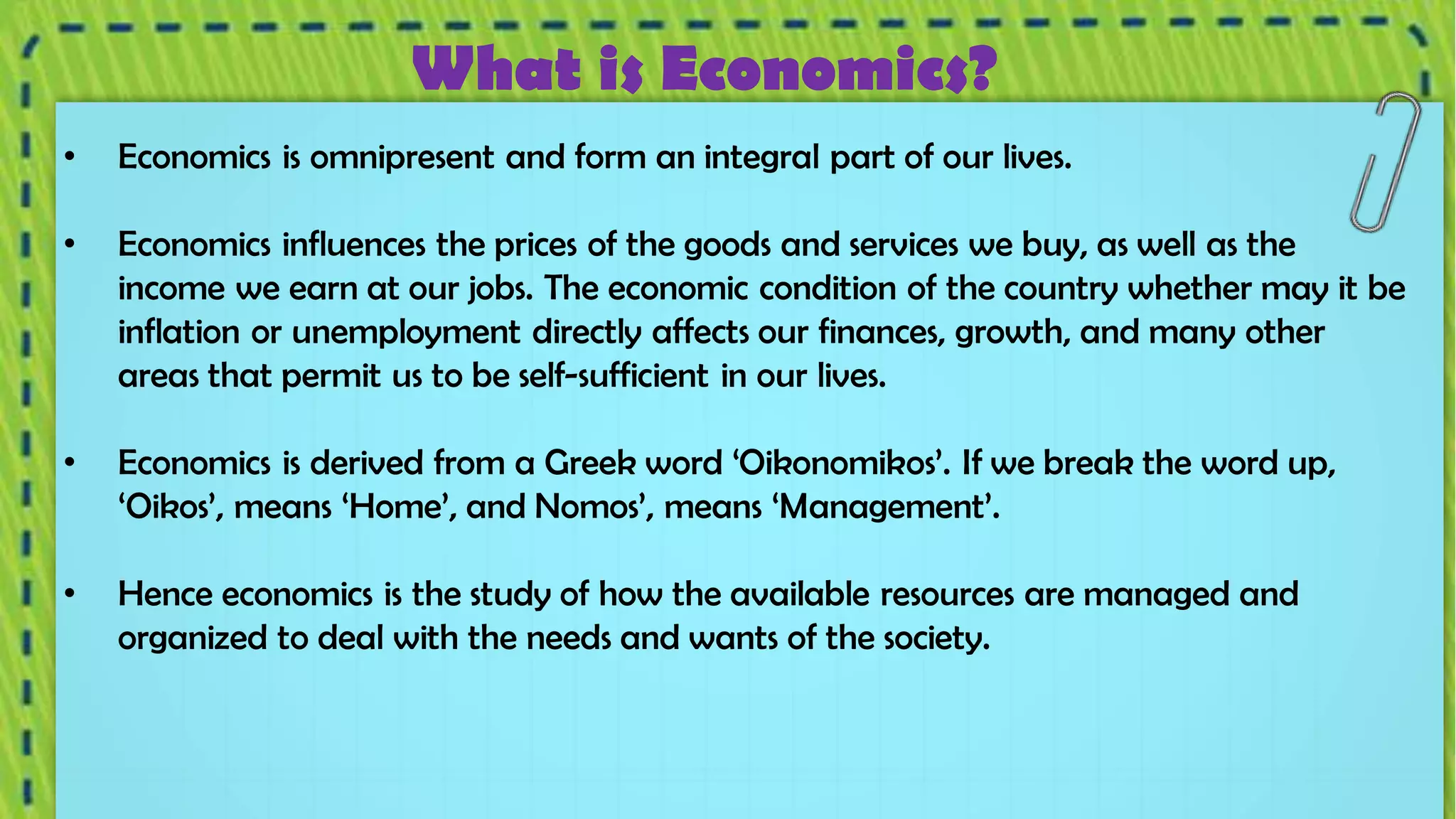
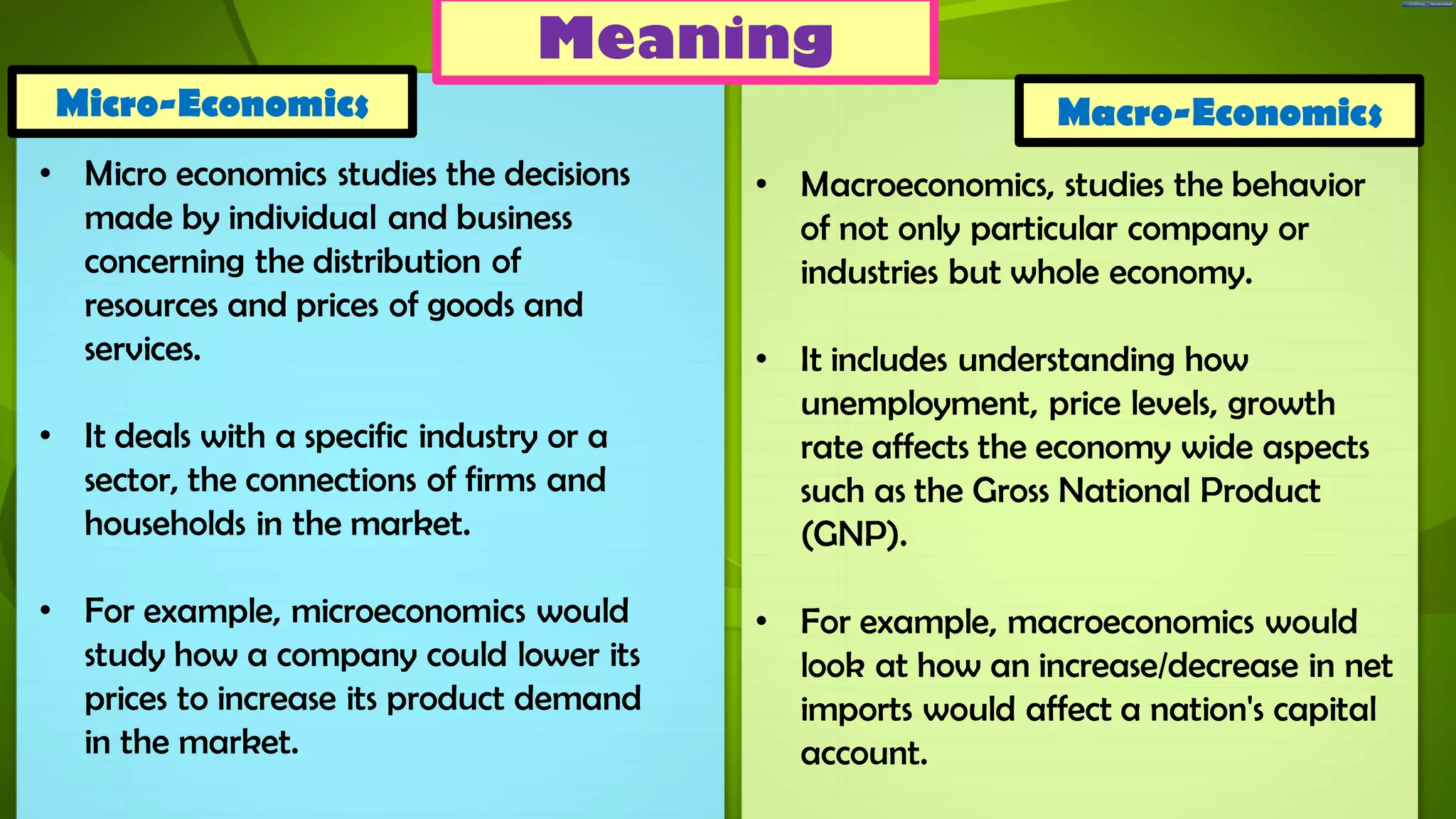
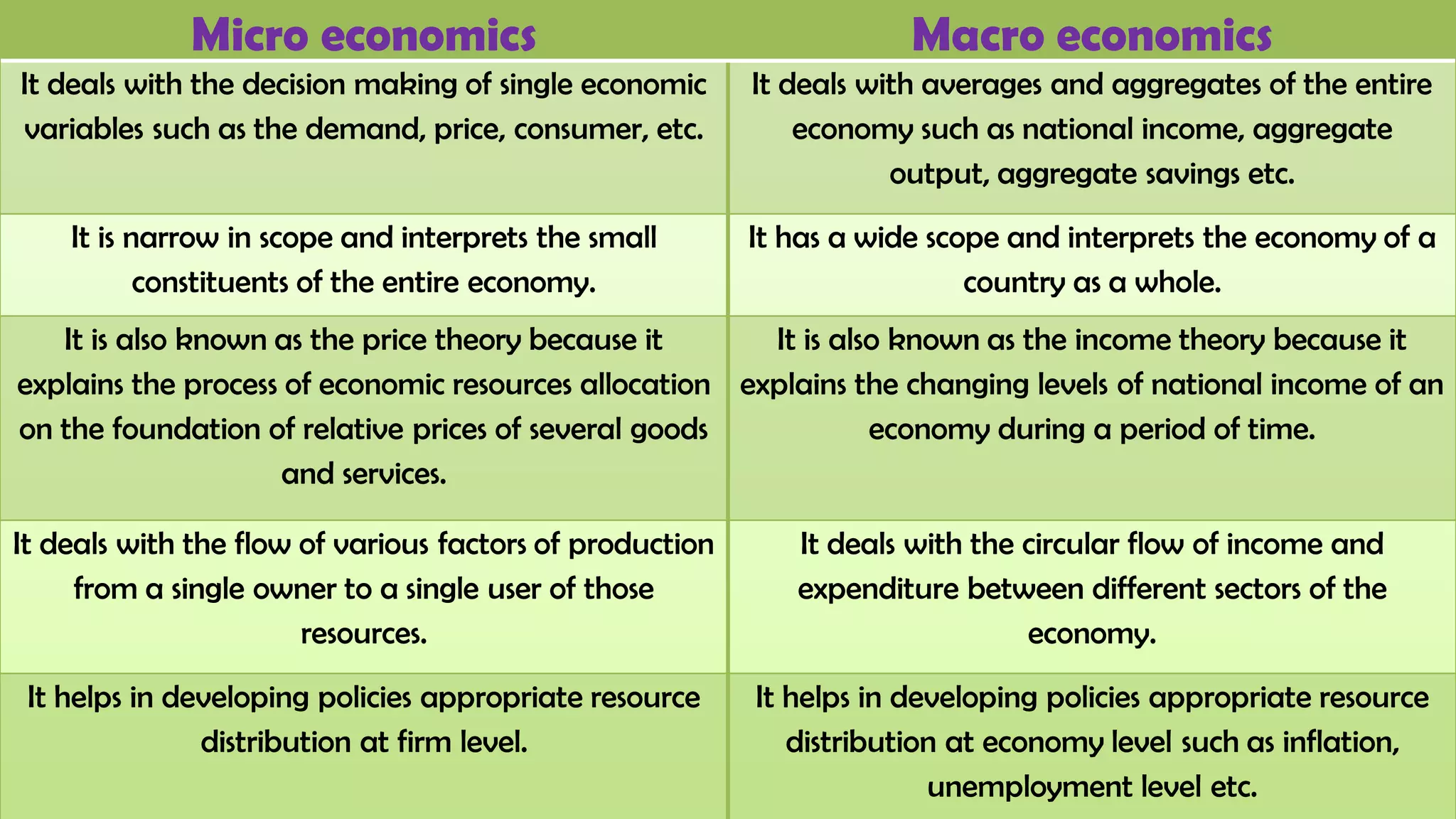
The document discusses the differences between microeconomics and macroeconomics, highlighting that microeconomics focuses on individual and business decisions regarding resource distribution and pricing, while macroeconomics examines the economy as a whole, including national income and aggregate output. It explains how these two areas of economics interact and influence one another, particularly in relation to factors like inflation and fiscal policies, which affect stock market performance. Additionally, the document touches on how external factors, such as conditions in the foreign market and interest rates, can impact economic conditions.