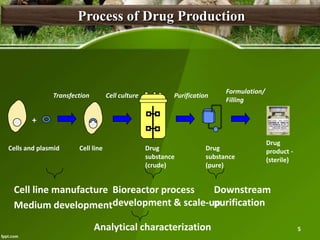
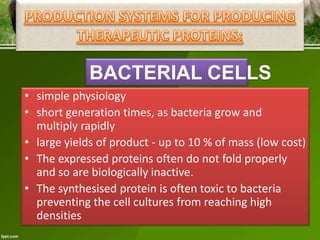
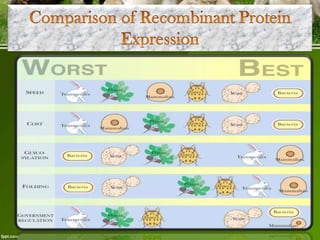
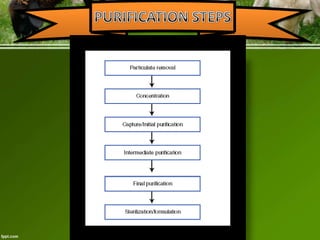
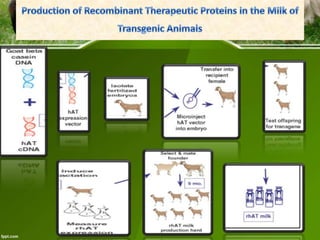
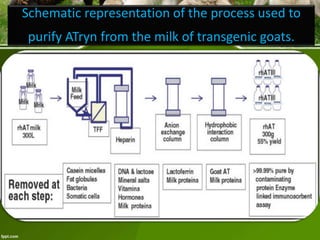
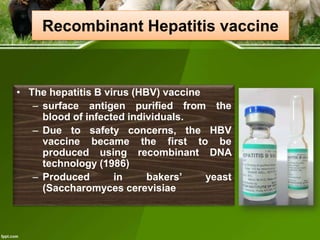
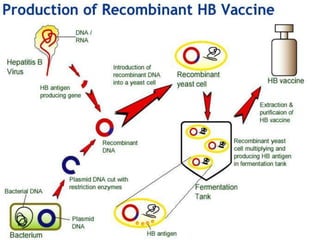
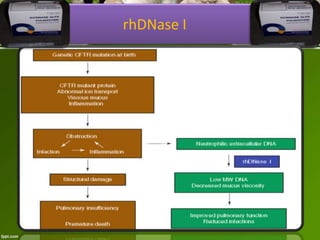
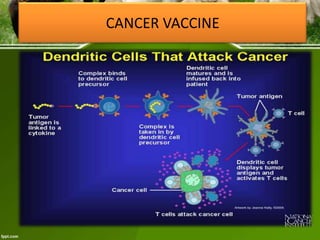
This document discusses the production of recombinant therapeutic proteins. It provides a timeline of important developments including the approval of the first recombinant human insulin in 1982. It outlines the typical process of drug production including transfection of cells, cell culture, purification and formulation. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of expressing proteins in bacterial cells, yeast cells, insect cells, plants and transgenic animals. Finally, it provides examples of some important recombinant proteins that have been approved for human use to treat disorders like hemophilia and diabetes.