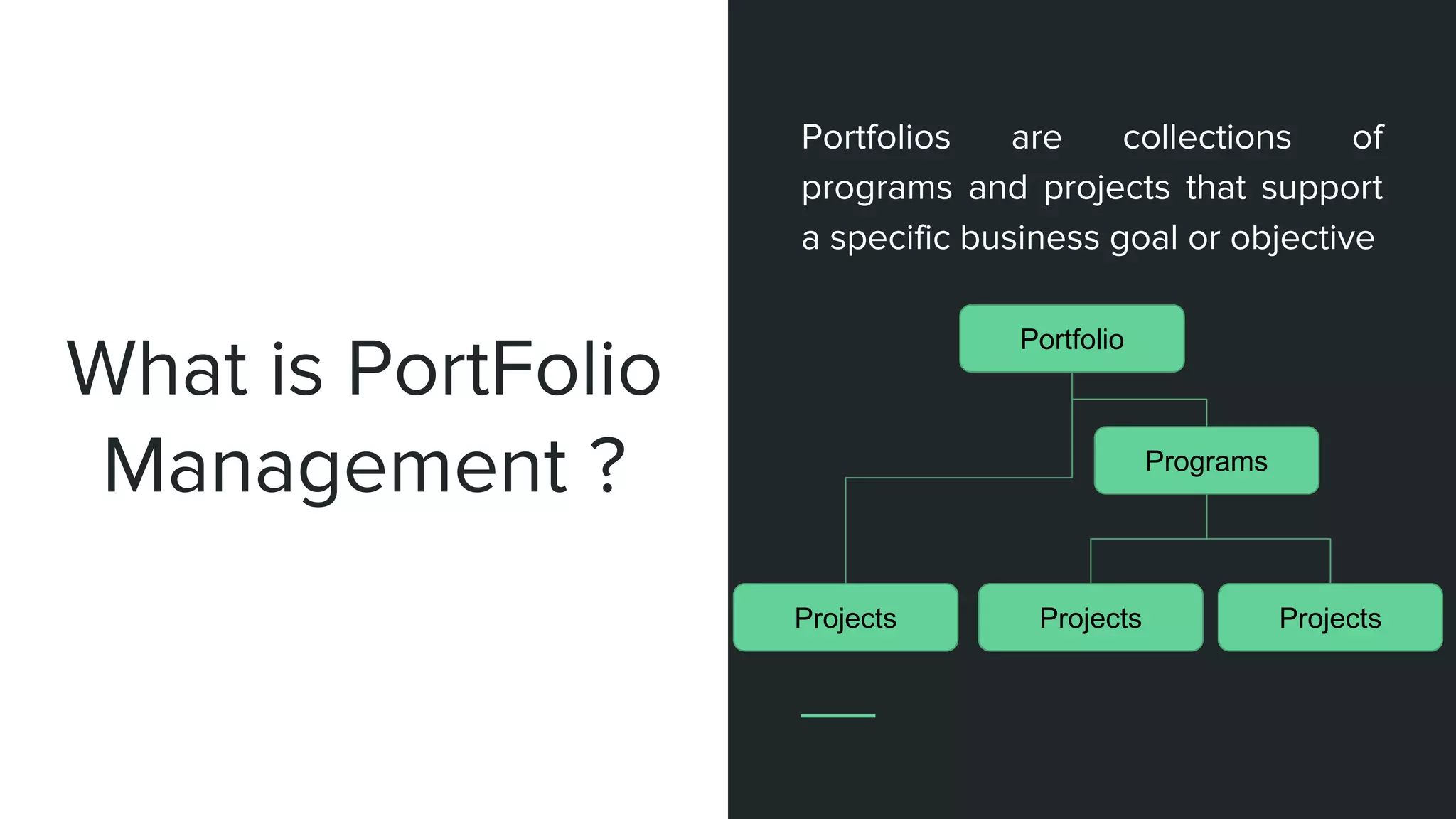
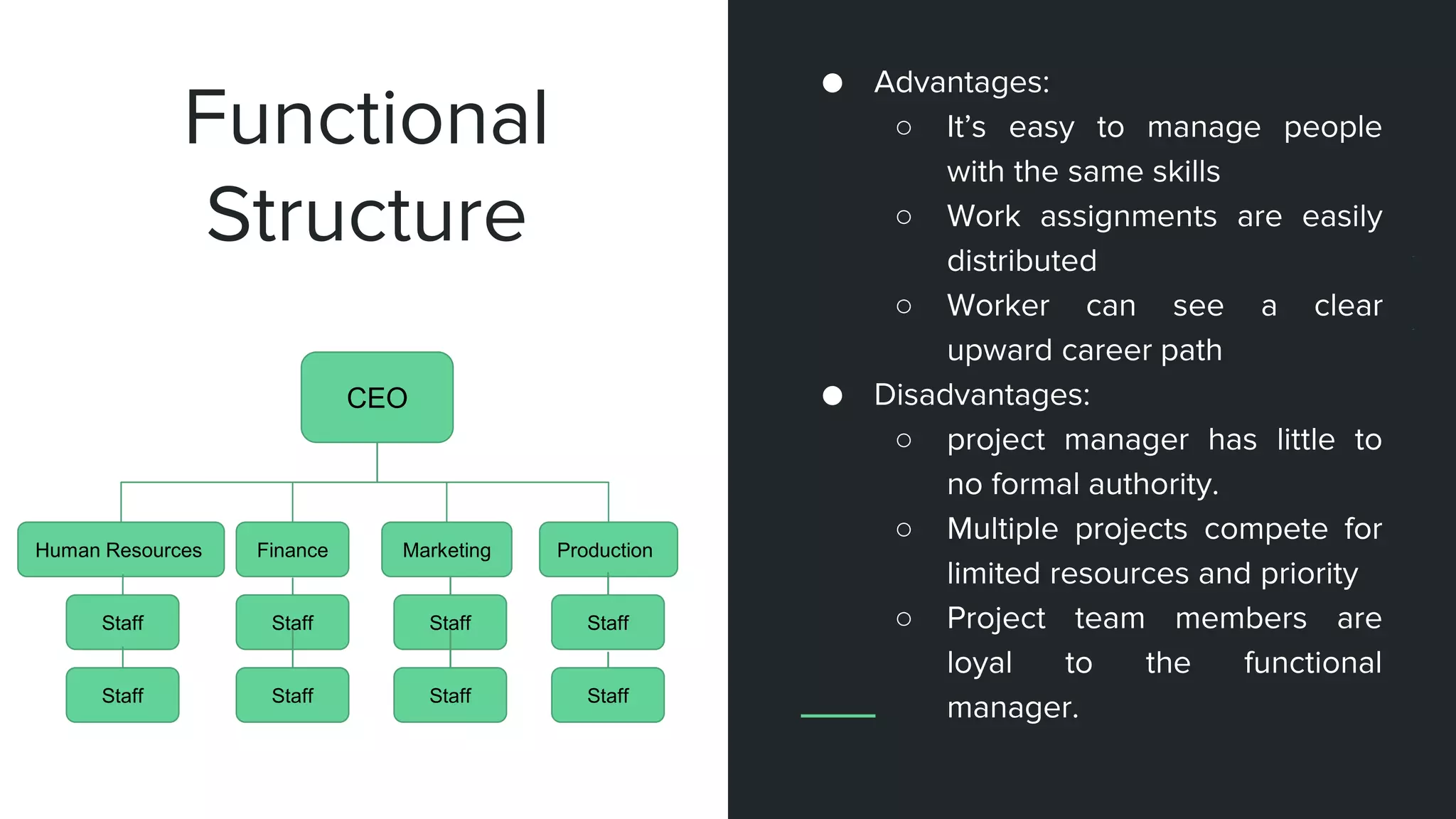
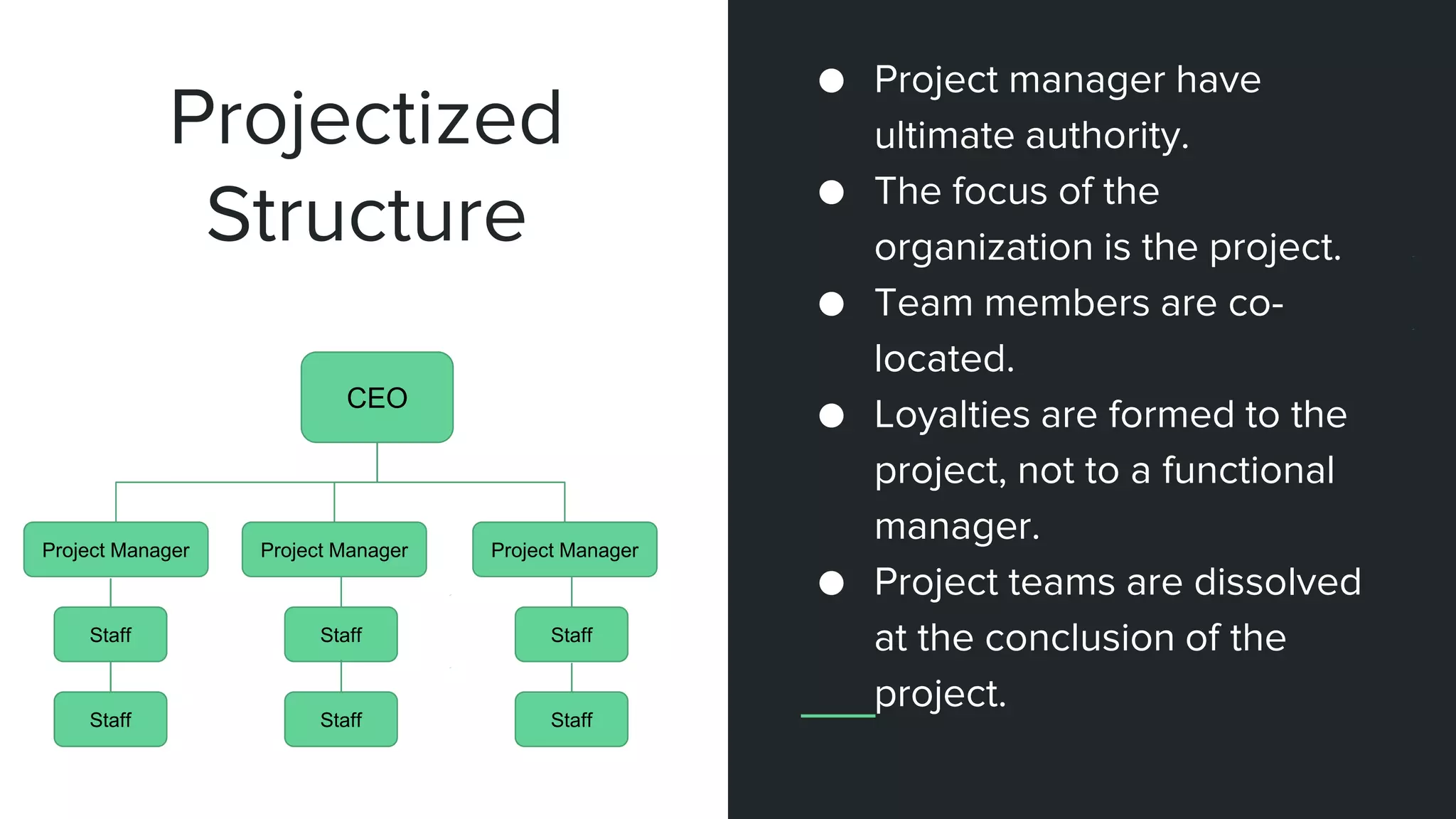
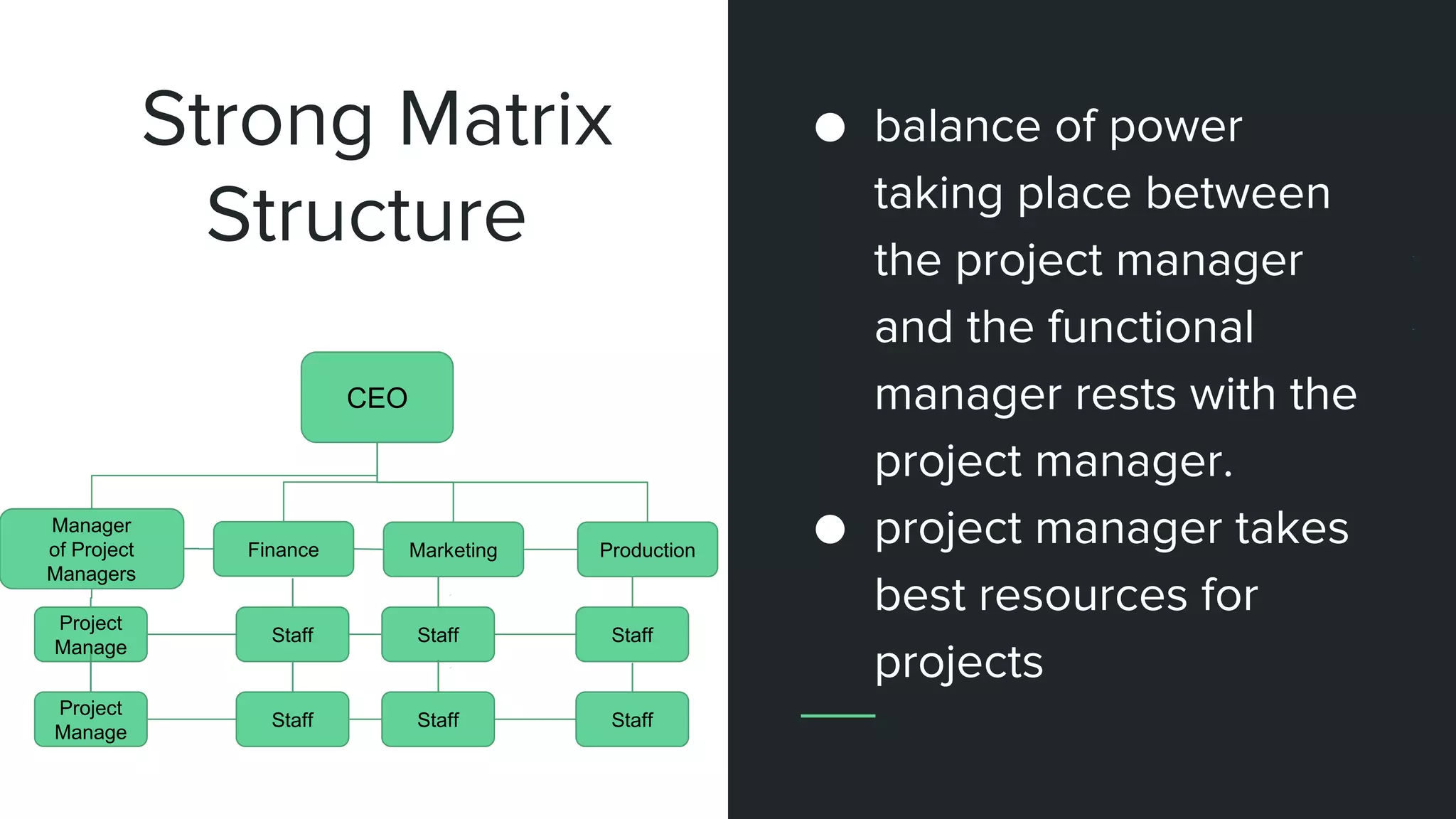
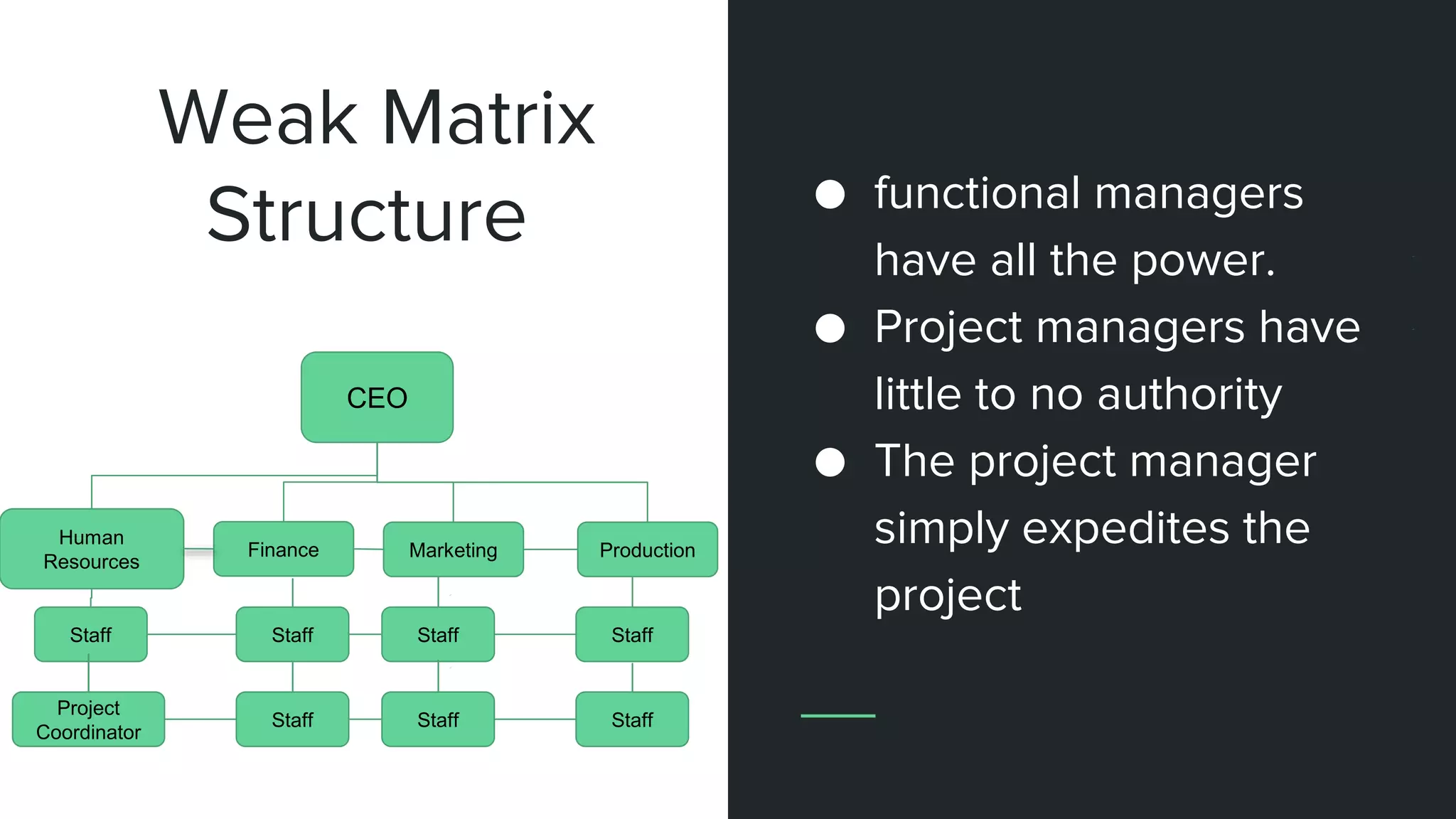
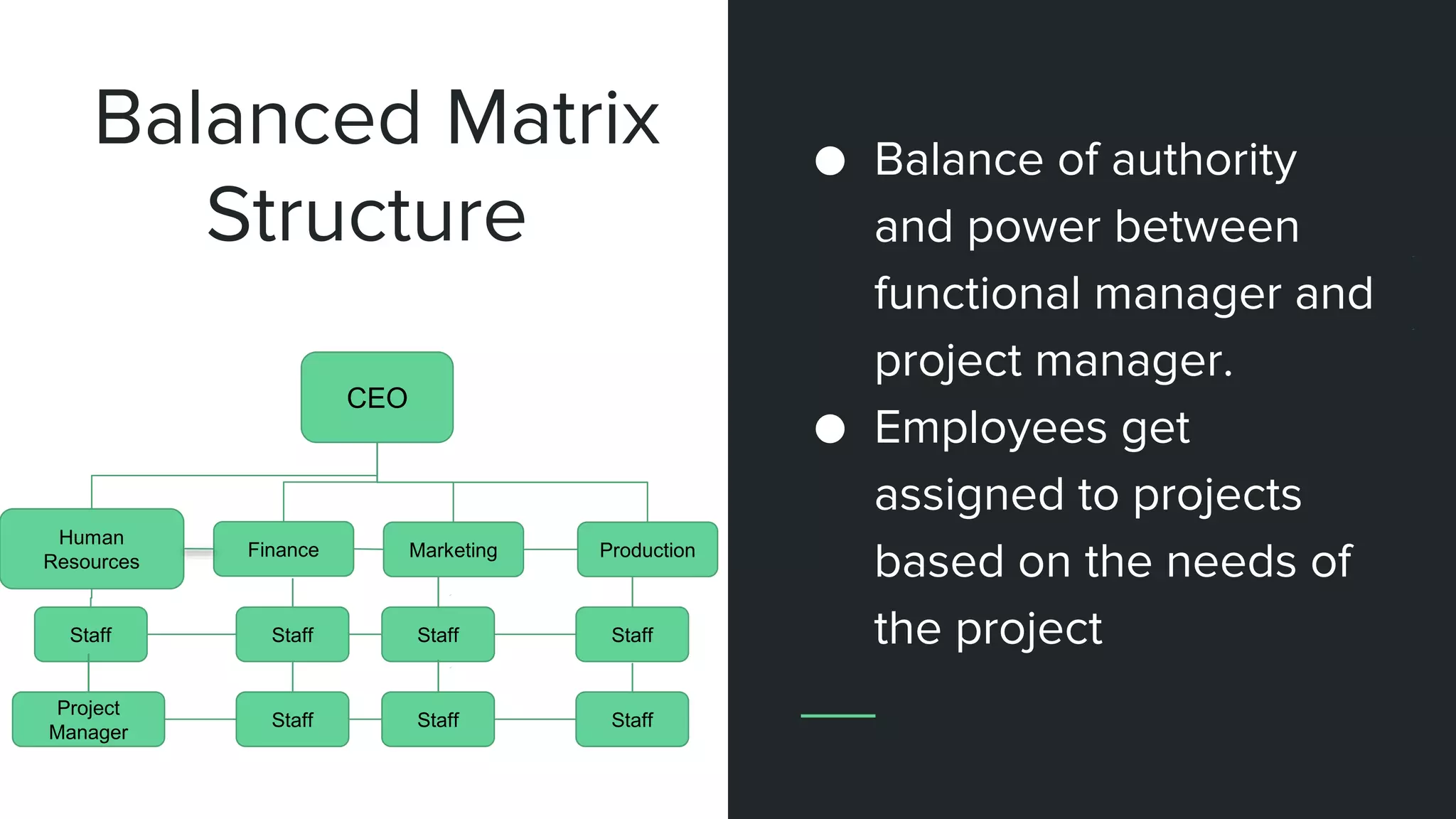
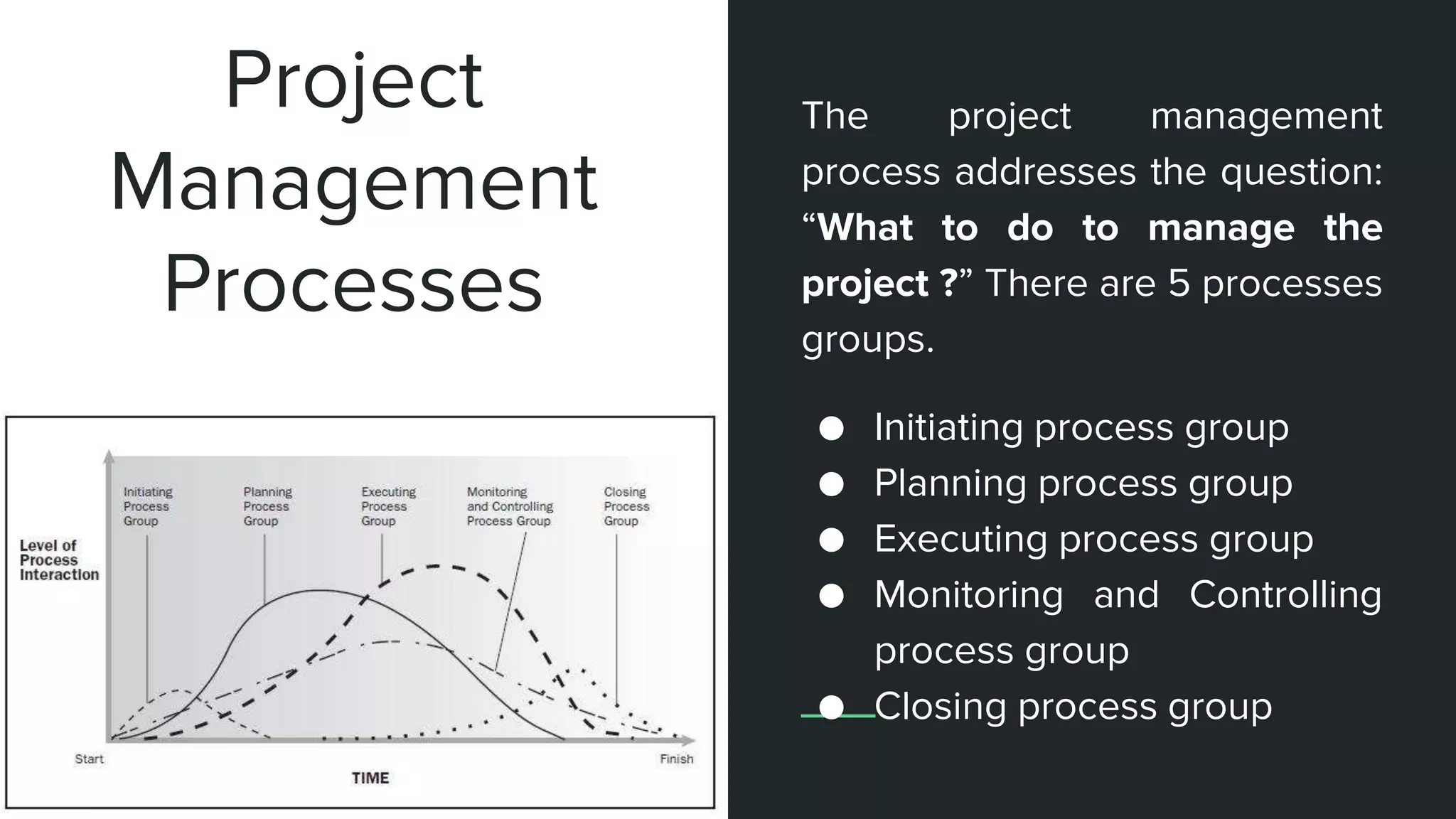
The document provides an overview of project management, including key concepts like PMP certification, project life cycles, and organizational structures. It outlines differences between projects and operational work, as well as the roles of program and portfolio management. The content also discusses the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) and the various management processes involved in directing projects.