JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight text data interchange format that is easy to read and parse, making it faster than XML for data exchange in applications. It is language independent, uses straightforward syntax rules for representing data in name/value pairs, and allows for flexible data structures. The document provides examples of JSON syntax, its usage in AJAX applications, and how it interacts with various programming languages like JavaScript and PHP.


![JSON Example { "employees": [ { "firstName":"John" , "lastName":"Doe" }, { "firstName":"Anna" , "lastName":"Smith" }, { "firstName":"Peter" , "lastName":"Jones" } ] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-120202042138-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Object-Notation-JSON-3-320.jpg)


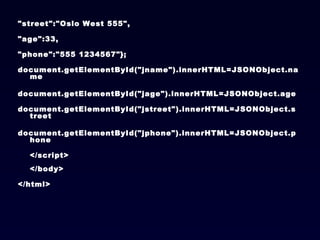





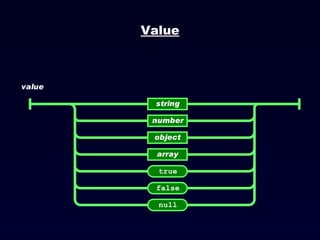

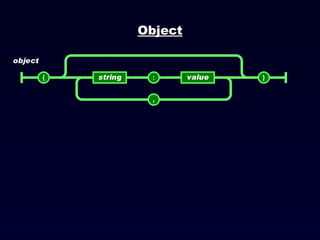

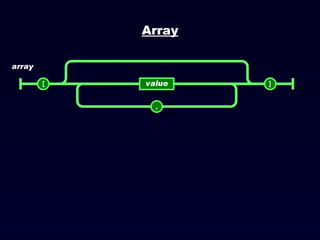
![JSON Arrays JSON arrays are written inside square brackets. An array can contain multiple objects: { "employees": [ { "firstName":"John" , "lastName":"Doe" }, { "firstName":"Anna" , "lastName":"Smith" }, { "firstName":"Peter" , "lastName":"Jones" } ] } In the example above, the object "employees" is an array containing three objects. Each object is a record of a person (with a first name and a last name).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-120202042138-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Object-Notation-JSON-16-320.jpg)

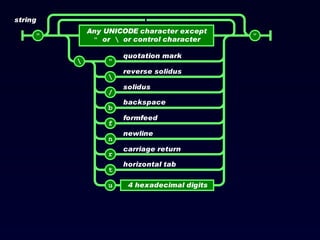








![Json_decode : <?php $json = '{"a":1,"b":2,"c":3,"d":4,"e":5}'; var_dump(json_decode($json)); var_dump(json_decode($json, true)); ?> The above example will output: object(stdClass)#1 (5) { ["a"] => int(1) ["b"] => int(2) ["c"] => int(3) ["d"] => int(4) ["e"] => int(5) } array(5) { ["a"] => int(1) ["b"] => int(2) ["c"] => int(3) ["d"] => int(4) ["e"] => int(5) }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-120202042138-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Object-Notation-JSON-28-320.jpg)

![function validate() { var p = document.forms['personal']; var JSONObject = new Object; JSONObject.firstname = p['firstname'].value; JSONObject.email = p['email'].value; JSONObject.hobby = new Array; for ( var i=0; i<3; i++) { JSONObject.hobby[i] = new Object; JSONObject.hobby[i].hobbyName = p['hobby'][i].value; JSONObject.hobby[i].isHobby = p['hobby'][i].checked; } JSONstring = JSON.stringify(JSONObject); runAjax(JSONstring); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-120202042138-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Object-Notation-JSON-30-320.jpg)
![JSON object to PHP with AJAX var request; function runAjax(JSONstring) { request = getHTTPObject(); request.onreadystatechange = sendData; request.open("GET", "parser.php?json="+JSONstring, true); request.send(null);} // function is executed when var request state changes function sendData() { // if request object received response if(request.readyState == 4) { // parser.php response var JSONtext = request.responseText; // convert received string to JavaScript object var JSONobject = JSON.parse(JSONtext); // notice how variables are used var msg = "Number of errors: "+JSONobject.errorsNum+ "\n- "+JSONobject.error[0]+ "\n- "+JSONobject.error[1]; alert(msg); }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-120202042138-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Object-Notation-JSON-31-320.jpg)
![JSON To PHP <?php // decode JSON string to PHP object $decoded = json_decode($_GET['json']); // do something with data here // create response object $json = array(); $json['errorsNum'] = 2; $json['error'] = array(); $json['error'][] = 'Wrong email!';$json['error'][] = 'Wrong hobby!'; // encode array $json to JSON string $encoded = json_encode($json); // send response back to index.html// and end script execution die($encoded); ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-120202042138-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Object-Notation-JSON-32-320.jpg)
![OUTPUT stdClass Object ( [firstname] => fgfg [email] => [hobby] => Array ( [0] => stdClass Object ( [hobbyName] => sport [isHobby] => 1 ) [1] => stdClass Object ( [hobbyName] => reading [isHobby] => ) [2] => stdClass Object ( [hobbyName] => music [isHobby] => ) ))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-120202042138-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Object-Notation-JSON-33-320.jpg)

![BOSS Webtech is a process oriented design house specializing in web design, web development, backend web programming, mobile application development and other web and mobile related design and support services. Recently launched BizPlus – Mobile based survey software. Check it more here http://bizplusonline.com/ More products here http://www.bosswebtech.com/products/products.html Contact BOSS Webtech Call 831-998-9121 at US EST/CST/MST/PST Zone or email [email_address] About BOSS Webtech](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-120202042138-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Object-Notation-JSON-35-320.jpg)