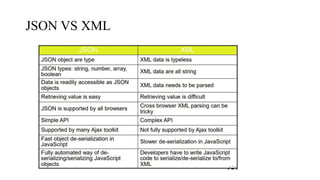
JSON is a lightweight data-interchange format that is easy for humans and machines to read and write. It is built on two structures: a collection of name/value pairs and an ordered list of values. A JSON object holds properties whose names are strings, and values can be strings, numbers, booleans, arrays, or null. JSON is commonly used to transmit data between a server and web application, without requiring a page refresh.






![• Booleans & Null
o Booleans: true or false
o Null: A value that specifies nothing or no value.
• Objects & Arrays
oObjects: Unordered key/value pairs wrapped in { }
oArrays: Ordered key/value pairs wrapped in [ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-180311175726/85/Json-8-320.jpg)

![Arrays in JSON
• An ordered collection of values
oBegins with [ (left bracket)
o Ends with ] (right bracket)
oName/value pairs are separated by , (comma)
Example:
{ "employee_id": 1236937, "name": "Jeff Fox", "hire_date": "1/1/2013", "location":
"Norwalk, CT", "consultant": false, "random_nums": [ 24,65,12,94 ] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/json-180311175726/85/Json-10-320.jpg)

