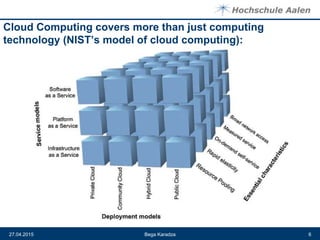
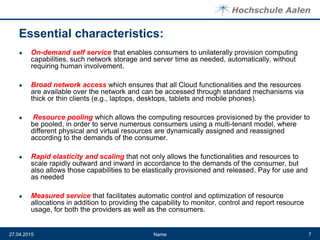
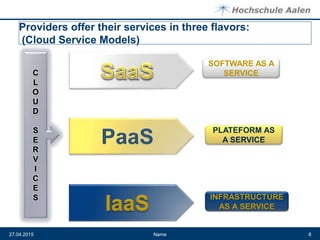
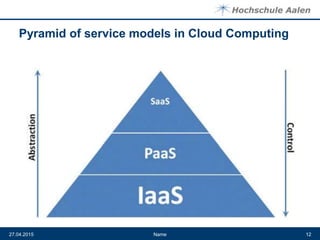
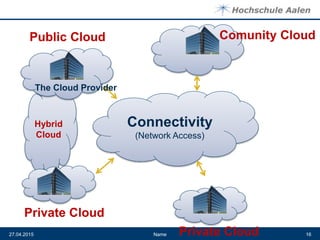
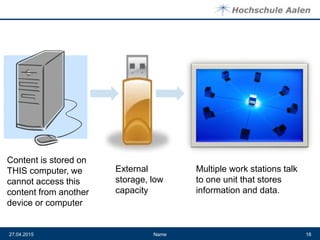
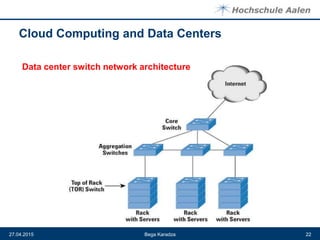
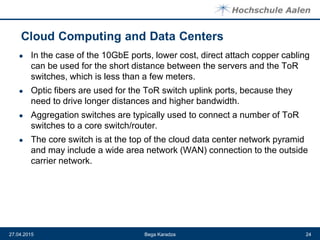
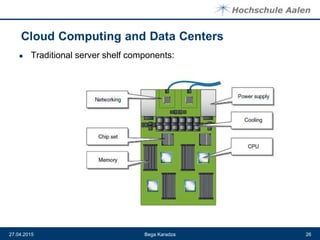
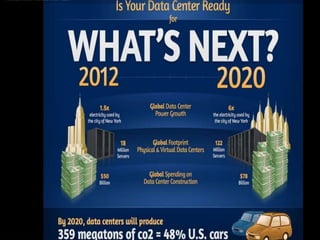
The document discusses cloud computing and data centers. It defines cloud computing as a style of computing where scalable IT capabilities are provided as an internet-based service. It describes the different cloud service models including SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. It also discusses cloud deployment models like public, private, community and hybrid clouds. The document then explains how growing adoption of cloud computing requires large data centers to host servers. It provides details on data center network architectures, use of Ethernet, and the role data centers play in processing user requests and transactions.