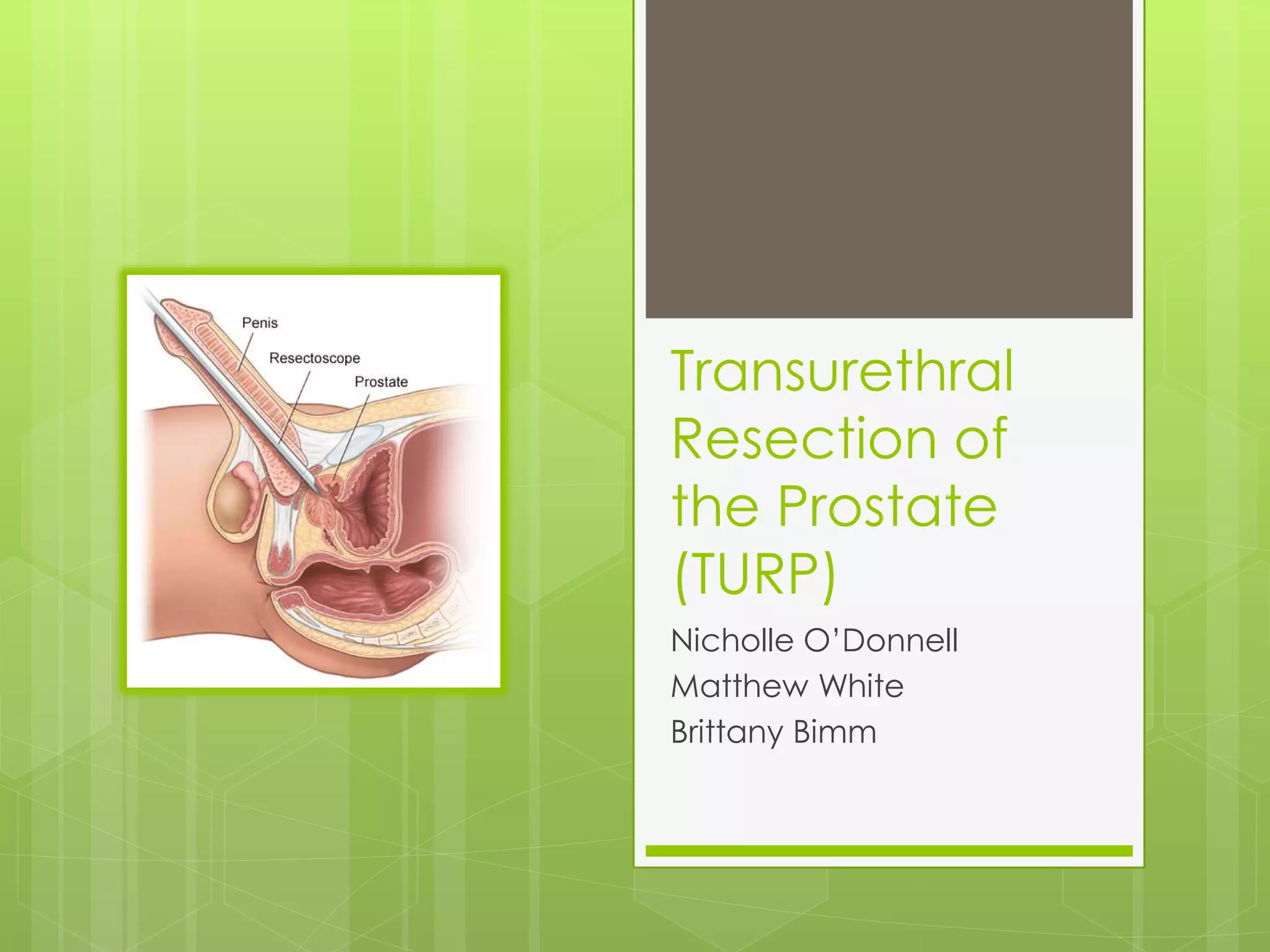
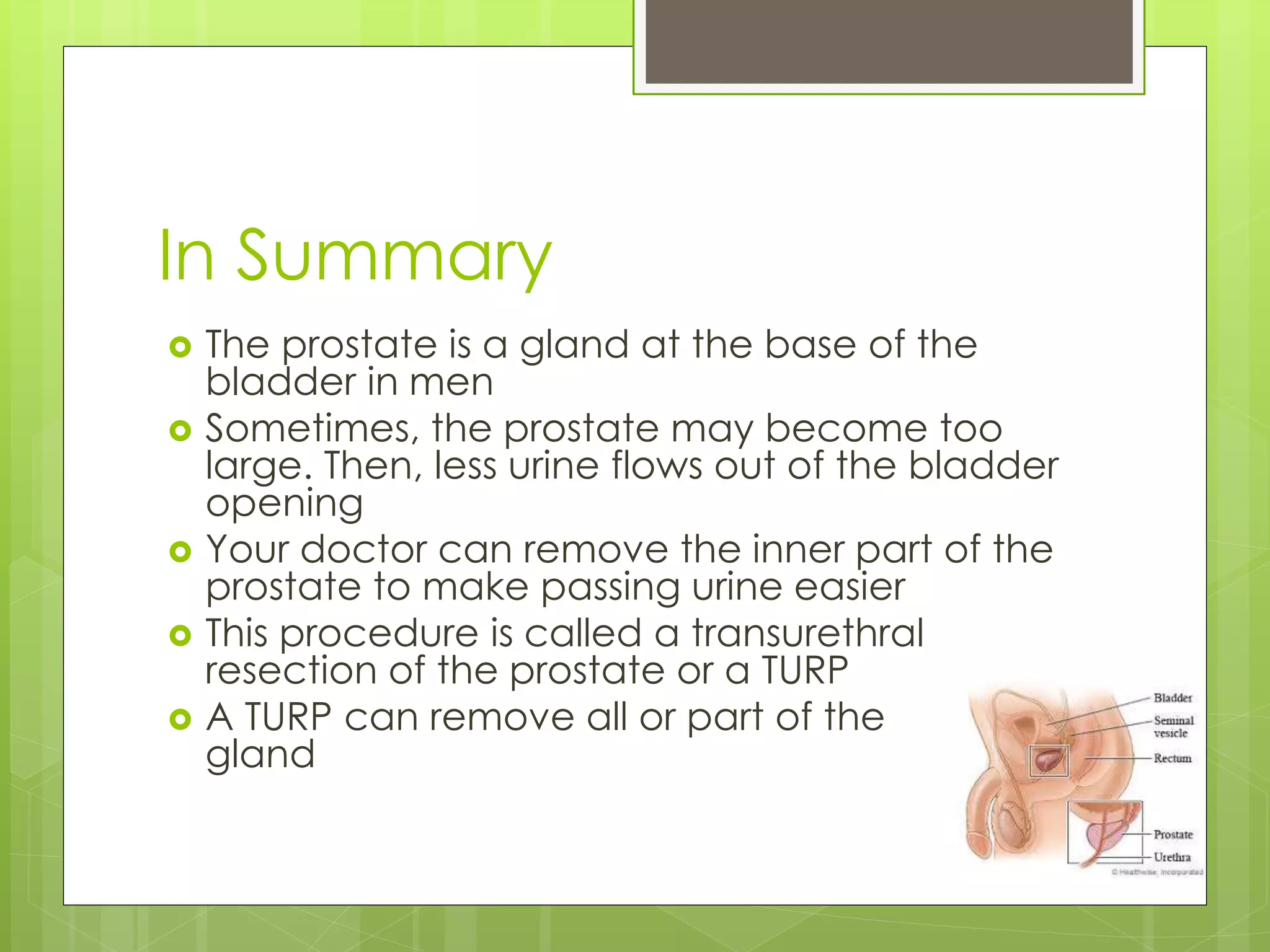
A transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a surgical procedure to remove part of the enlarged prostate gland to relieve urinary obstruction. During a TURP, a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra to cut or ablate prostatic tissue. General or spinal anesthesia is used. Post-operative care focuses on monitoring for complications like infection, bleeding, or a deep vein thrombosis (DVT). While anticoagulants are typically used to treat DVTs, they cannot be given to TURP patients due to the risk of bleeding. Instead, prevention techniques like ambulation and compression stockings are emphasized.