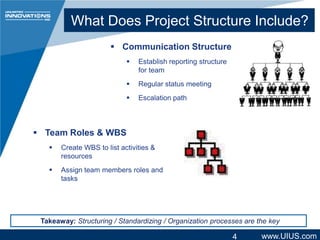
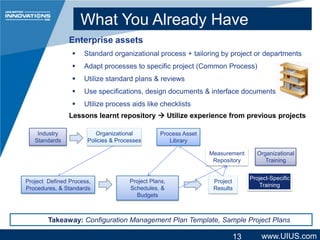
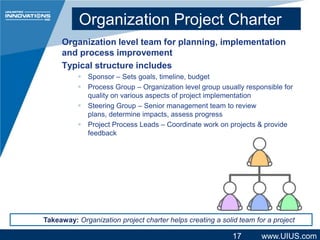
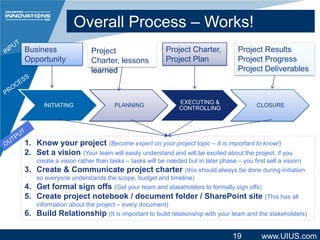
The document discusses project management structure and outlines key areas to focus on when planning a project. It emphasizes establishing clear communication structures, work breakdown structures (WBS), documentation standards, and change control processes. The document also stresses the importance of understanding stakeholders, selecting an effective project team, and providing necessary training. Overall, it advocates for a structured approach to project planning and management to achieve predictable performance, capture lessons learned, and ensure quality outcomes.