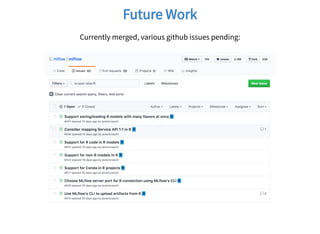
The document discusses MLflow, a tool for managing the machine learning lifecycle, and its integration with R, highlighting R's capabilities for statistical computing and data visualization. It covers various MLflow functionalities, including tracking experiments, managing models, and running projects, while also providing R coding practices and examples. Additionally, it details installation steps, tracking methods, and saving and serving models using MLflow in R.








![How to NOT write R codeHow to NOT write R code
This is how I would have written R code as a so ware engineer before
knowing R:
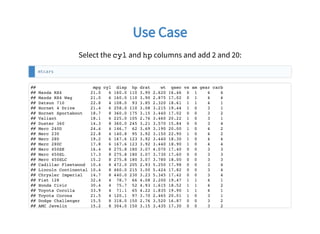
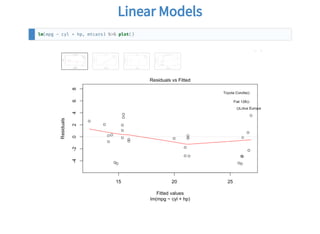
# Select columns subset
data = data.frame(mtcars$cyl, mtcars$hp)
colnames(data) = c("cyl", "hp")
# Transform each row
for (idx in 1:nrow(data)) {
data$cyl[idx] = data$cyl[idx] + 2
}
# One column at a time to use the CPU cache efficiently
for (idx in 1:nrow(data)) {
data$hp[idx] = data$hp[idx] + 20
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlflow-with-r-javier-luraschi-180924235830/85/MLflow-with-R-11-320.jpg)










![Models - SavingModels - Saving
mlflow_save_model(model)
Generic functions are serialized with crate:
column mlflow_log_param("column", 1)
model lm(
Sepal.Width ~ x,
data.frame(Sepal.Width = iris$Sepal.Width, x = iris[,column])
)
mlflow_save_model(
crate(~ stats predict(model, .x), model)
)
However, mlflow_save_model() can be extended by packages:
#' @export
mlflow_save_flavor.tensorflow function( ) {}
mlflow_load_flavor.tensorflow function( ) {}
mlflow_predict_flavor.tensorflow function( ) {}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlflow-with-r-javier-luraschi-180924235830/85/MLflow-with-R-26-320.jpg)
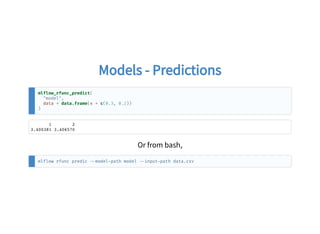
![Models - ServingModels - Serving
mlflow_rfunc_serve("model")
mlflow rfunc serve model path model
curl -X POST "http: 127.0.0.1 8090/predict/" -H "accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type:
application/json" d '[{"x": [0.3, 0.2]}]'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlflow-with-r-javier-luraschi-180924235830/85/MLflow-with-R-28-320.jpg)