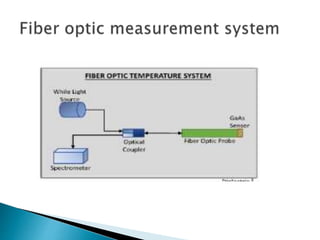
Optical fibers are made of transparent materials that guide light over long distances. Fiber optic sensors are used in industries to monitor quantities such as displacement, pressure, temperature, and flow rate. Fiber optic thermometers specifically measure temperature using either blackbody radiation physics for higher temperatures from 400-1600°C or by activating sensing materials like phosphors, semiconductors, or liquid crystals for lower temperatures from -100°C to 400°C. Fiber optic sensors offer advantages of being passive, immune to electromagnetic and microwave interference, resistant to harsh environments, small in size, and able to monitor physical and chemical parameters remotely.