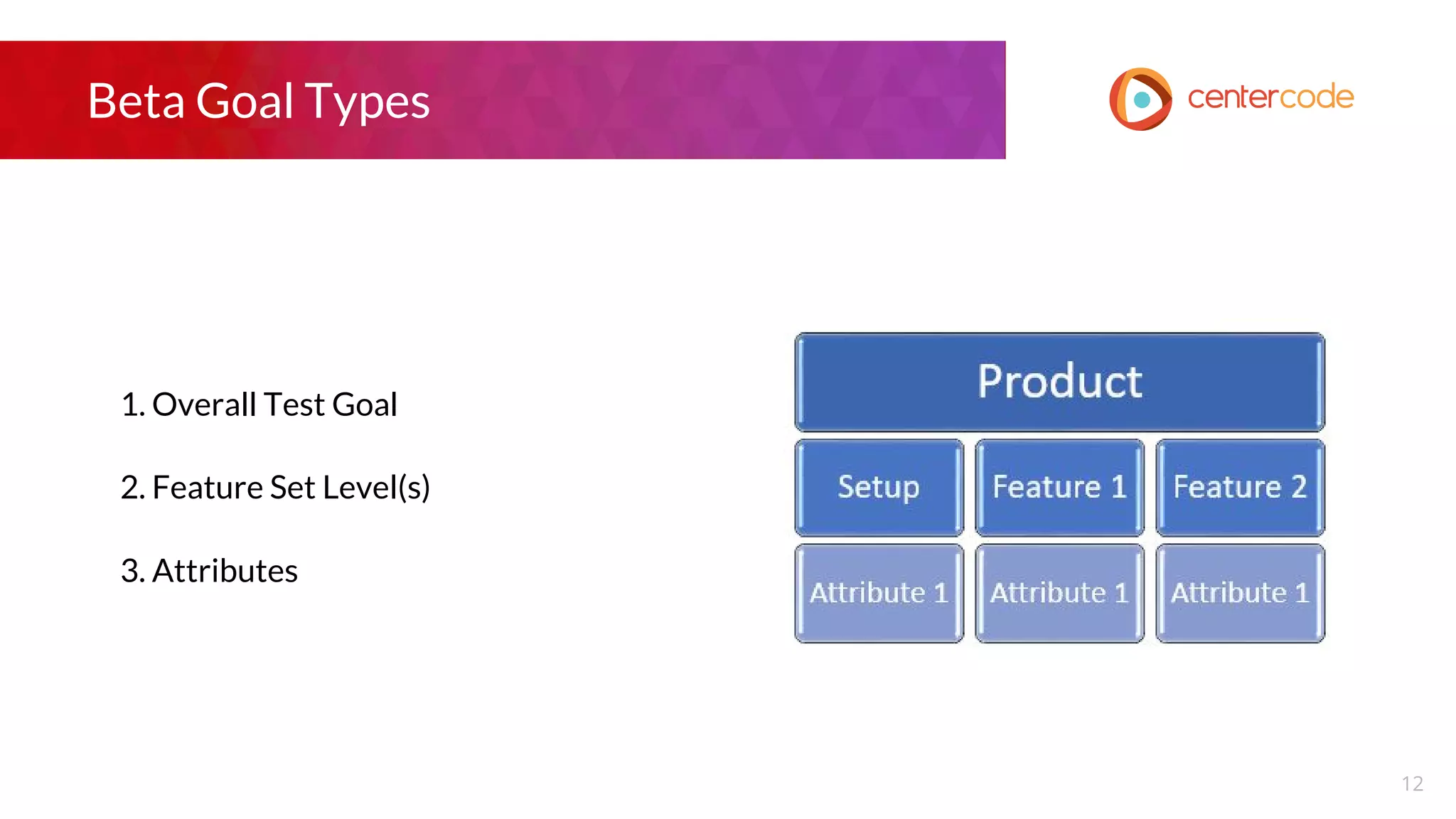
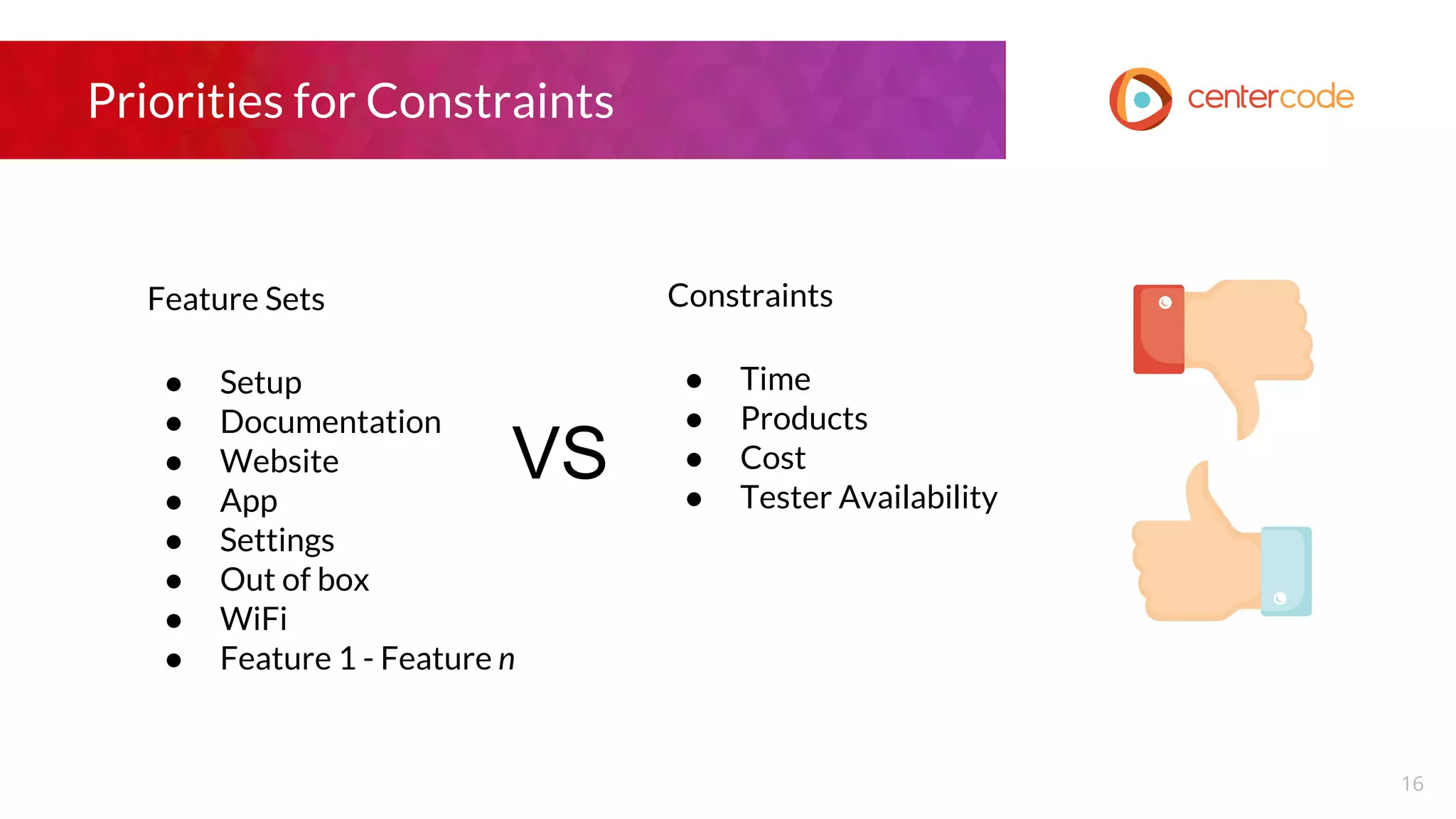
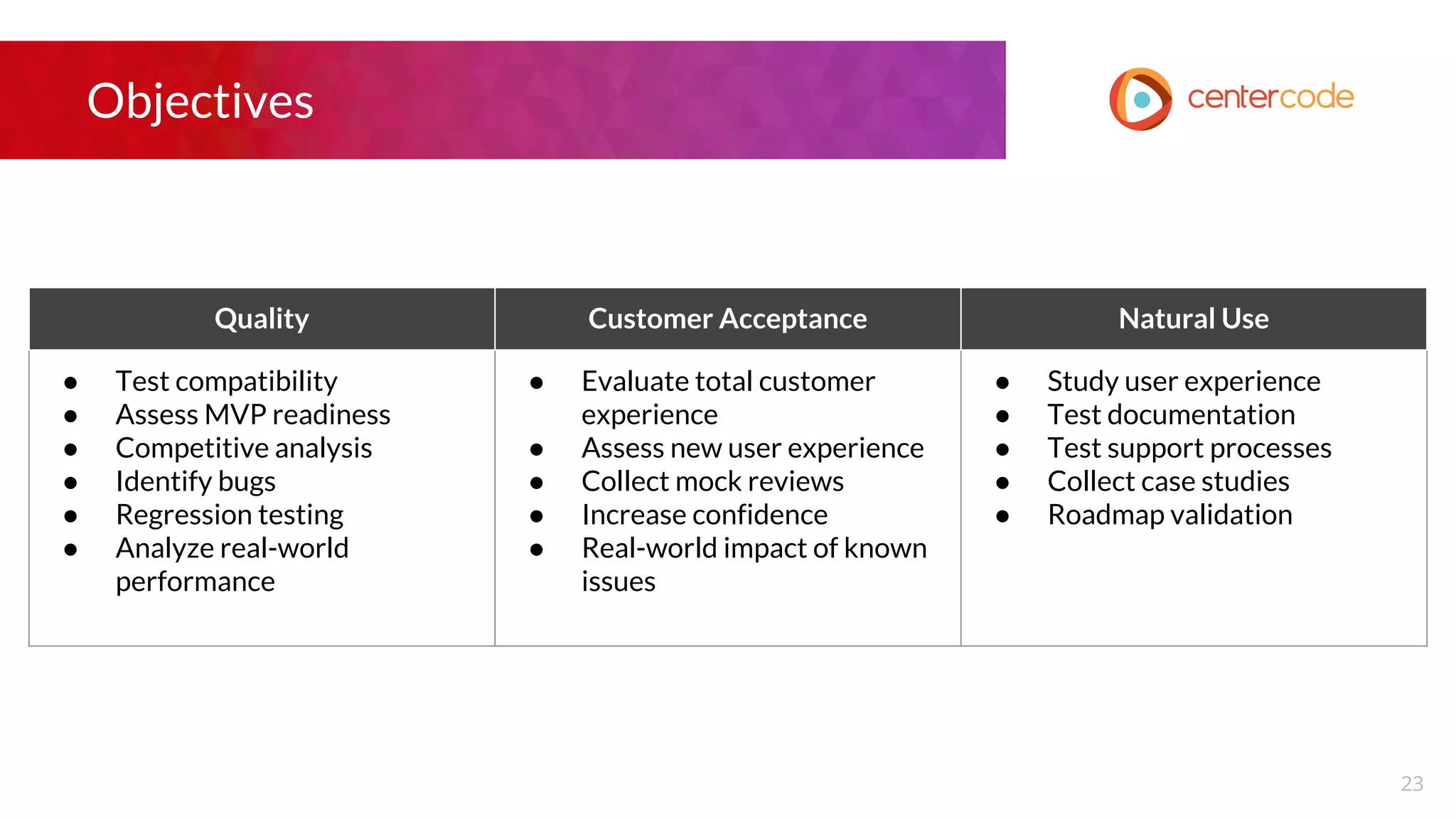
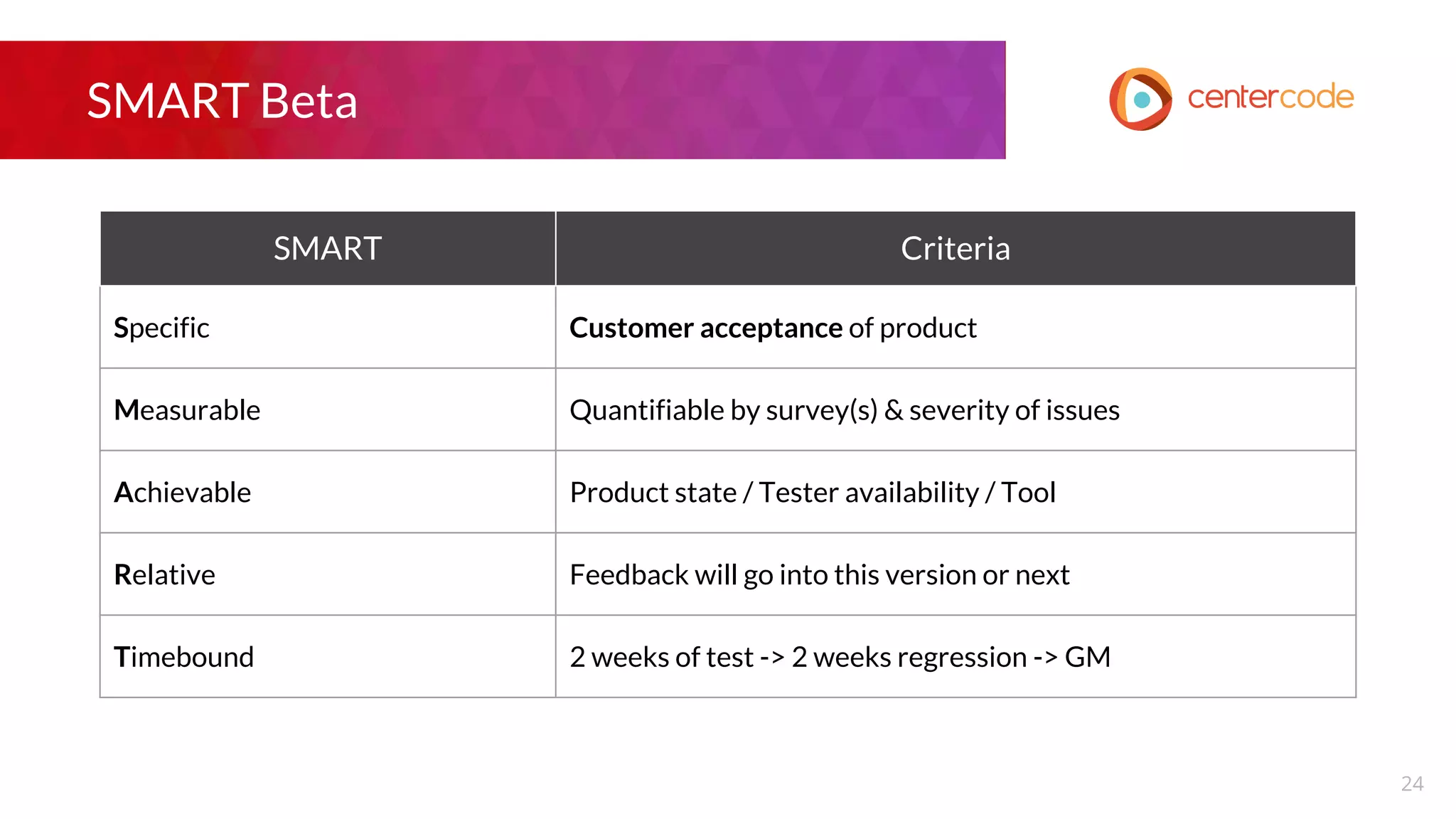
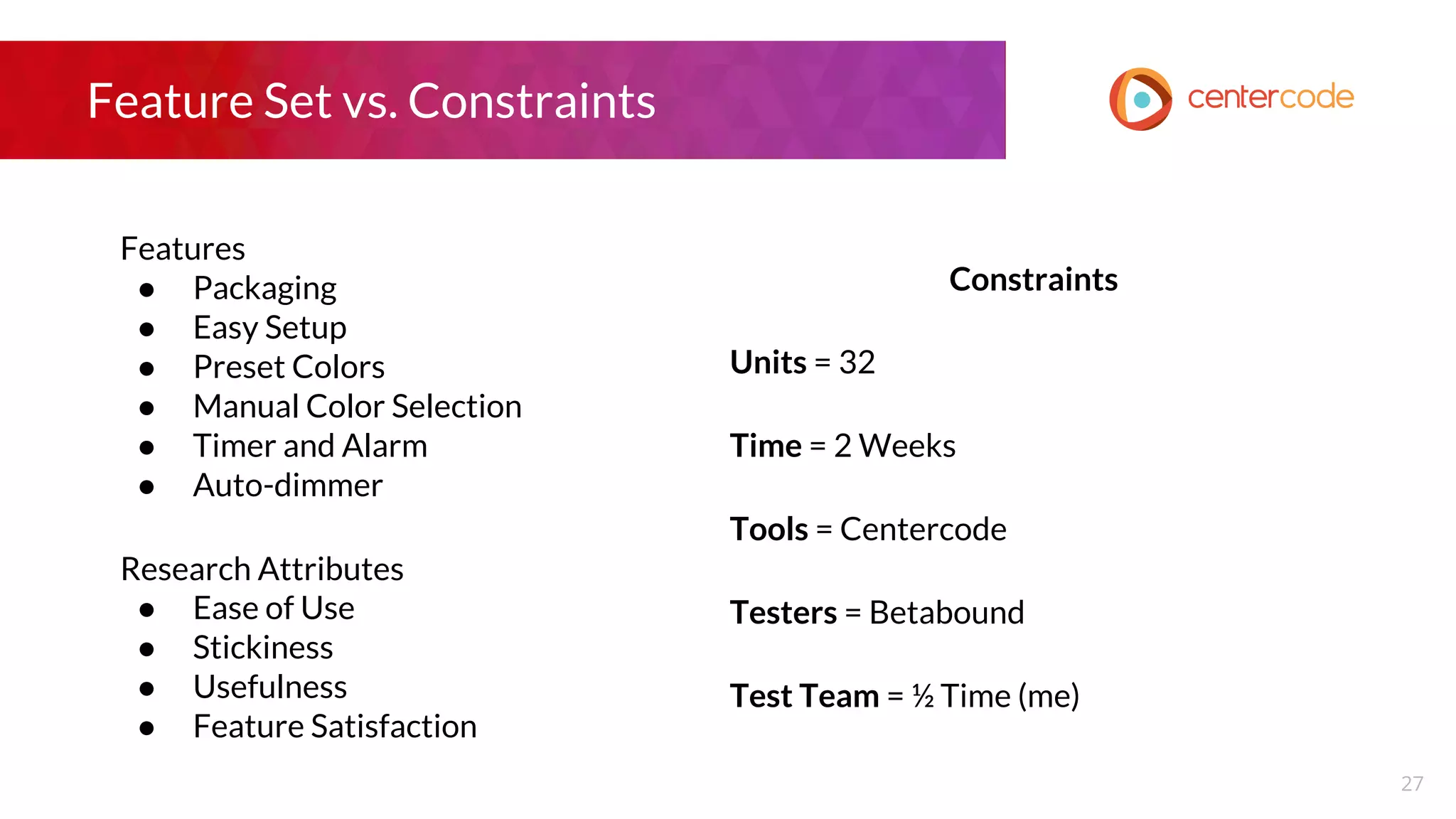
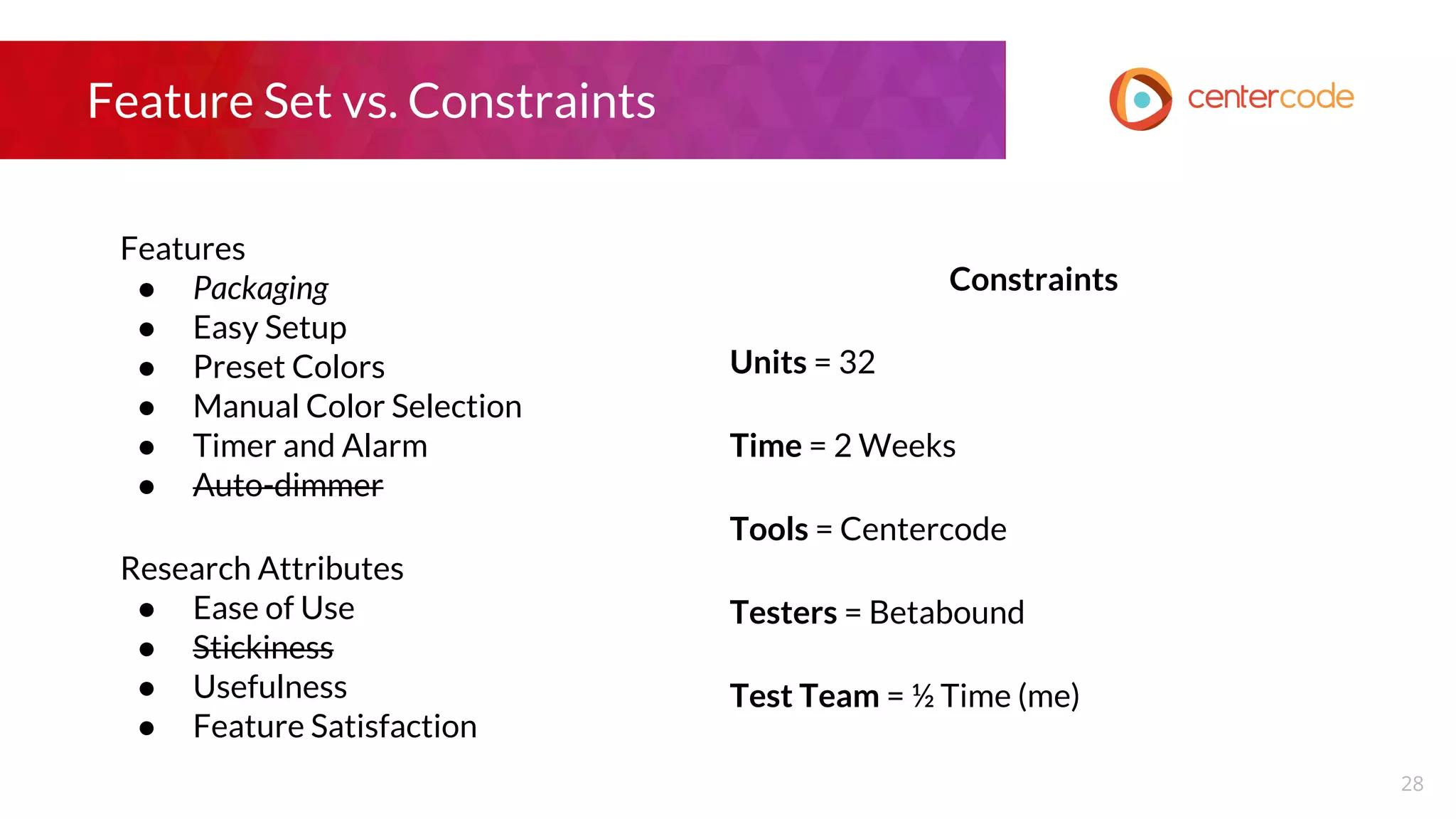
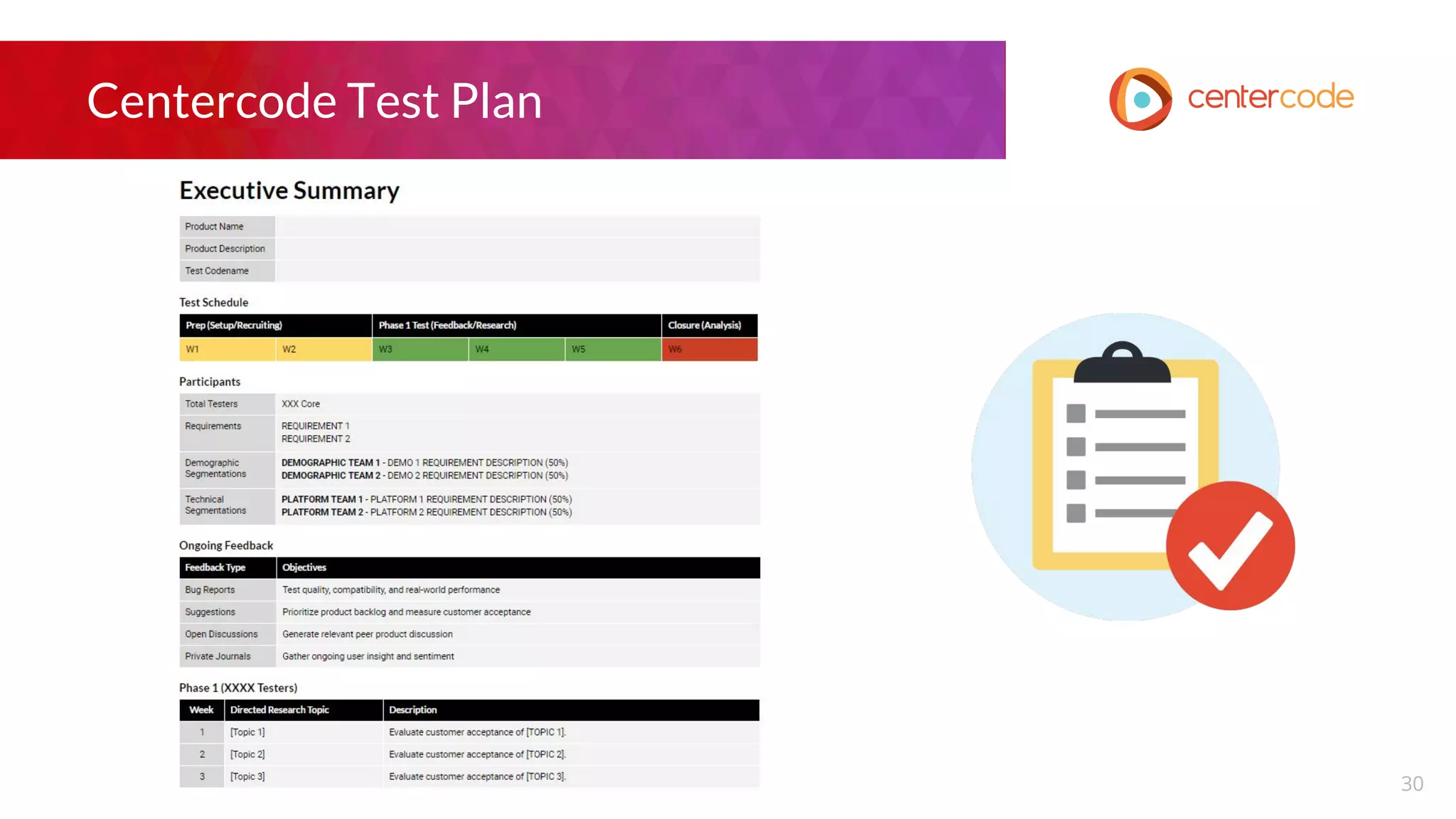
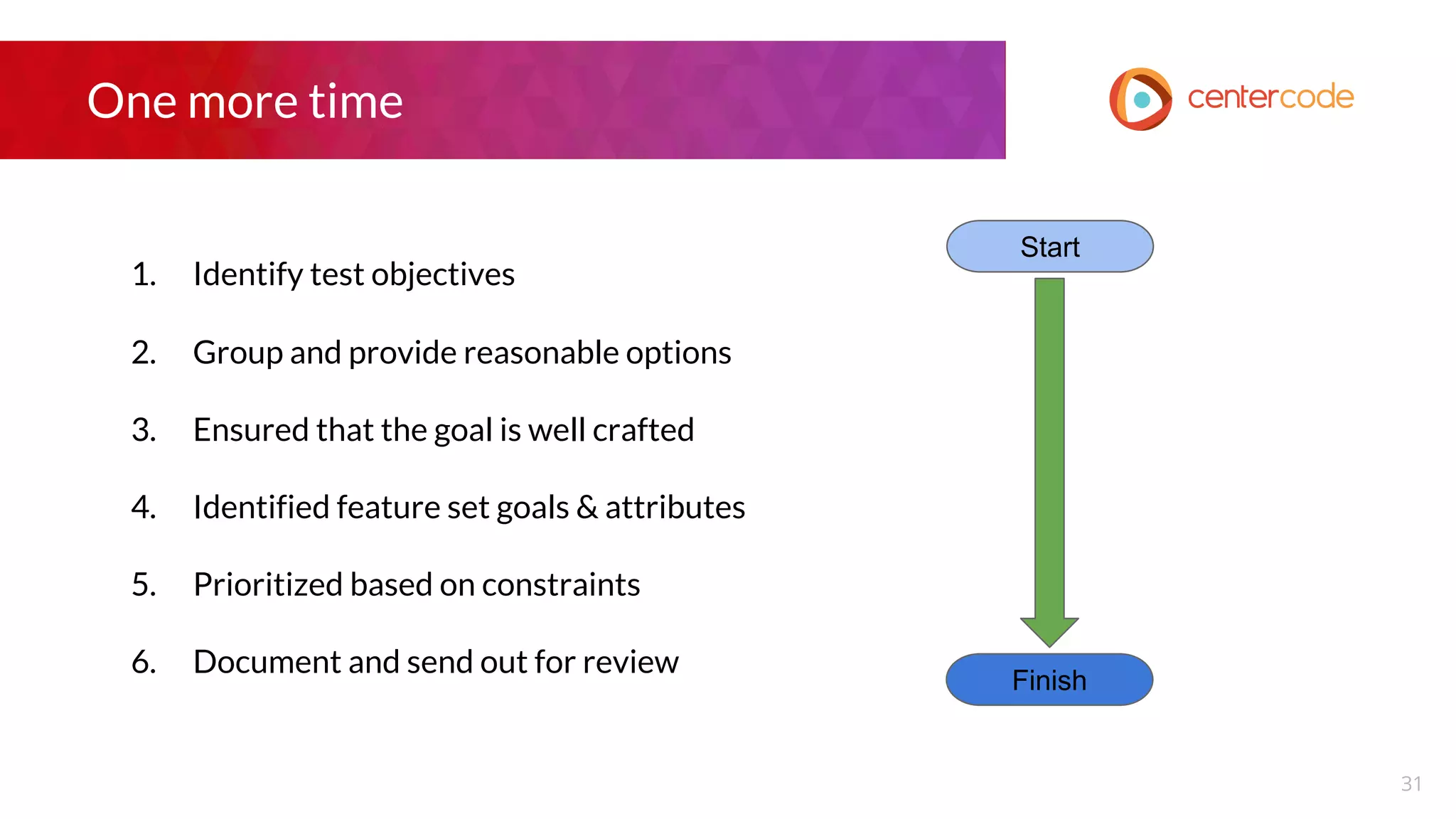
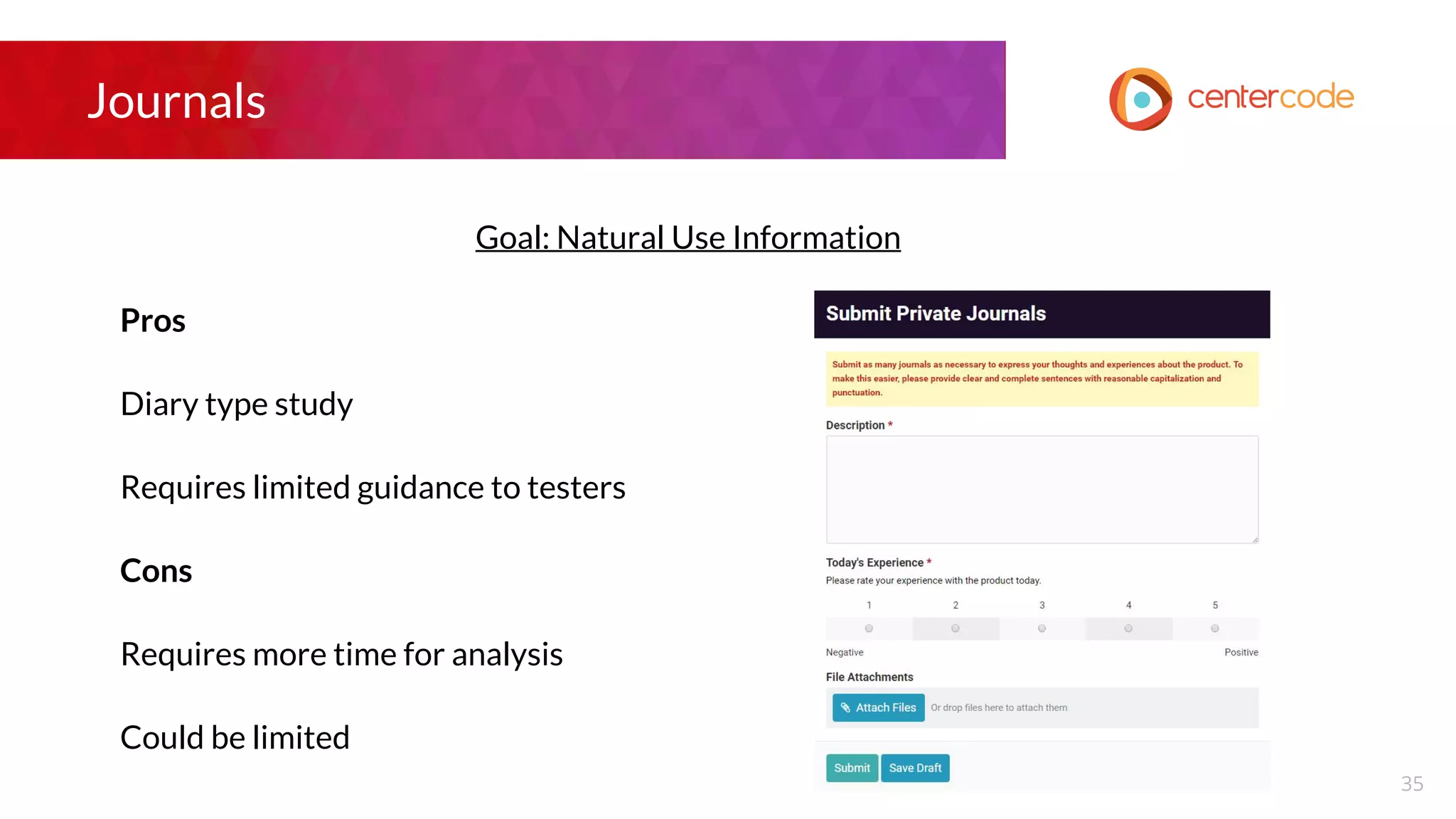
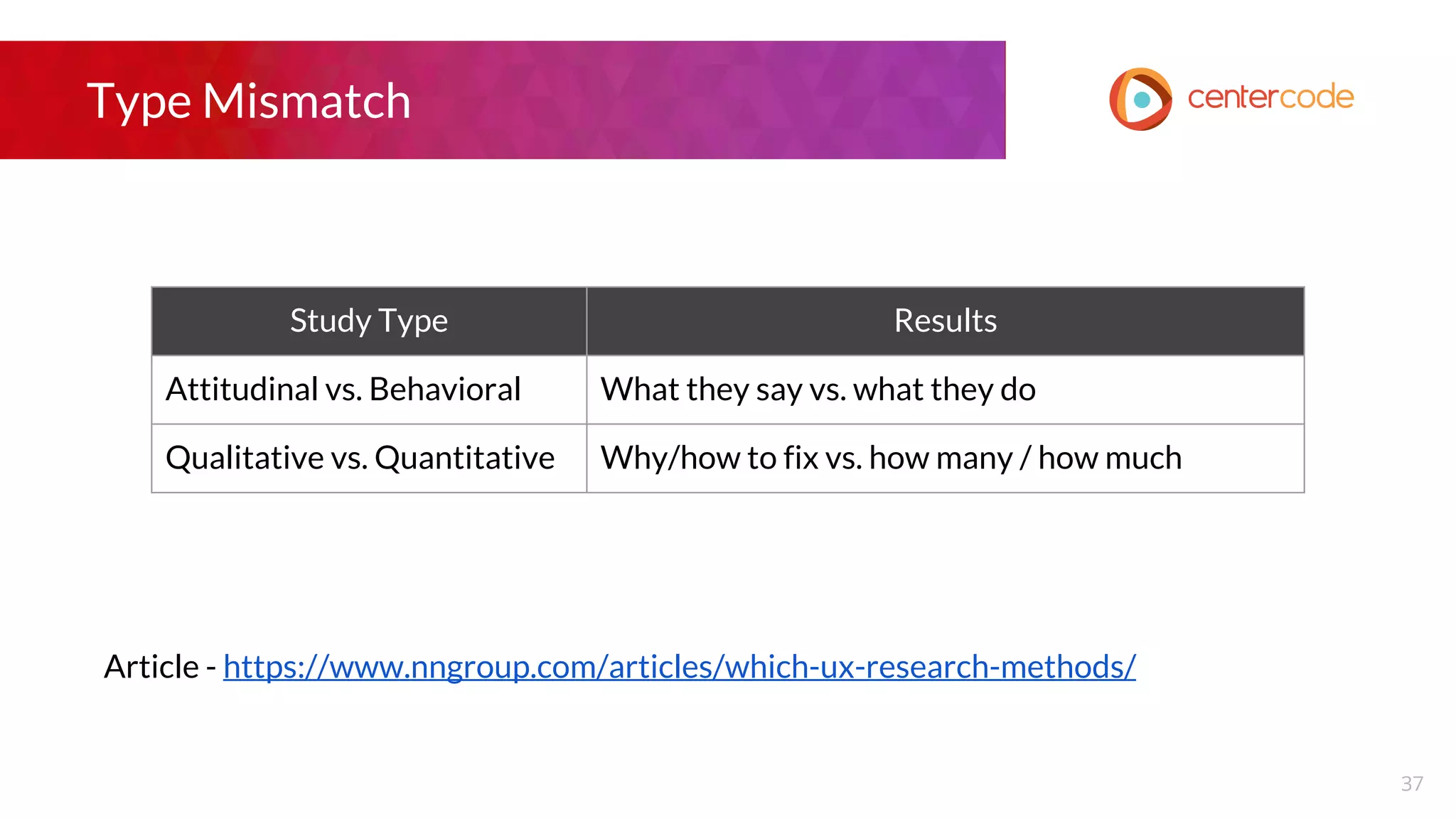
The document outlines a webinar hosted by John S. Little from Centercode on setting effective goals for beta tests. It covers definitions of goals, types of goals specific to beta testing, and the methods to maintain these goals throughout the testing phase. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of clearly defining goals, focusing on them throughout the process, and employing appropriate research methods to connect insights back to the goals.