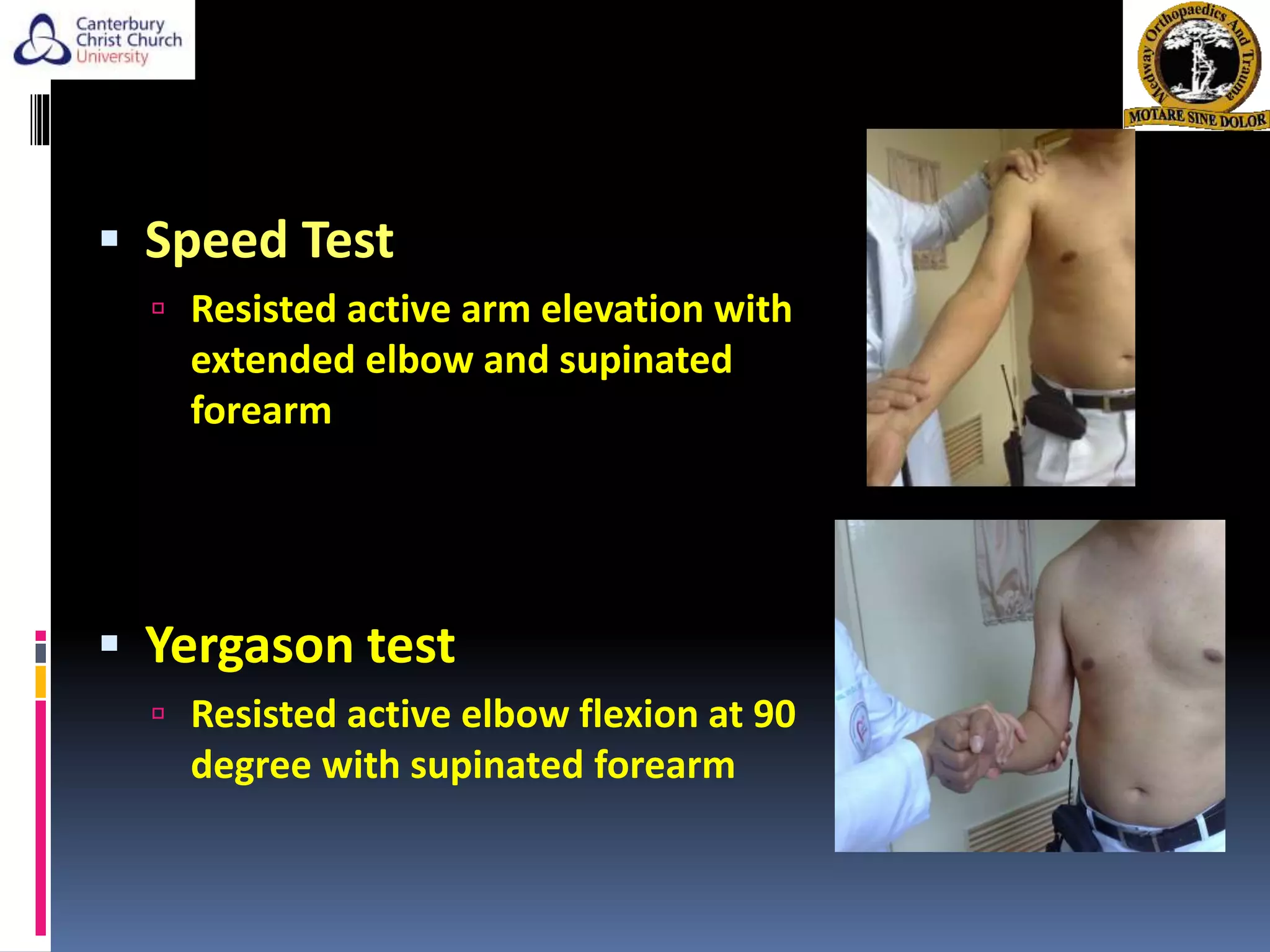
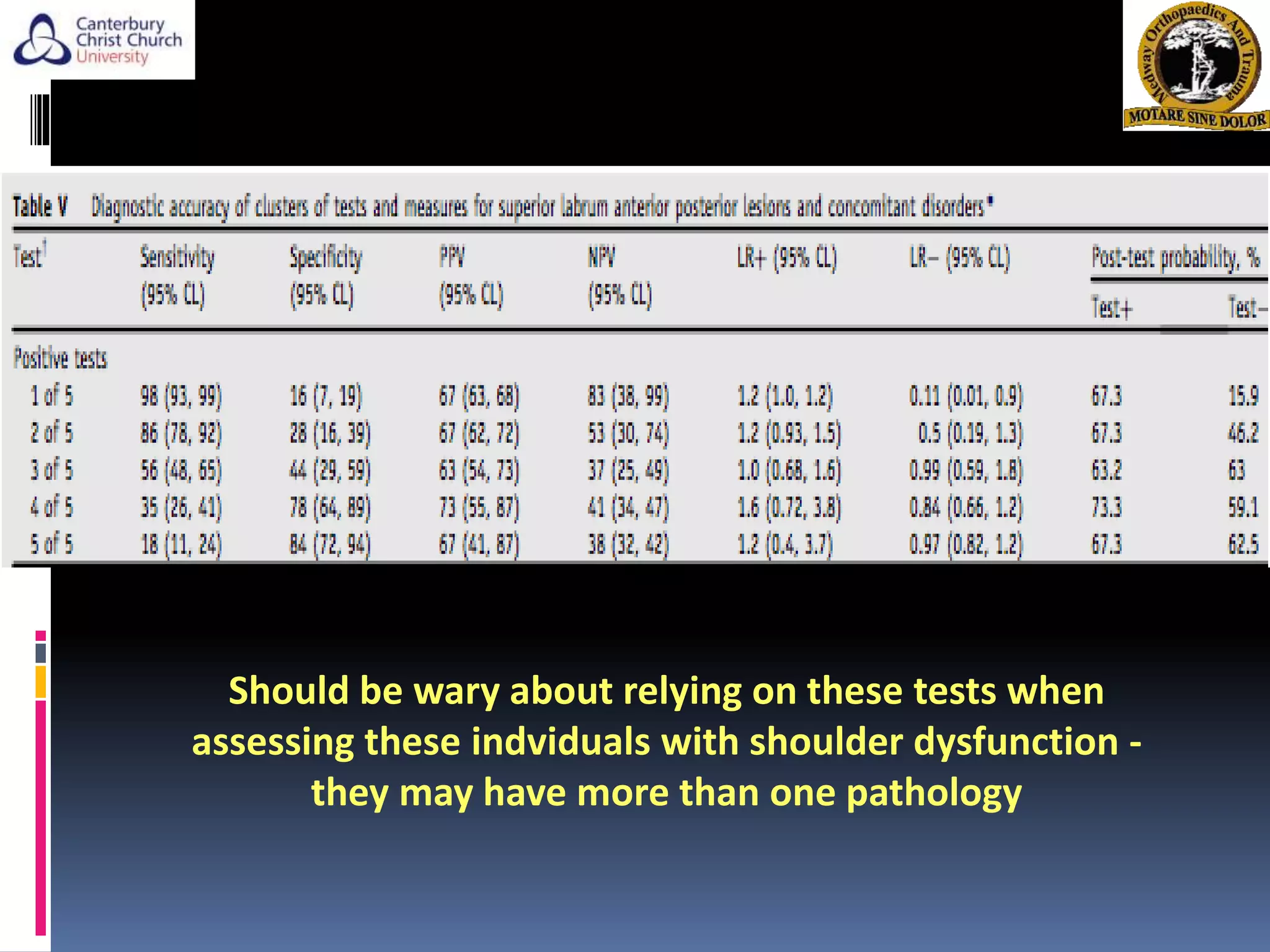
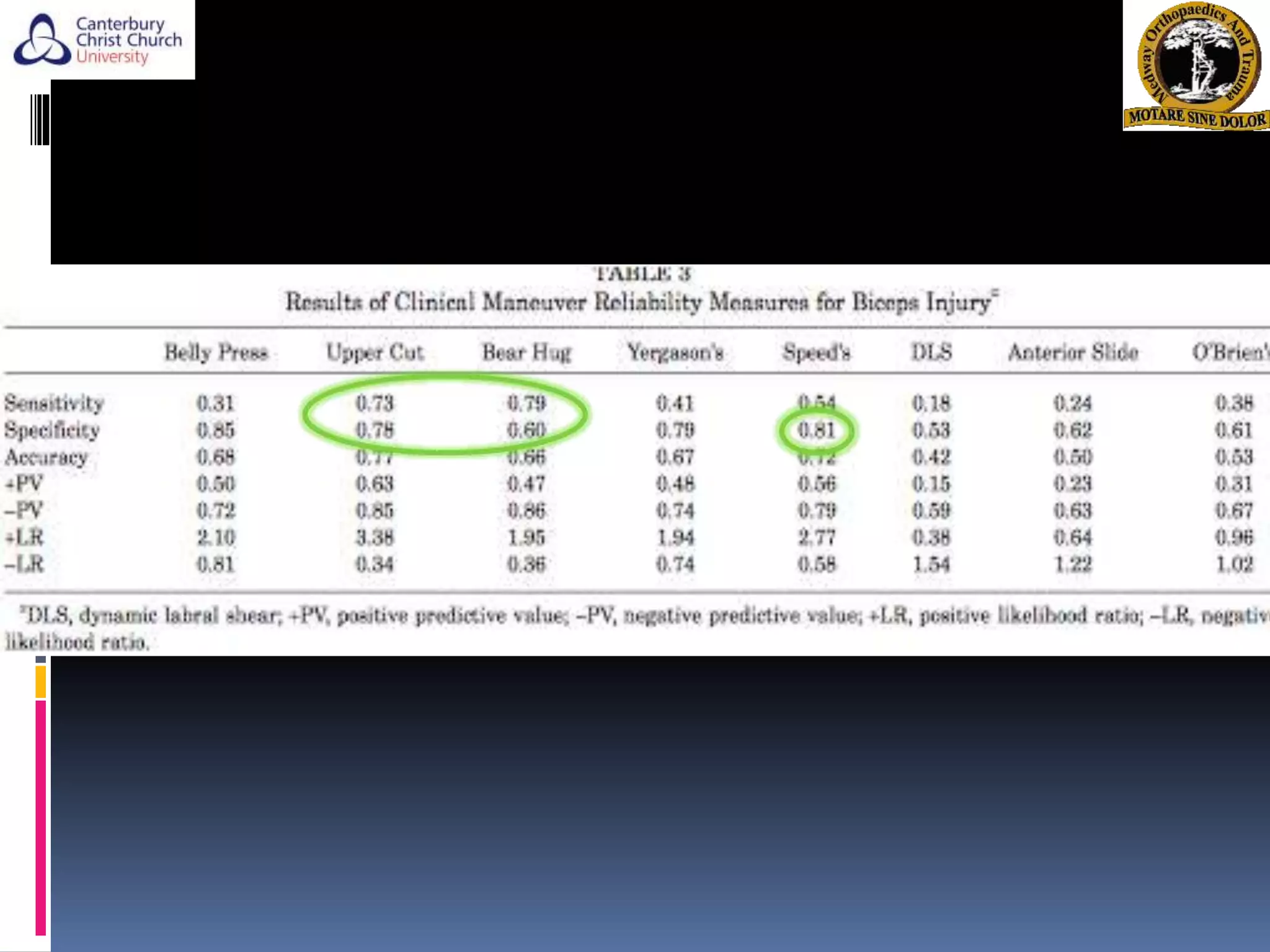
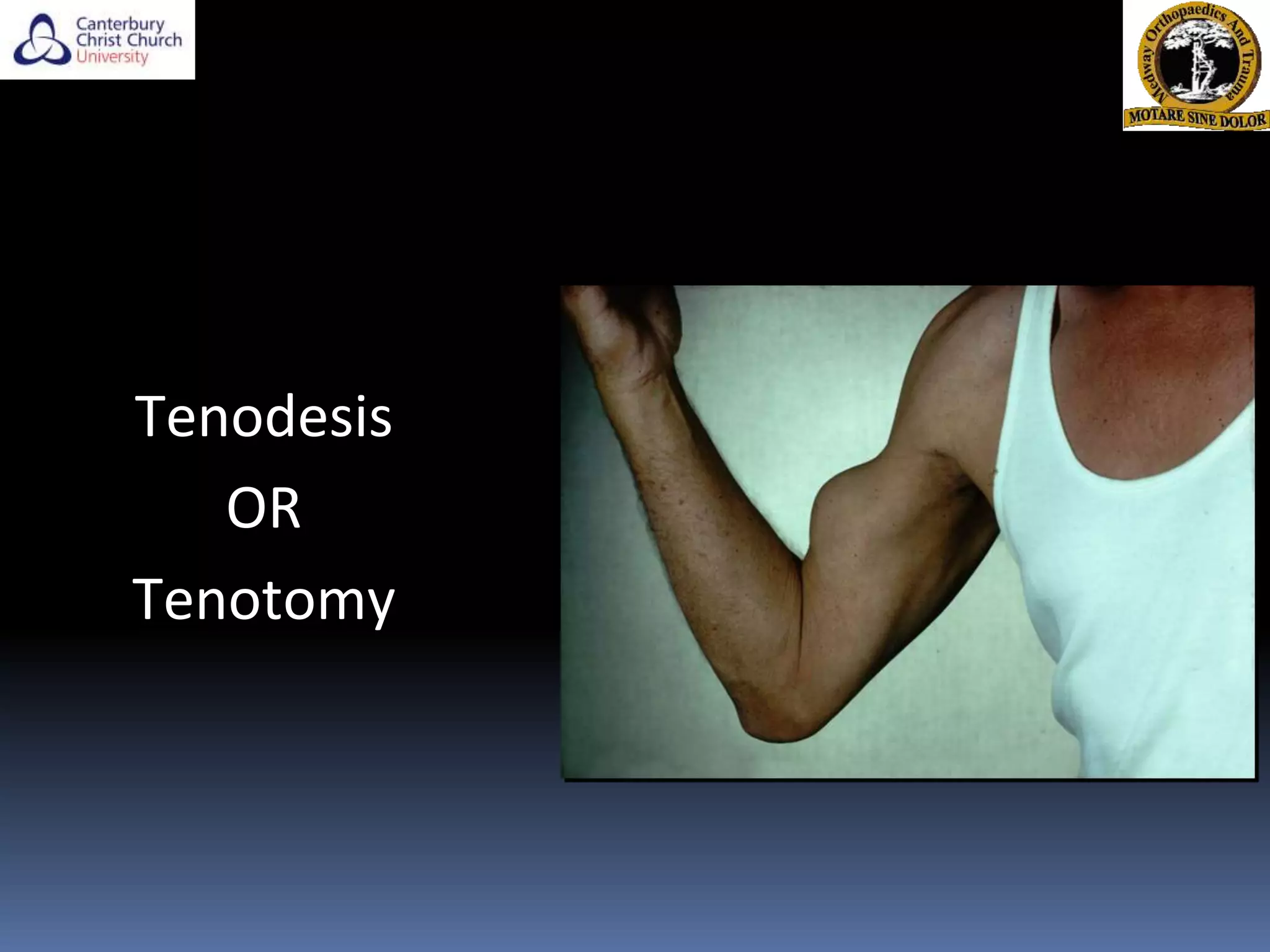
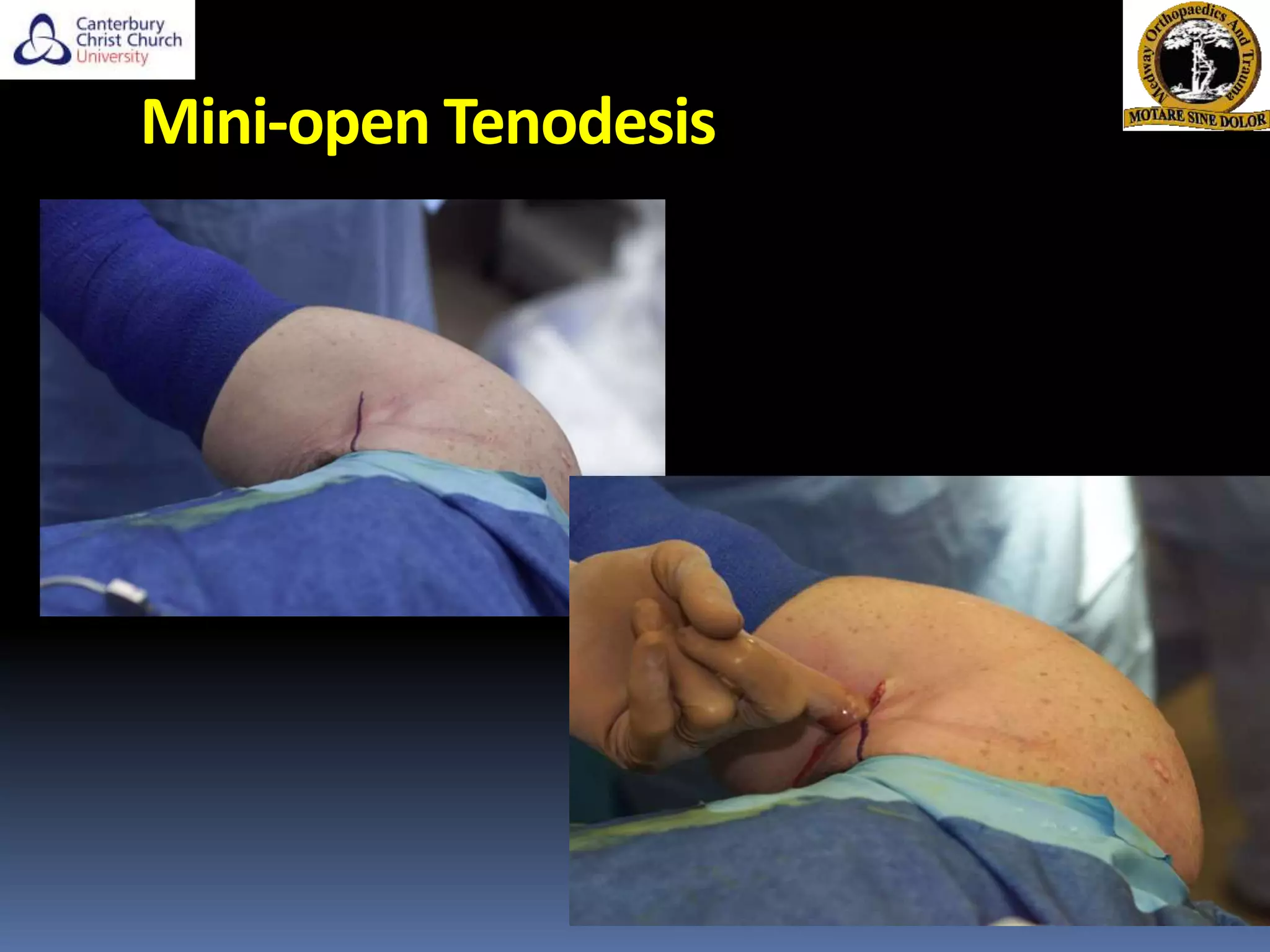
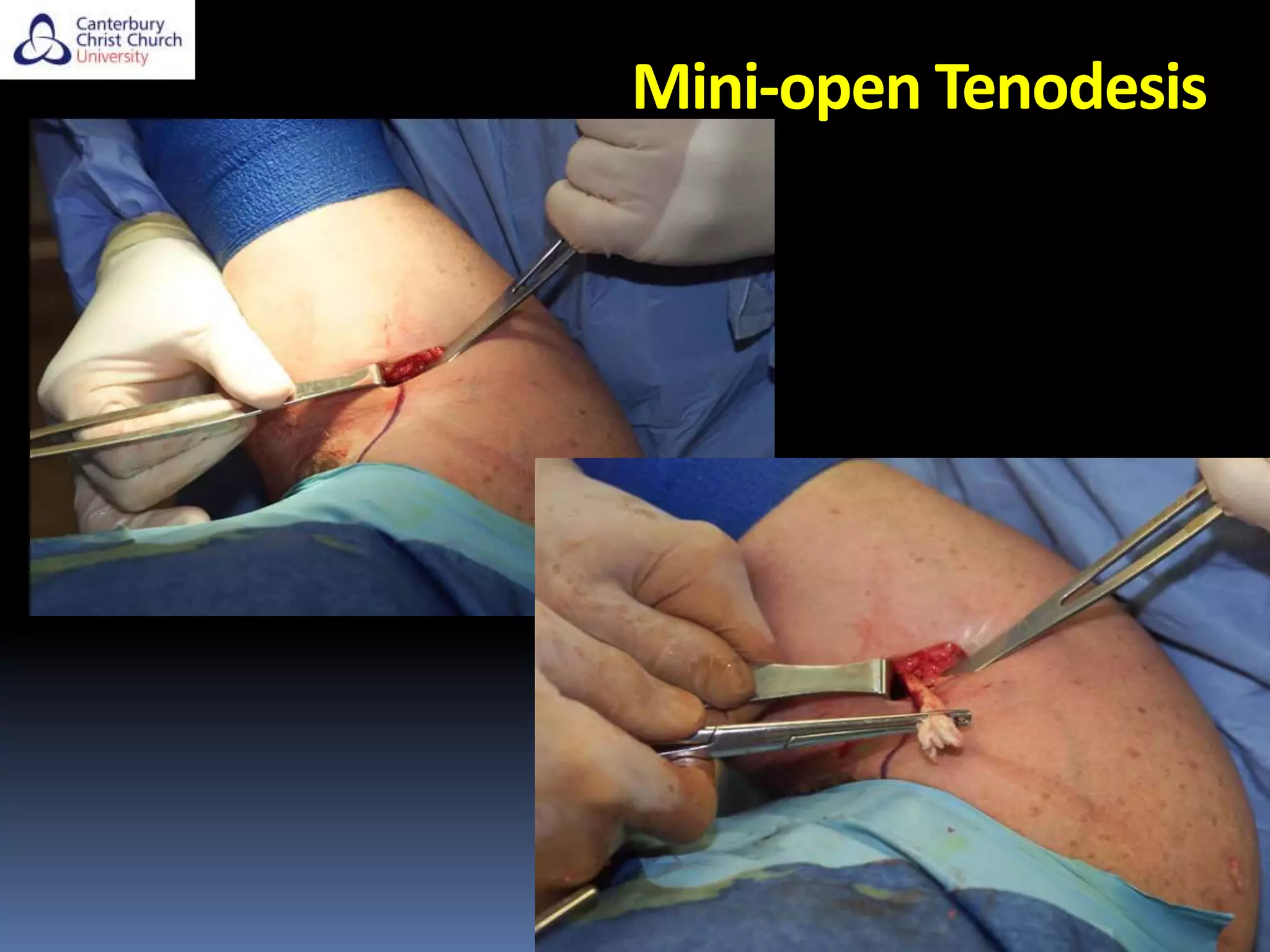
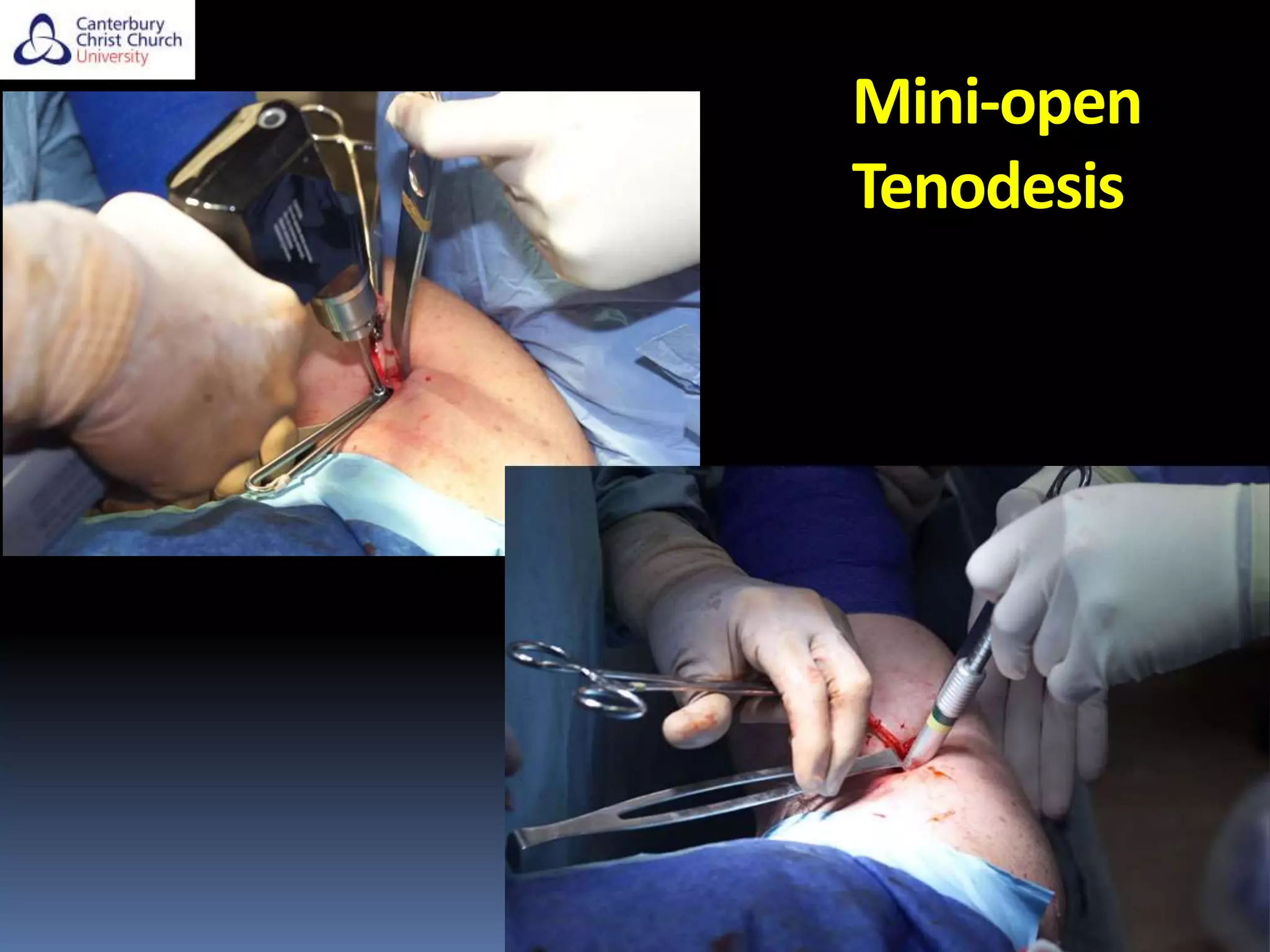
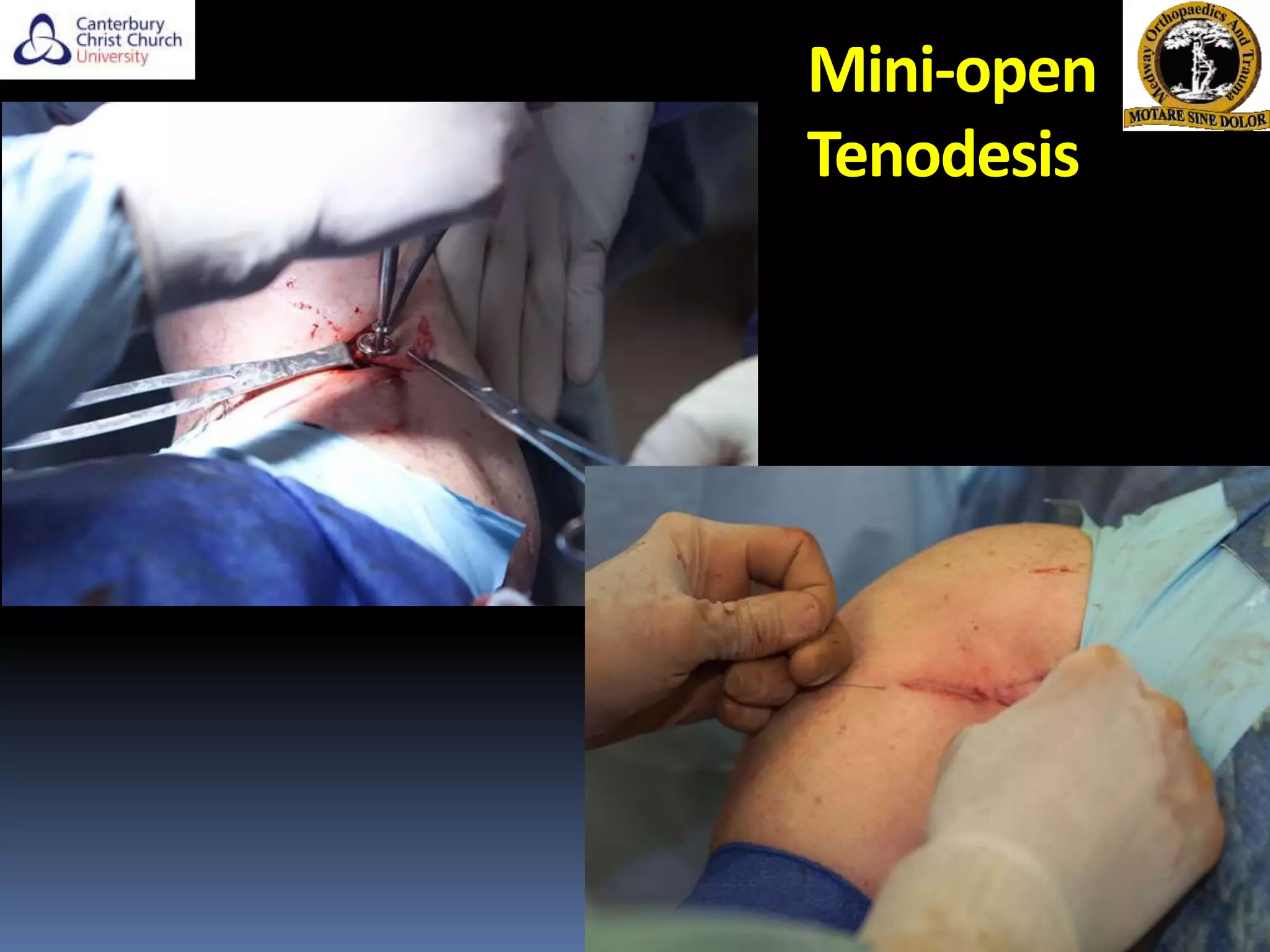
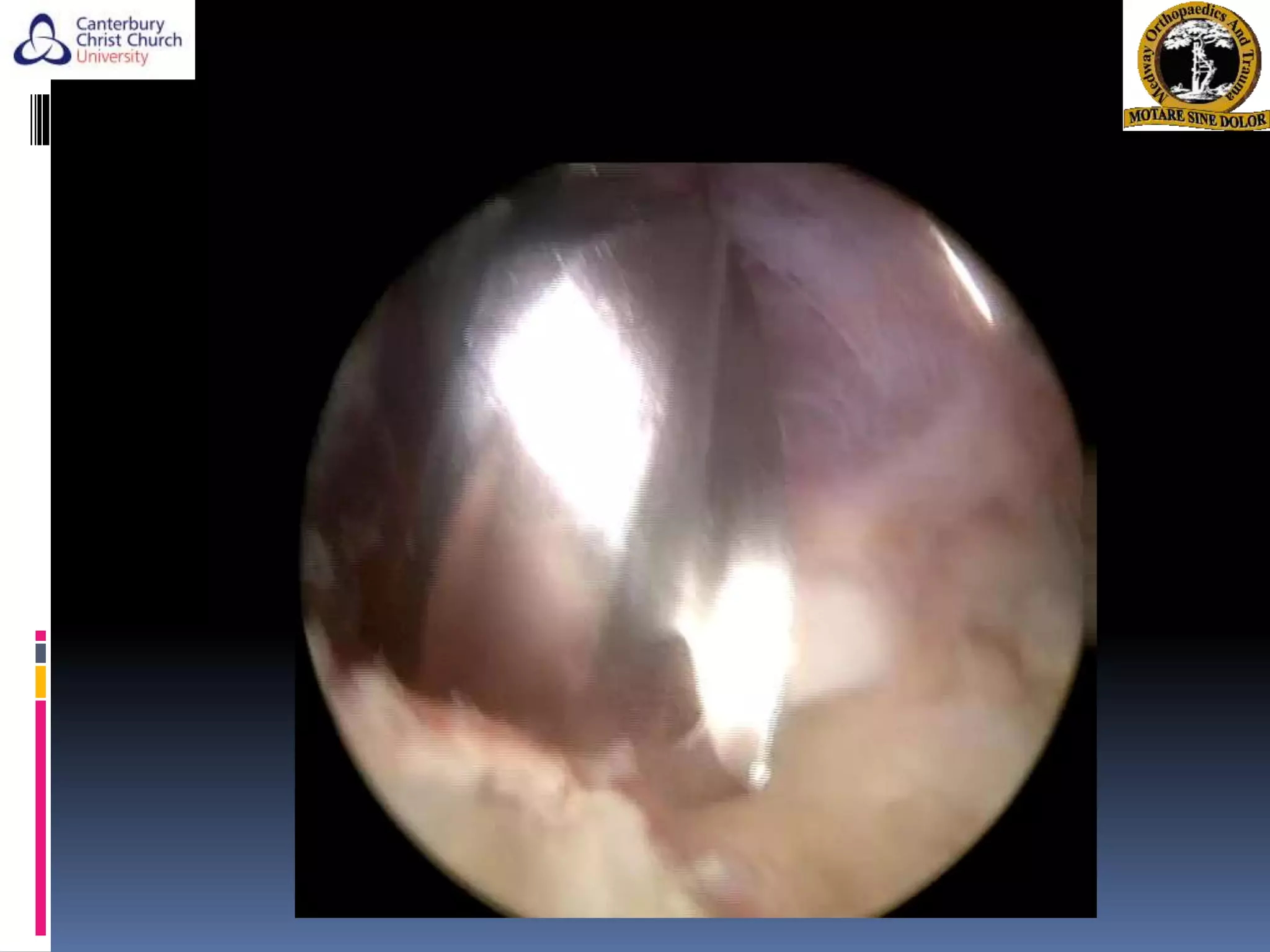
The document discusses the anatomy, function, pathology, clinical evaluation, and treatment of biceps pain. It notes that the biceps helps with elbow flexion, supination, and stability of the humeral head. Common pathologies include inflammation, instability from tears or subluxation, and trauma. Clinical tests evaluate for pain and instability. Treatment options depend on the pathology and include rest, injections, physical therapy, and surgery such as tenodesis or tenotomy. Tenodesis maintains length-tension but has more pain, while tenotomy has less pain but risks a cosmetic deformity. The best approach considers patient factors and functional demands.