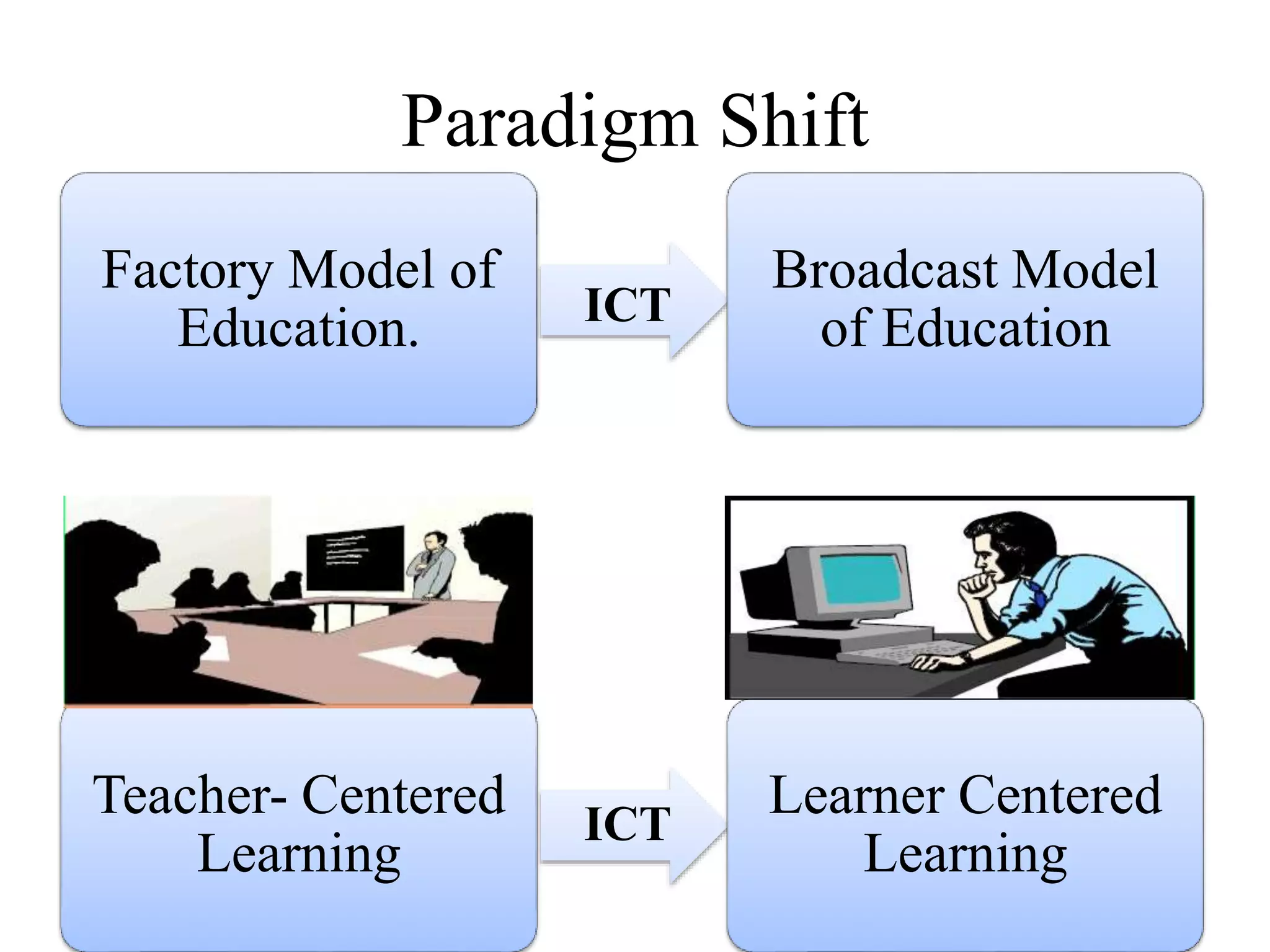
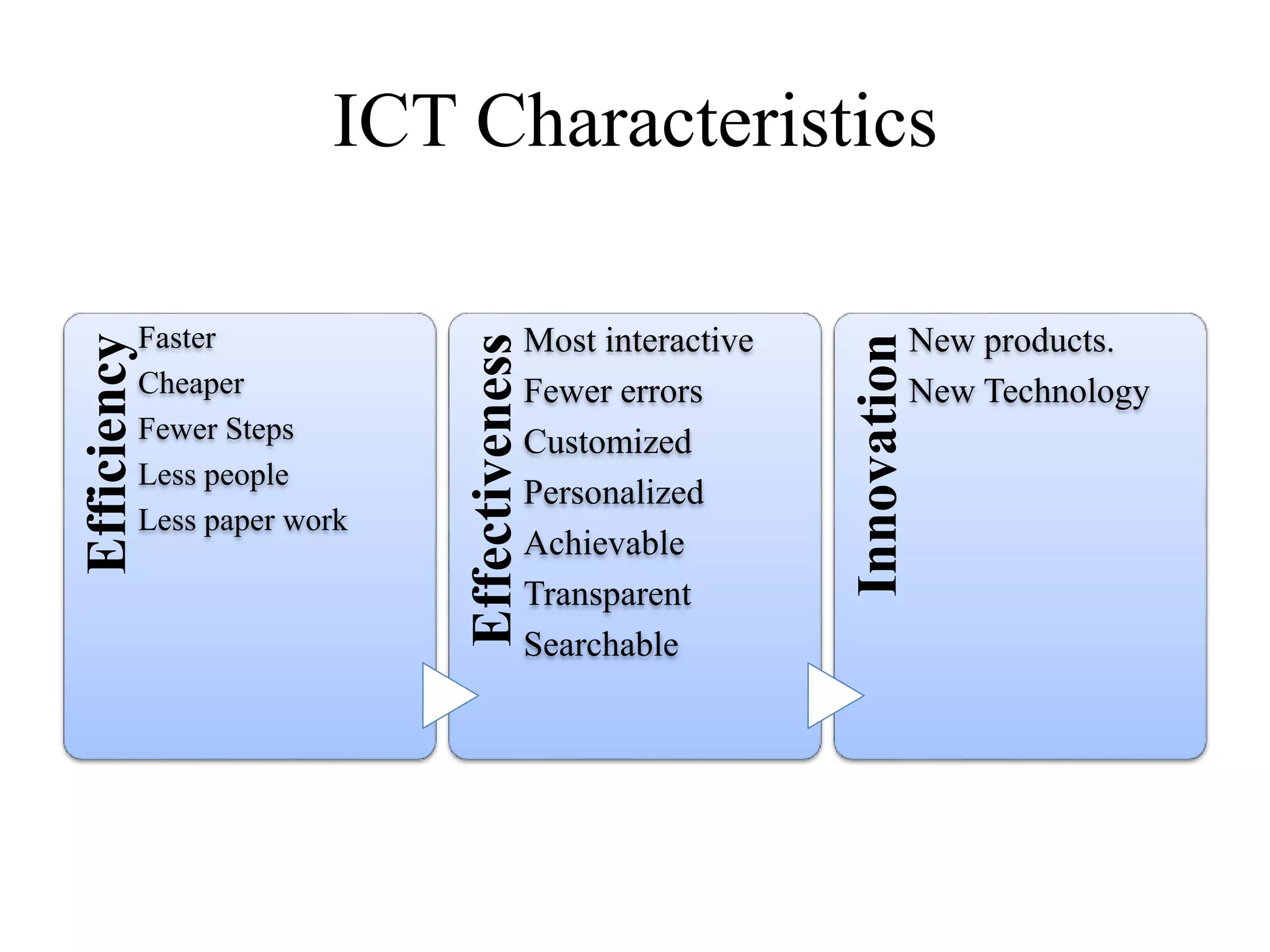
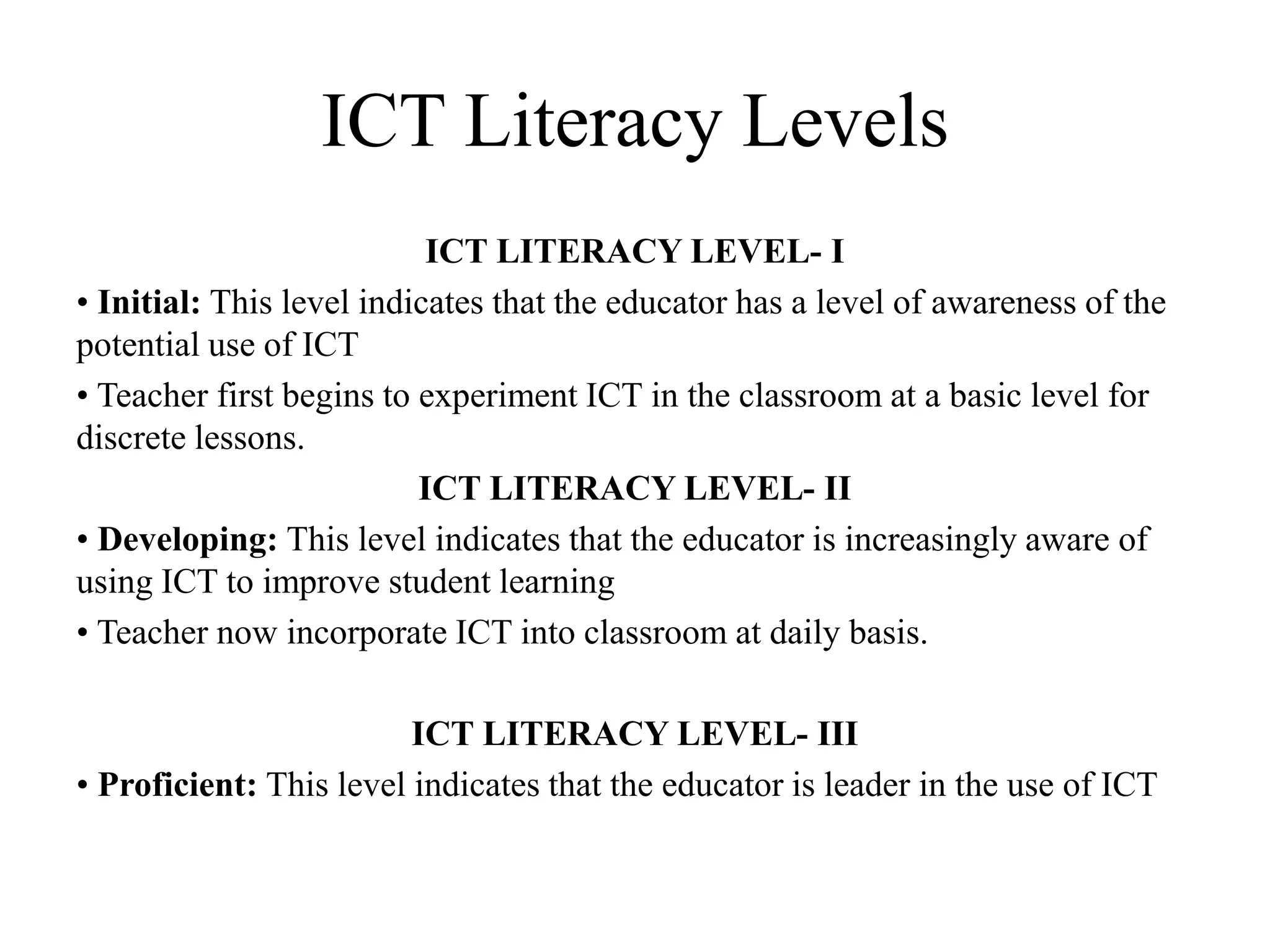
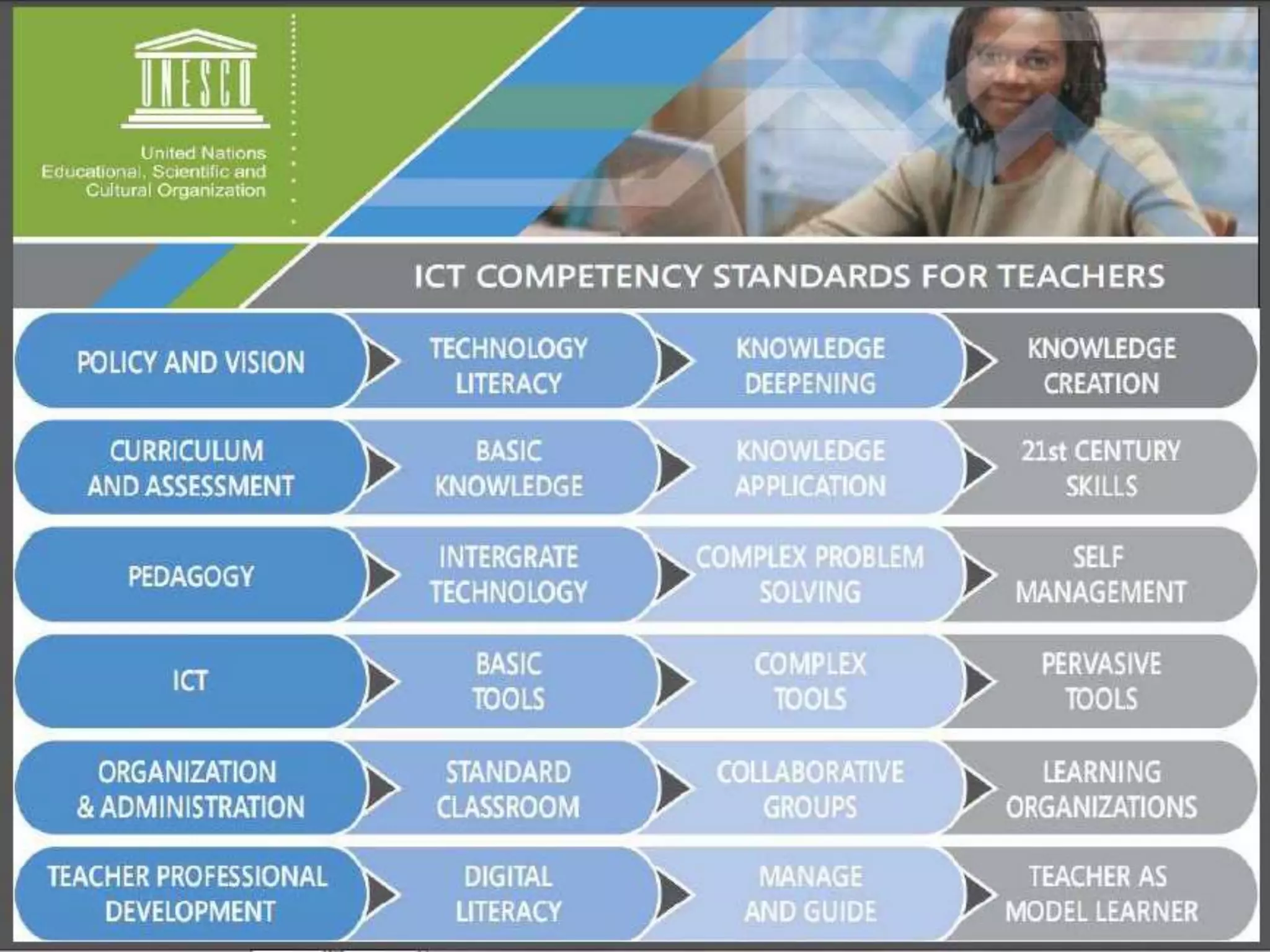
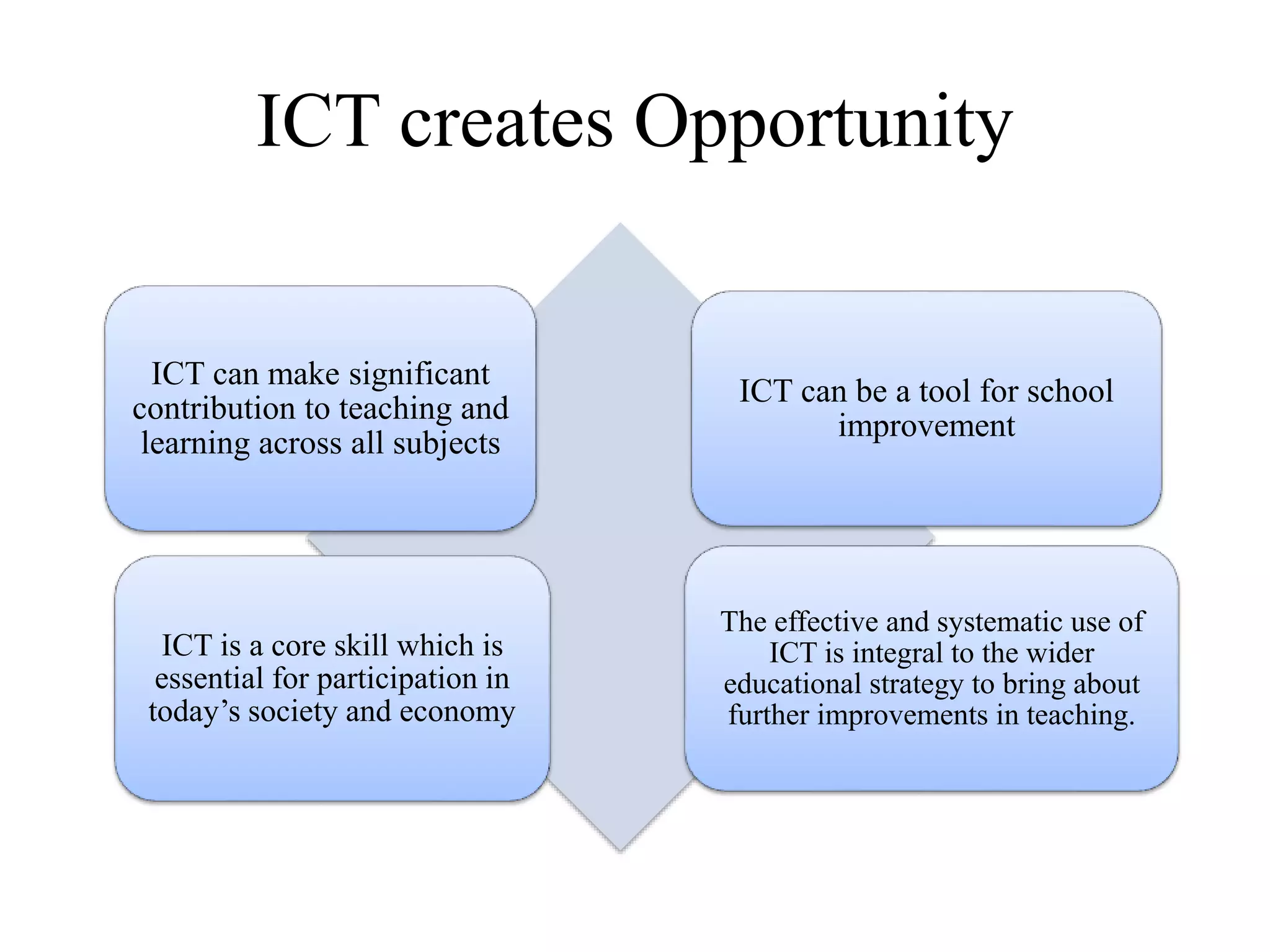
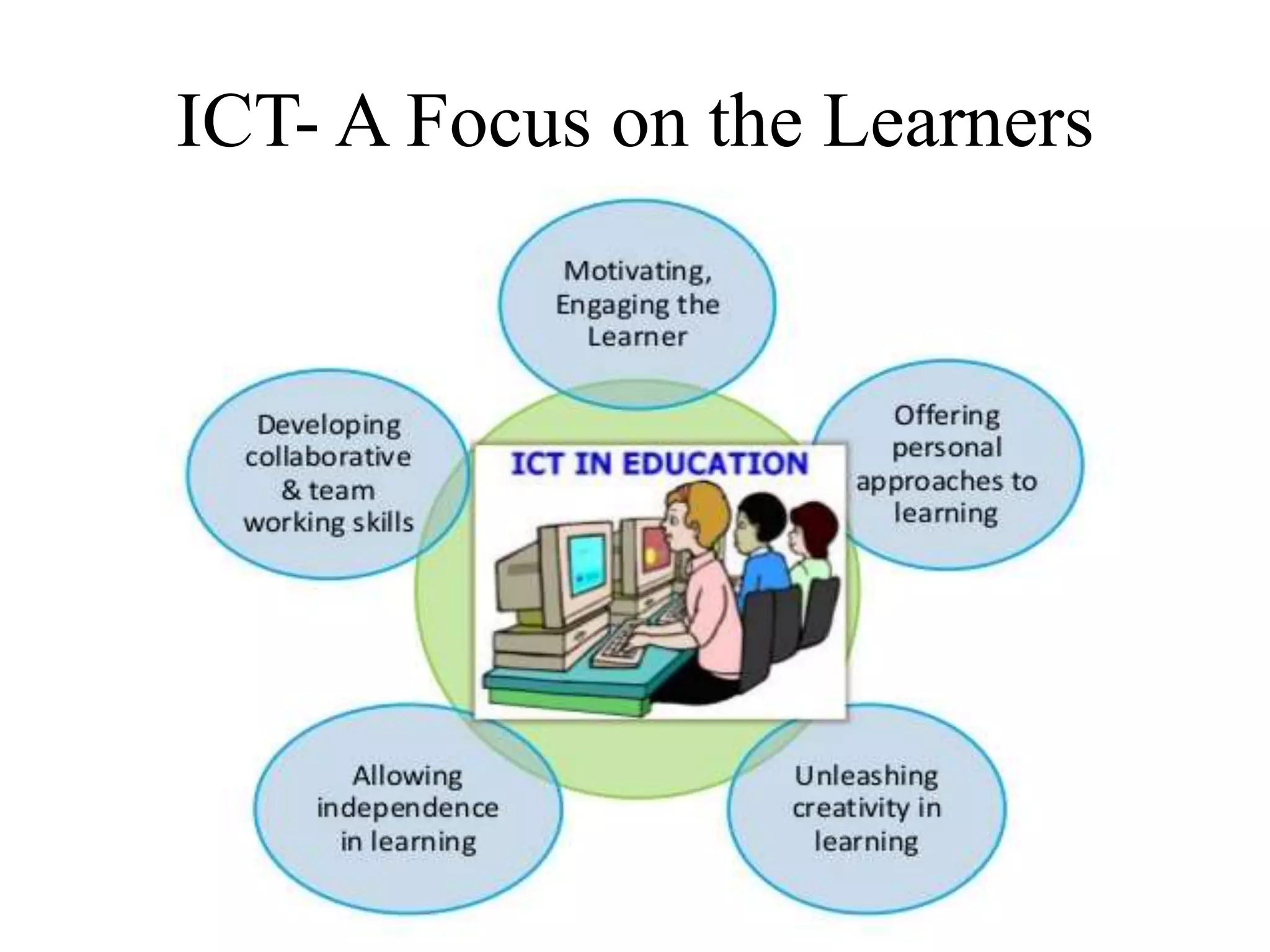
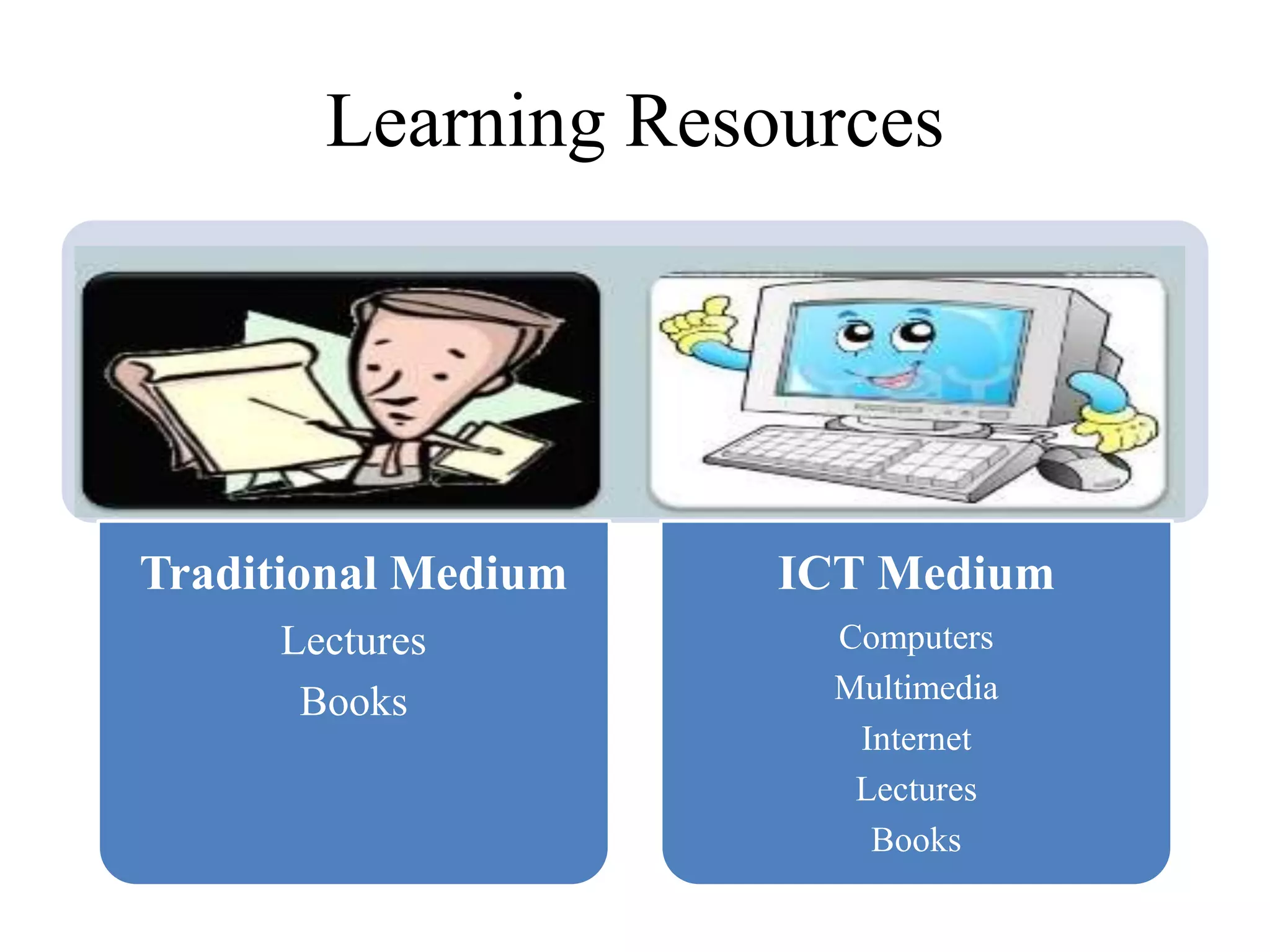
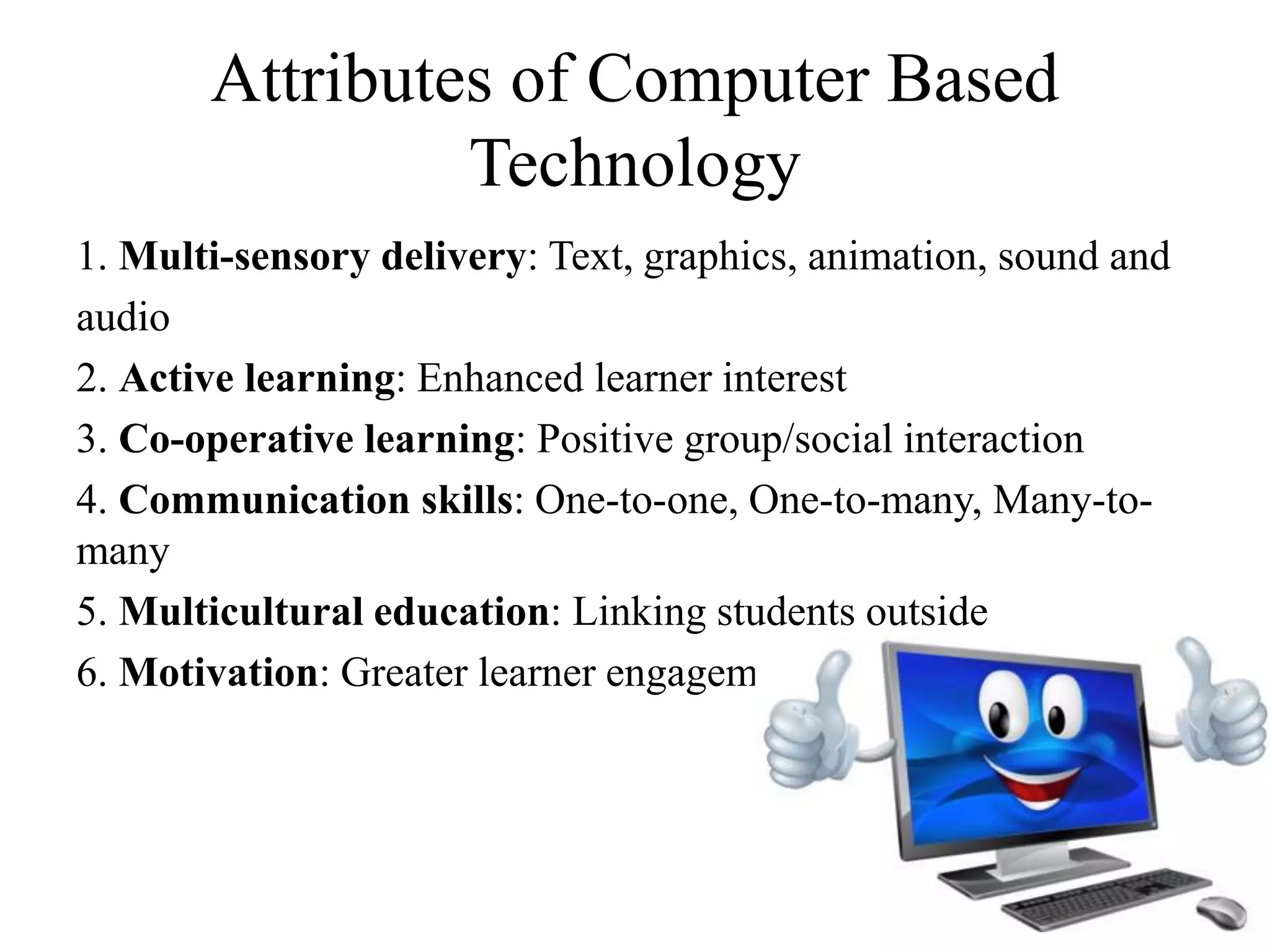
This document discusses the role of information and communication technology (ICT) in 21st century education. It begins by stating that students now need to be taught how to engage global connections and communicate collaboratively in a skilled way. ICT is then defined as newer digital technologies like computers and the Internet that can powerfully change and reform education. The document outlines how ICT provides interactive tools that can transform classrooms from teacher-centered to student-focused learning environments. It also discusses different ICT literacy levels teachers can achieve and examines the paradigm shift from traditional to ICT-based models of education. In conclusion, the document states that while ICT does not automatically improve teaching, it can accelerate and enhance learning when applied effectively.