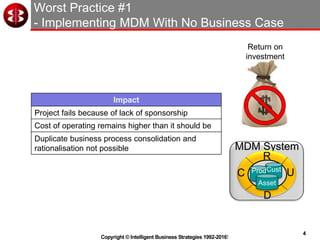
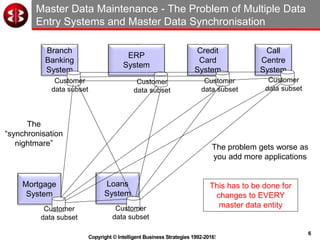
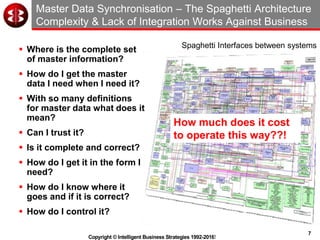
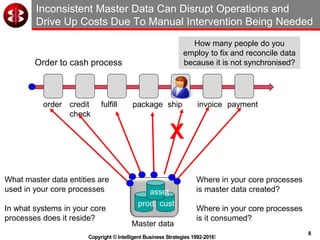
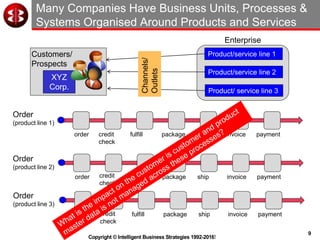
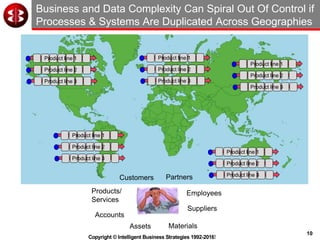
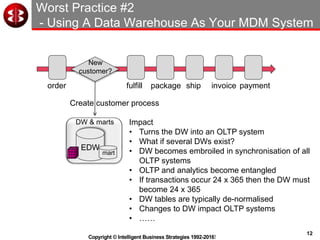
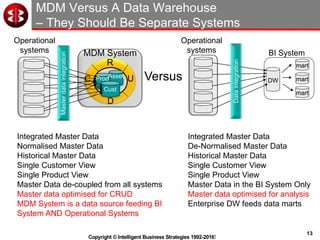
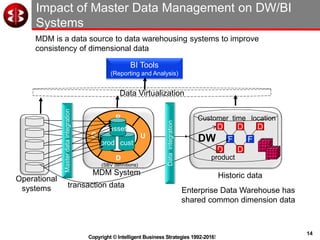
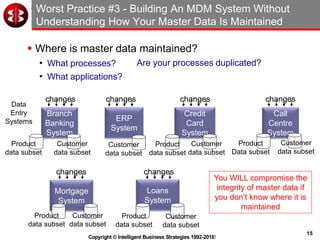
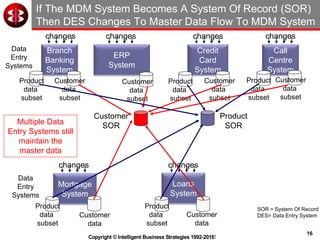
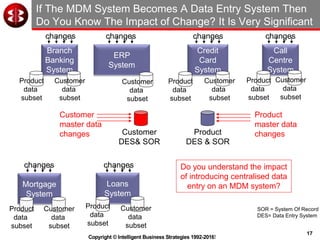
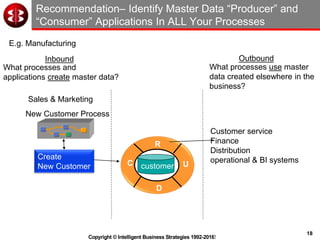
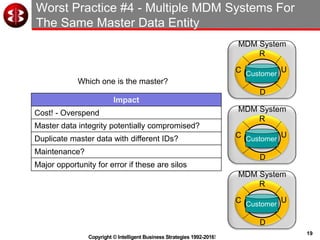
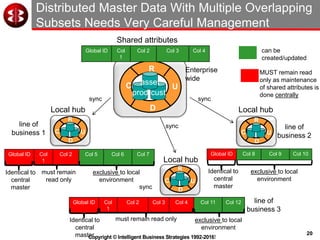
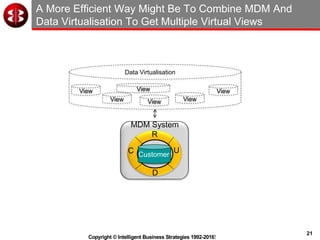
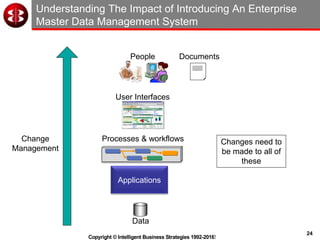
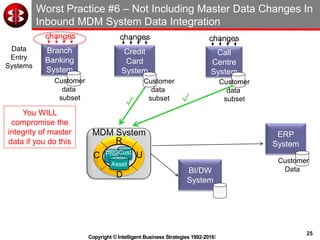
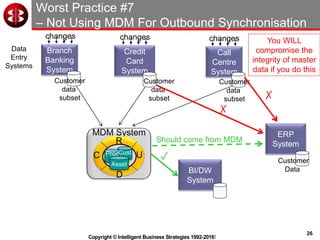
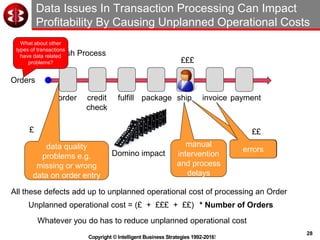
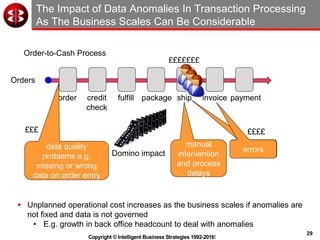
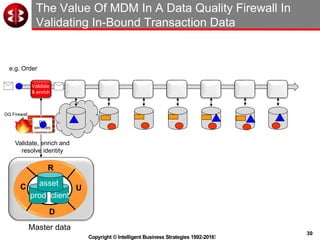
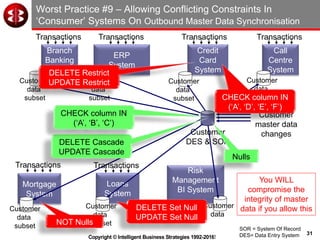
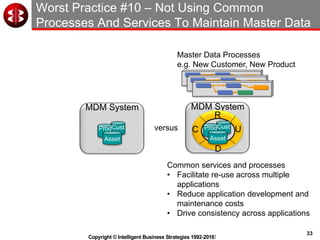
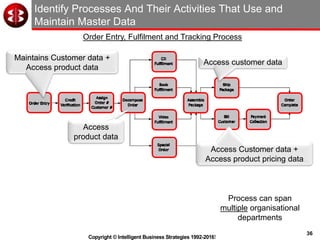
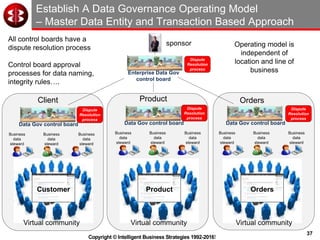
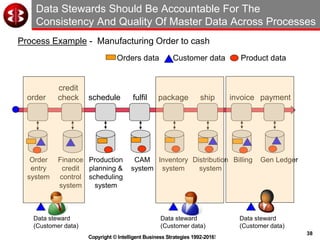
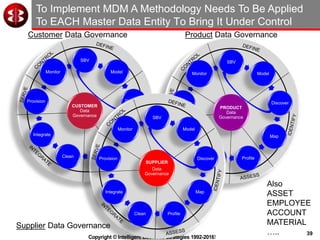
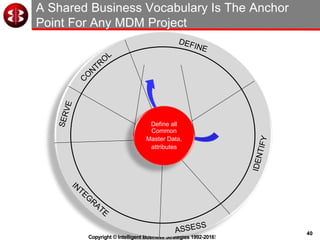
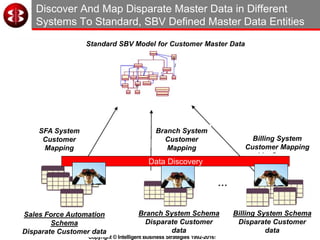
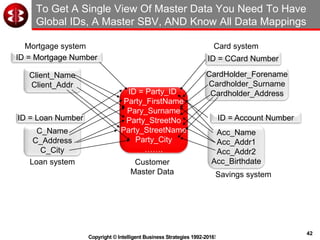
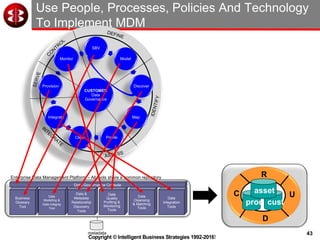
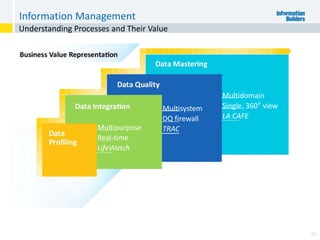
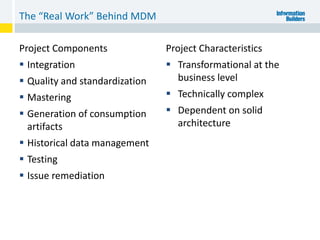
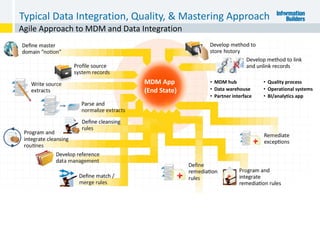
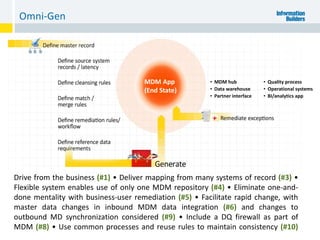
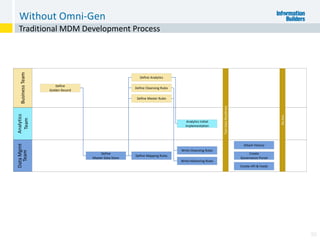
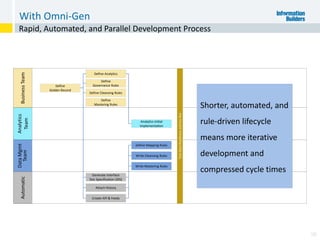
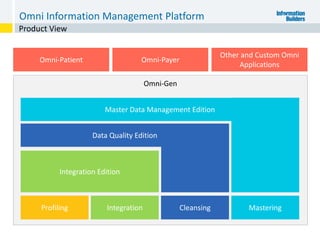
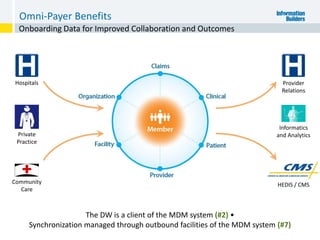
The document outlines the ten worst practices in Master Data Management (MDM), emphasizing the pitfalls of inadequate business cases, poor integration of MDM with data warehouses, and the consequences of managing multiple MDM systems. It underscores the importance of understanding processes and systems that maintain master data to ensure integrity and effective synchronization. Recommendations are provided for establishing data governance and managing data effectively across the enterprise.