JSON is a lightweight data-interchange format that is language independent and easy for humans to read and write. It uses JavaScript syntax to transmit data objects consisting of attribute-value pairs and arrays, and can be parsed by JavaScript. Unlike XML, JSON has no end tags or reserved words. JSON is commonly used to transmit data between a server and web page by parsing a JSON string into a JavaScript object using the built-in JSON.parse() method.


![Example JSON
{
"id":1,
"name":”Anoop",
"billingAddress":[{"city":”Bangalore"}]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-230417060205-26e9fa9b/85/JSON-pptx-3-320.jpg)



![JSON Syntax
Data is in name/value pairs
Data is separated by commas
Curly braces hold objects
Square brackets hold arrays
{
"id":1,
"name":”Anoop",
"billingAddress":[{"city":”Bangalore"}]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-230417060205-26e9fa9b/85/JSON-pptx-7-320.jpg)
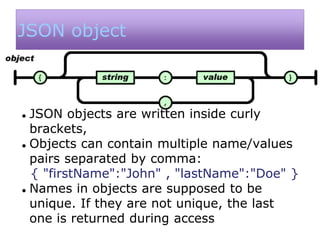
![JSON Array
JSON arrays are written inside square brackets.
An array can contain multiple objects:
{
"employees": [
{ "firstName":”Sanjay" , "lastName":”Adiwal" },
{ "firstName":”Shubham" , "lastName":”Parikh" },
{ "firstName":”Anoop" , "lastName":”Pandey" }
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-230417060205-26e9fa9b/85/JSON-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![JSON and Javascript
var employees = ‘[
{ "firstName":”Sanjay" , "lastName":”Adiwal" },
{ "firstName":”Shubham" , "lastName":”Parikh" },
{ "firstName":”Anoop" , "lastName":”Pandey" }
]’;
obj = JSON.parse(employees)
obj[0].lastName //Adiwal
obj[0].firstName // “Sanjay";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-230417060205-26e9fa9b/85/JSON-pptx-11-320.jpg)
