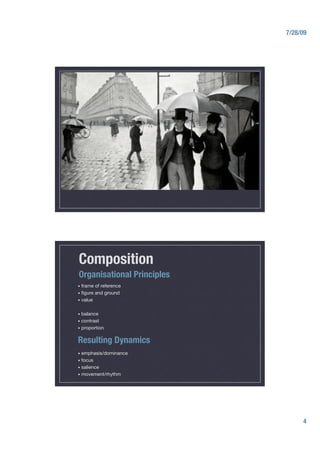
This document provides an overview of the Visual Interactions unit which includes lectures, tutorials, and case studies covering topics such as image, narrative, time, action, interaction and culture. It examines the primary elements of form in images including line, shape, texture and colour. It also discusses principles of composition and how they create dynamics like emphasis, focus, and movement. Additional sections explore content, context, interpretive models, and the interface between images and actions. Project criteria and examples are also mentioned.