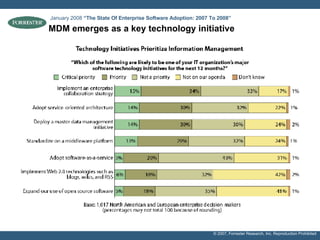
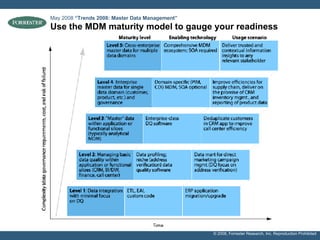
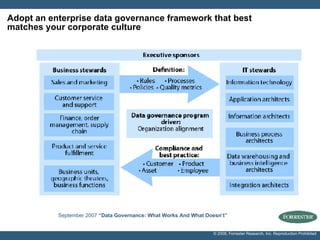
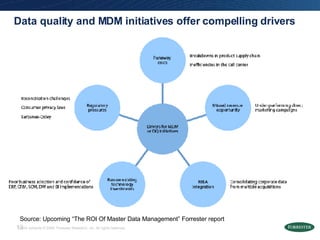
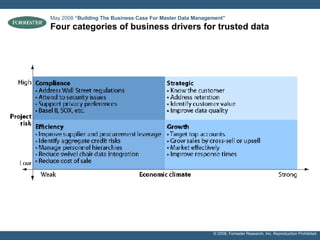
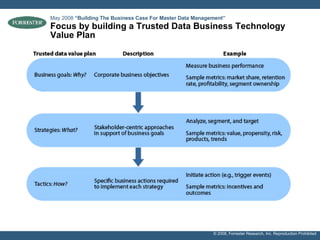
- The document discusses building a business case for trusted data and master data management (MDM) initiatives through a bottom-up valuation approach. It recommends starting with an individual line-of-business process to identify and address data quality issues to quickly realize value.
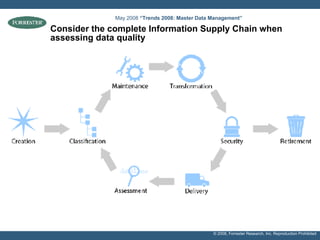
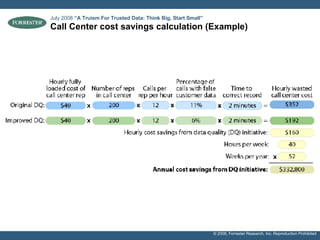
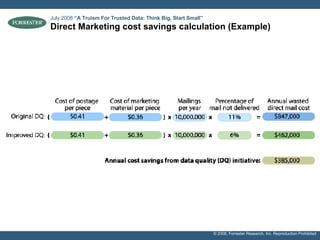
- Examples of target processes include reducing call center inefficiencies through better customer data, decreasing wasted marketing costs from improved targeting, and lowering supply chain breakdowns by ensuring data integrity. Metrics like data freshness, accuracy, and completeness should be used to ensure initiatives are on track.
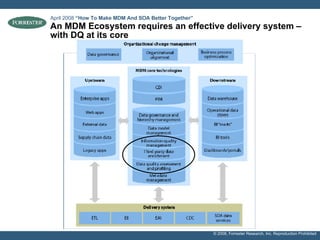
- A multi-phase, long-term view of data governance as a "trusted data program" is advocated over viewing MDM as the goal in itself. Buy-








!["It took me three years and millions of dollars to recognize that data management is an enabler supporting the business, but [it] does not in and of itself reduce costs or deliver revenue." VP of data management for large global technology firm Welcome to the trusted data business case crossroads](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rob-karel-ensuring-the-value-of-your-trusted-data-v2-1226607754904311-9/85/Rob-Karel-Ensuring-The-Value-Of-Your-Trusted-Data-Data-Quality-Summit-2008-17-320.jpg)











![Thank you Rob Karel +1 650/581-3821 [email_address] www.forrester.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rob-karel-ensuring-the-value-of-your-trusted-data-v2-1226607754904311-9/85/Rob-Karel-Ensuring-The-Value-Of-Your-Trusted-Data-Data-Quality-Summit-2008-31-320.jpg)
