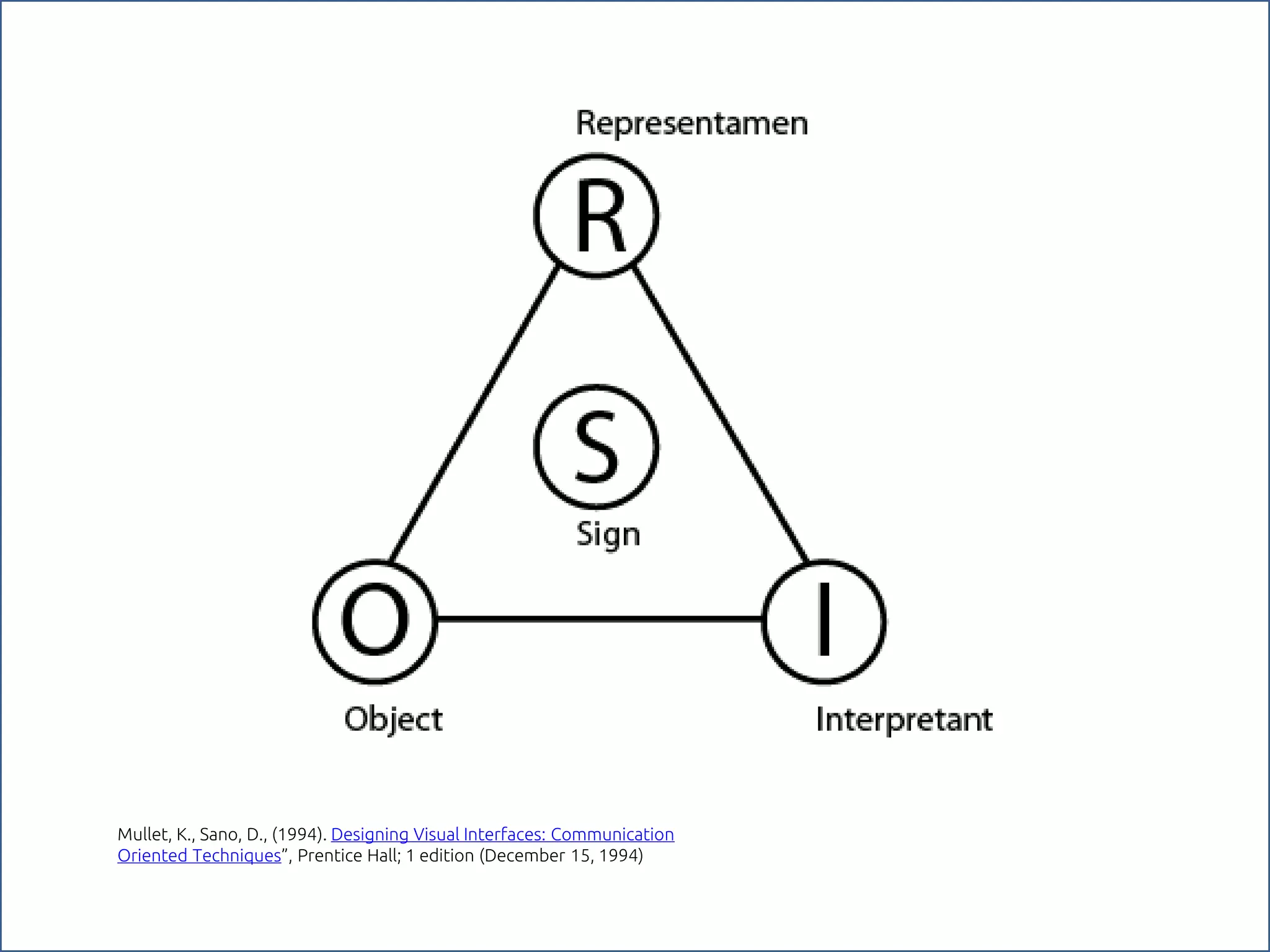
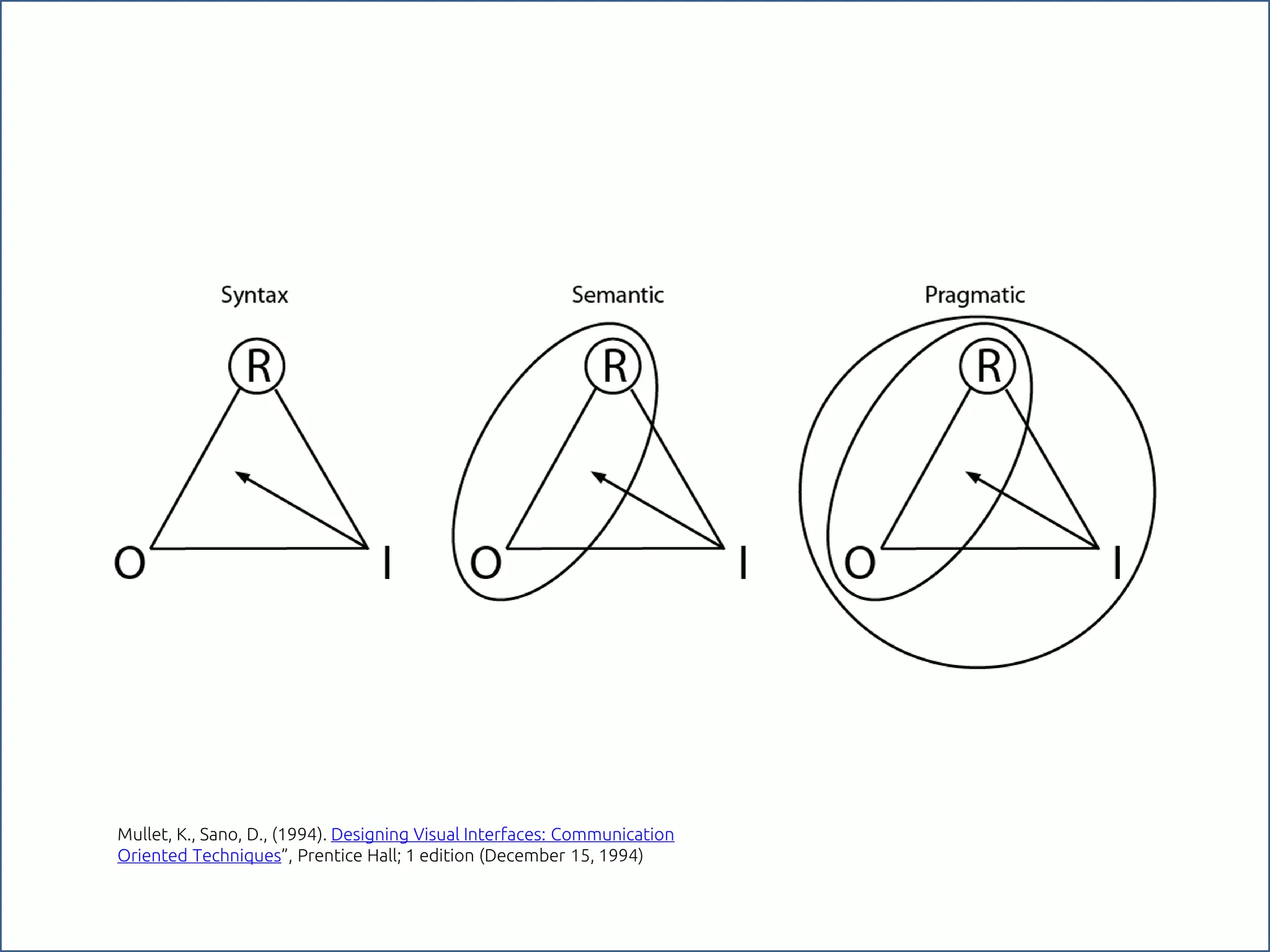
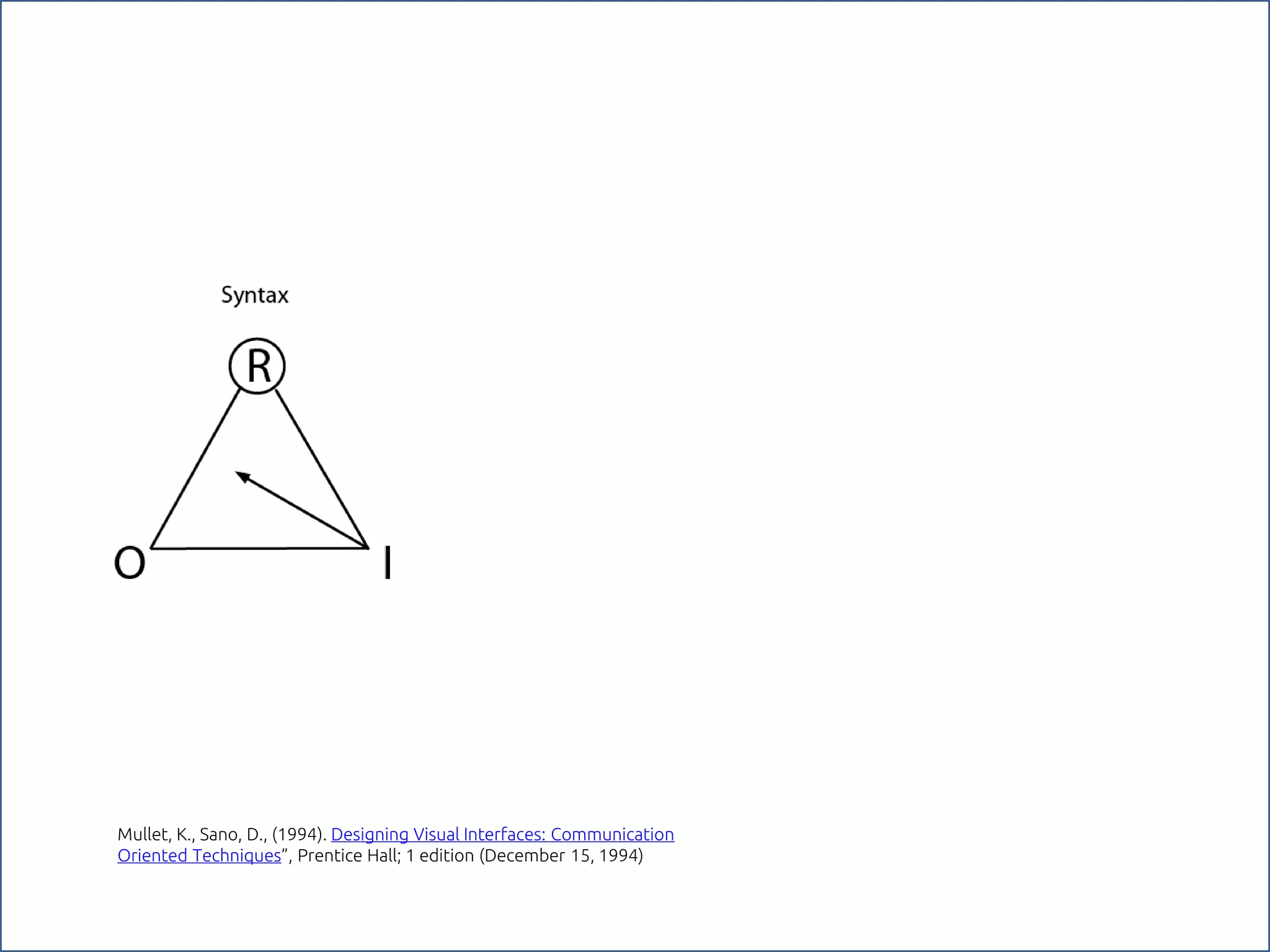
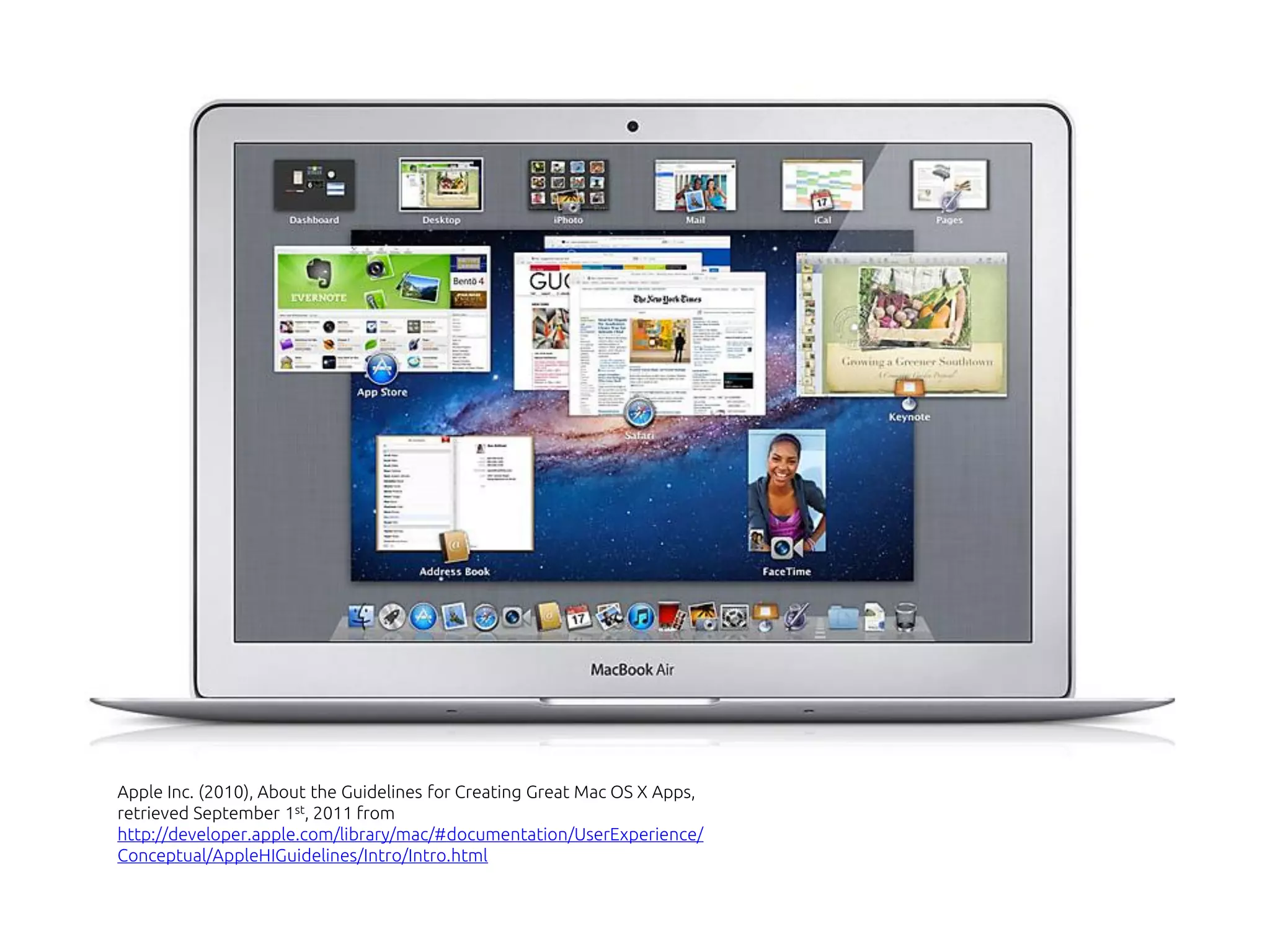
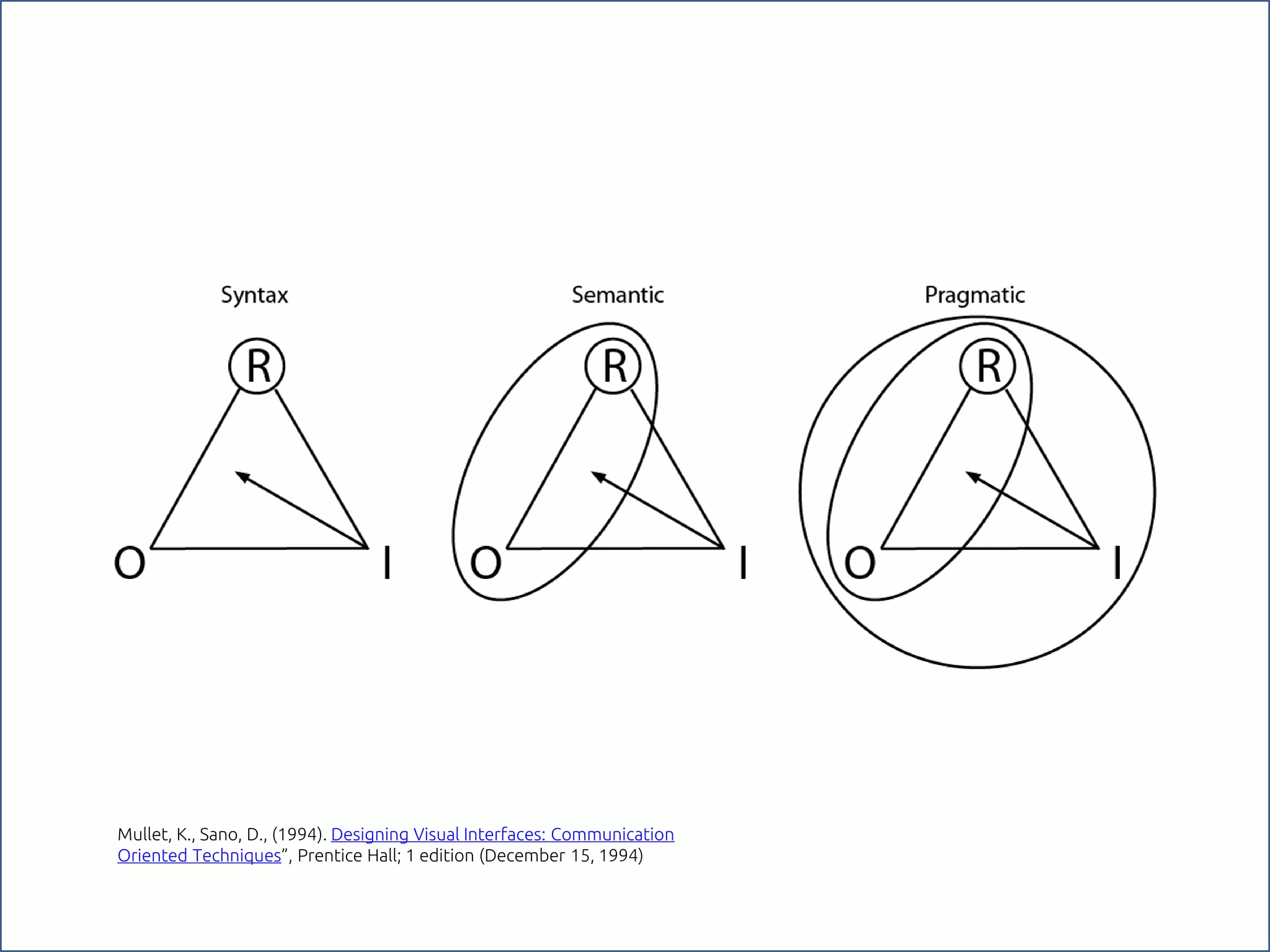
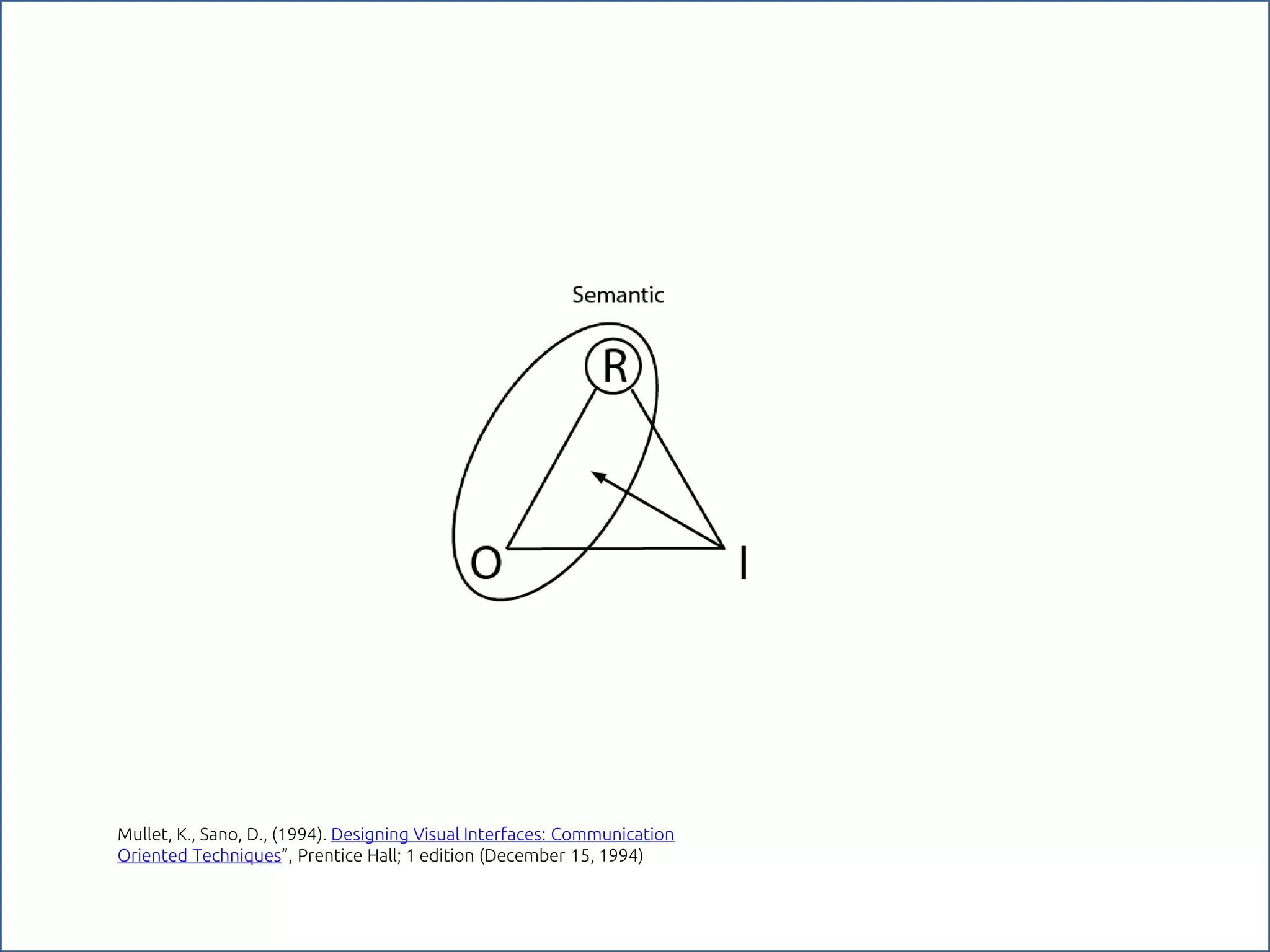
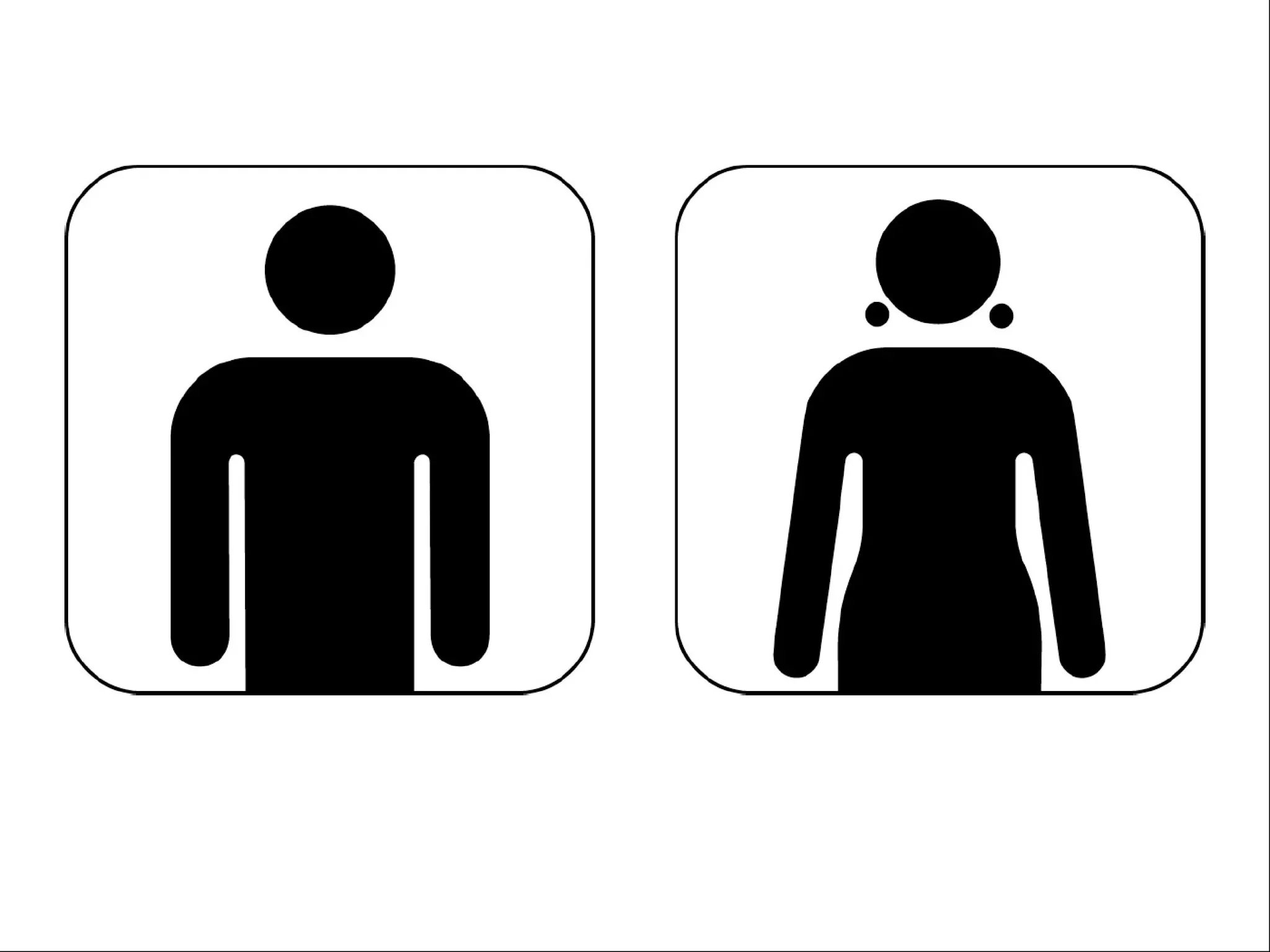
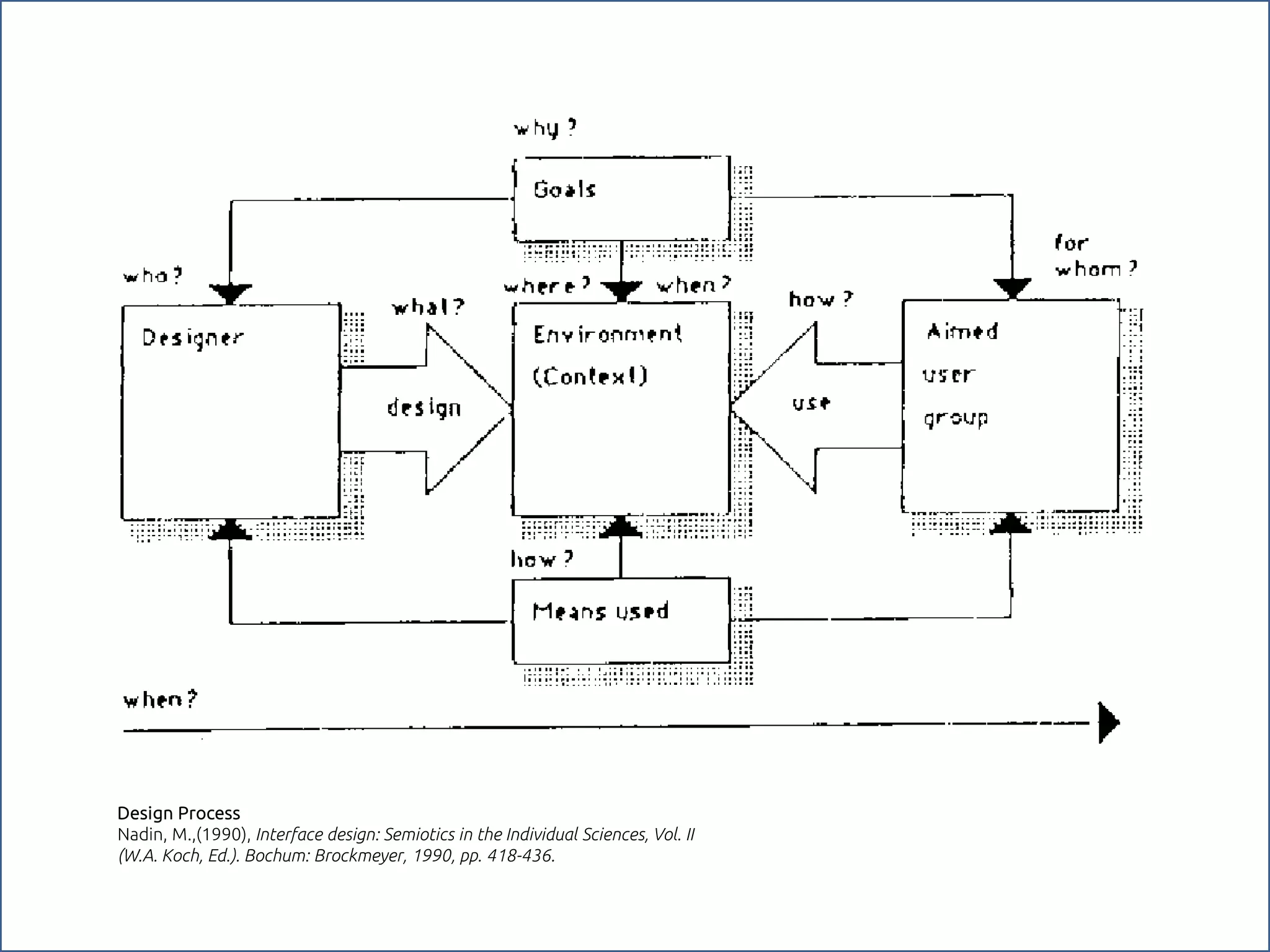
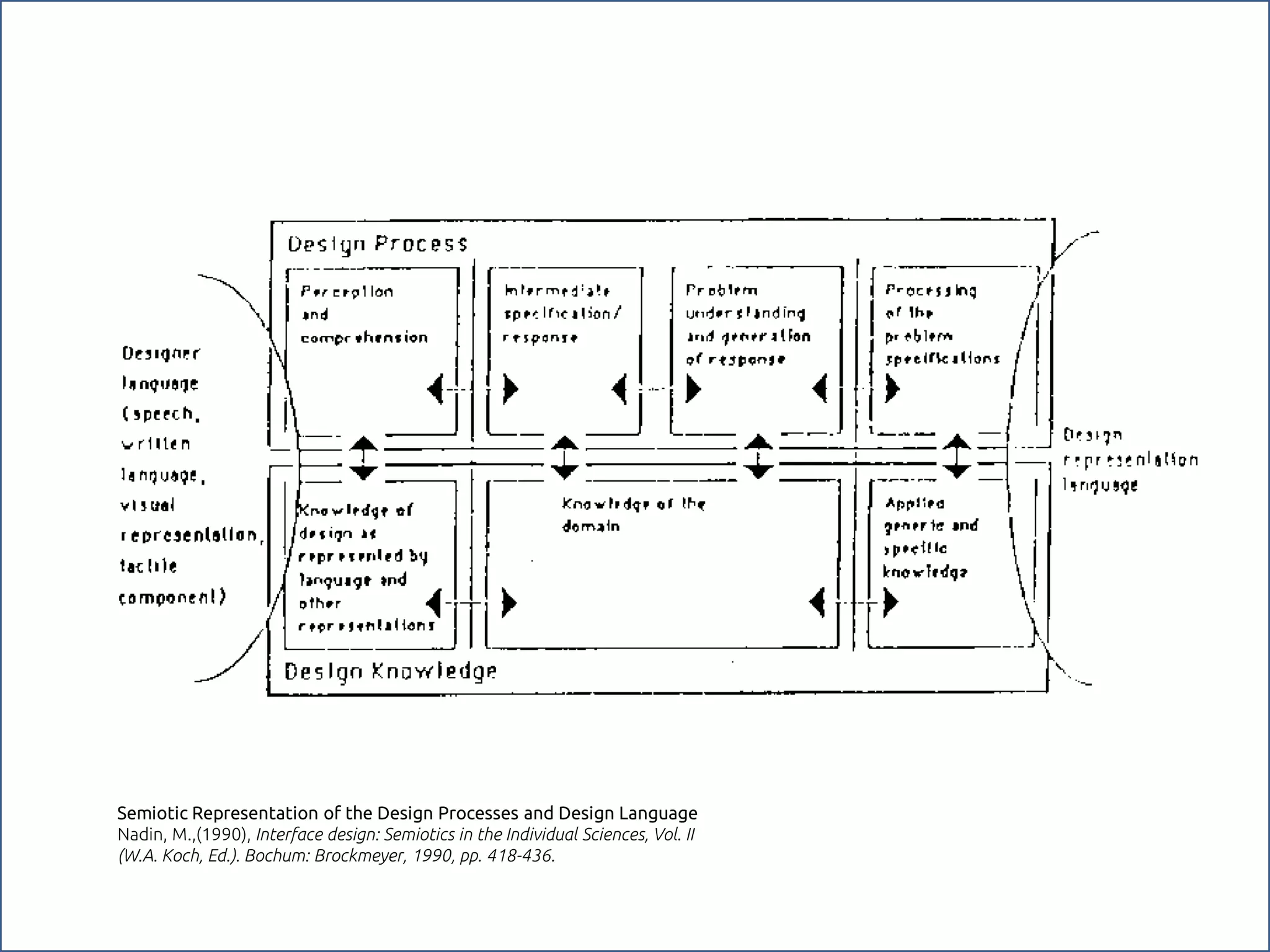
The document discusses the role of metaphors in information design, emphasizing their importance for helping users comprehend conceptual models. It covers various aspects including semiotics, principles of interaction design, and exercises to apply these concepts in practice. Additionally, it provides a framework for evaluating products and services based on their visual communication and conceptual clarity.