The document discusses concepts from game theory and behavioral economics including:
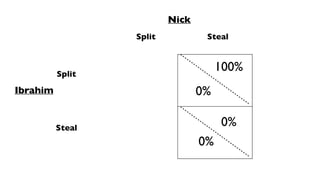
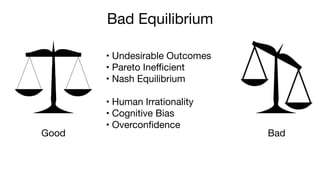
- Bad equilibrium, where no player has an incentive to change their strategy despite undesirable outcomes for all
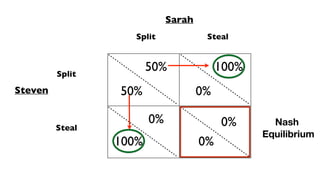
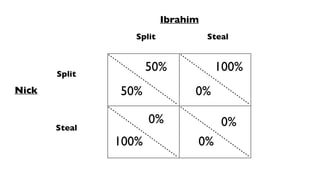
- Nash equilibrium, where the optimal strategy for each player depends on the other players' strategies
- Pareto efficiency and inefficiency, relating to situations where someone can be made better off without making others worse off
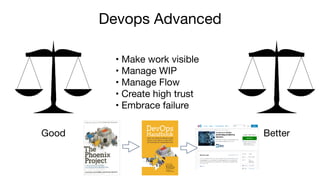
It also discusses cognitive biases and human irrationality that can lead to suboptimal decisions, as highlighted by the work of Kahneman and Tversky, and suggests strategies like increasing visibility, flow management, and embracing failure to change equilibrium to a better outcome.