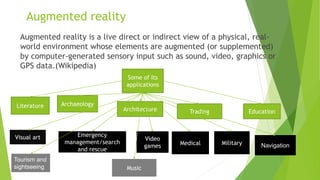
The document summarizes how humans have changed the earth from 4000 BC to present day through developments in transportation, infrastructure, industry, and technology. It describes key inventions and advancements such as the domestication of animals, wheeled vehicles, ships, roads, the steam engine, railroads, planes, telecommunications, and space exploration. These developments enabled migration, trade, war, and globalization, fundamentally transforming humans' ability to interact and impact the world.























![Example - The cellphone
John F. Mitchell and Martin Cooper of Motorola developed
the first handheld mobile phone in 1973.
The “DynaTAC8000x” in 1983, was the first commercially
available handheld mobile phone. It used analog technology
[first-generation ( 1G )].
The contemporary type of cell phone is the smartphone
which has many more advantages than every other type of
cell phone
The
evolution
of the cell
phone
Its usage is
diverse
Long-distance
communication Information
BusinessEntertainment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2davakispanagiotisg2-170420091741/85/The-Athropocene-27-320.jpg)