Muscle contraction and movement
•Download as DOCX, PDF•
5 likes•695 views
muscles contraction and movement
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Structure of skeletal muscle

Structure of skeletal muscleDr. Alamzeb Associate professor ,HOD Physiology Saidu Medical College saidu Sharif Swat Pakistan
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Mechanism and chemical changes occuring during muscle contraction

Mechanism and chemical changes occuring during muscle contraction
General and molecular mechanism of Muscle contraction

General and molecular mechanism of Muscle contraction
A summary of skeletal muscle contraction and relaxation

A summary of skeletal muscle contraction and relaxation
Types of skeletal muscle fibers, motor unit,isotonic and isometric contraction

Types of skeletal muscle fibers, motor unit,isotonic and isometric contraction
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (11)
Similar to Muscle contraction and movement
Similar to Muscle contraction and movement (20)
More from Aftab Badshah
More from Aftab Badshah (20)
The theory of endosymbiosis says that eukaryote cells have evolved from a sym...

The theory of endosymbiosis says that eukaryote cells have evolved from a sym...
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
❤Jammu Kashmir Call Girls 8617697112 Personal Whatsapp Number 💦✅.

❤Jammu Kashmir Call Girls 8617697112 Personal Whatsapp Number 💦✅.
Thyroid Physiology_Dr.E. Muralinath_ Associate Professor

Thyroid Physiology_Dr.E. Muralinath_ Associate Professor
Call Girls Ahmedabad +917728919243 call me Independent Escort Service

Call Girls Ahmedabad +917728919243 call me Independent Escort Service
The Mariana Trench remarkable geological features on Earth.pptx

The Mariana Trench remarkable geological features on Earth.pptx
Dubai Call Girls Beauty Face Teen O525547819 Call Girls Dubai Young

Dubai Call Girls Beauty Face Teen O525547819 Call Girls Dubai Young
Justdial Call Girls In Indirapuram, Ghaziabad, 8800357707 Escorts Service

Justdial Call Girls In Indirapuram, Ghaziabad, 8800357707 Escorts Service
9654467111 Call Girls In Raj Nagar Delhi Short 1500 Night 6000

9654467111 Call Girls In Raj Nagar Delhi Short 1500 Night 6000
chemical bonding Essentials of Physical Chemistry2.pdf

chemical bonding Essentials of Physical Chemistry2.pdf
Connaught Place, Delhi Call girls :8448380779 Model Escorts | 100% verified

Connaught Place, Delhi Call girls :8448380779 Model Escorts | 100% verified
Muscle contraction and movement
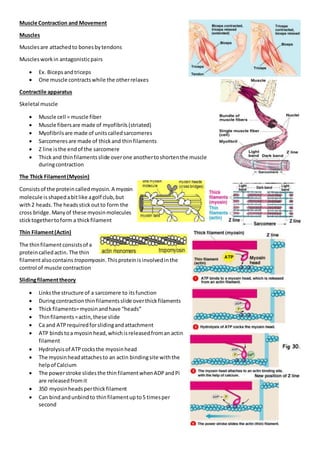
- 1. Muscle Contraction and Movement Muscles Musclesare attachedto bonesbytendons Musclesworkin antagonisticpairs Ex. Bicepsandtriceps One muscle contractswhile the otherrelaxes Contractile apparatus Skeletal muscle Muscle cell = muscle fiber Muscle fibersare made of myofibrils(striated) Myofibrilsare made of unitscalledsarcomeres Sarcomeresare made of thickand thinfilaments Z line isthe endof the sarcomere Thickand thinfilamentsslide overone anothertoshortenthe muscle duringcontraction The Thick Filament(Myosin) Consistsof the proteincalledmyosin. A myosin molecule isshapedabitlike agolf club,but with2 heads. The headsstickoutto form the cross bridge.Manyof these myosinmolecules sticktogethertoform a thickfilament Thin Filament(Actin) The thinfilamentconsistsof a proteincalledactin. The thin filamentalsocontains tropomyosin.Thisproteinisinvolvedinthe control of muscle contraction Slidingfilamenttheory Linksthe structure of a sarcomere to itsfunction Duringcontractionthinfilamentsslide overthickfilaments Thickfilaments=myosinandhave “heads” Thinfilaments=actin,these slide Ca and ATPrequiredforslidingandattachment ATP bindstoa myosinhead,whichisreleasedfroman actin filament Hydrolysisof ATPcocksthe myosinhead The myosinheadattachesto an actin bindingsite withthe helpof Calcium The powerstroke slidesthe thinfilamentwhenADPandPi are releasedfromit 350 myosinheadsperthickfilament Can bind andunbindto thinfilamentupto5 timesper second
- 2. Motor neurons and muscle contraction Motor neuronsstimulate musclecontraction Motor neuronsare branchedand can stimulate more thanone muscle fiber Motor unit= motor unitandall the muscle fibersitcontrols Neuromuscularjunctions=the synapse betweenamotorneuronand a muscle fiber The strengthof a muscularcontractioniscontrolledbythe numberof motor unitsactivated.More motorunits= strongercontractions Musclesrequiringprecise control have one motorneuronpermuscle fiber Mechanismof stimulation: An actionpotential releasesacetylcholine intothe neuromuscularjunction Acetylcholine depolarizesthe muscle cellchannelsinside onthe sarcoplasmicreticulumreleaseCasoit can reach the contractile apparatus Mechanismof relaxation Motor neuronstopsfiring Ca pumpedbackintothe SR Muscle injuries The Injury: The term'pulledmuscle'comesfromthe descriptionof how the injurytakesplace.Usuallythe muscleis forciblystretchedbeyonditslimitsandthe muscle tissue becomestorn.Dependinguponitsseverityitisclassifiedas a first,secondor thirddegree strain: A firstdegree strainisdamage toa fewmuscle fibers. A seconddegree strainisdamage toa more extensive numberof muscle fibers. A thirddegree strainisa complete rupture of the muscle itself. Signs and Symptoms Grade 1 Witha grade 1 the signsmay notbe presentuntil afterthe activityisover.There maybe asensationof cramp or tightnessanda slightfeelingof painwhenthe musclesare stretchedorcontracted. Grade 2 Witha grade 2 there isimmediate painwhichismore severe thanthe painof a grade one injury.Itis confirmedby painon stretchand contractionof the muscle.A grade 2 isusuallysore totouch. Grade 3 A grade 3 isa catastrophicinjury.There isanimmediate burningorstabbingpainandthe athlete isunable towalk. The muscle iscompletelytornandthere maybe a large lumpof muscle tissue above adepressionwherethe tearis.
