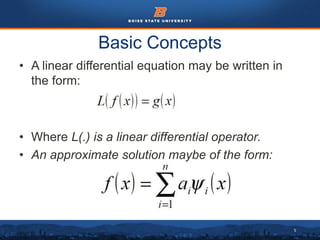
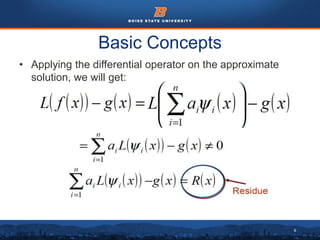
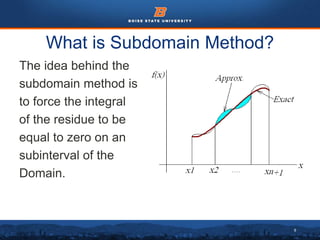
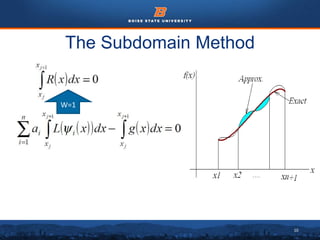
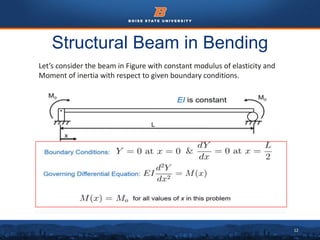
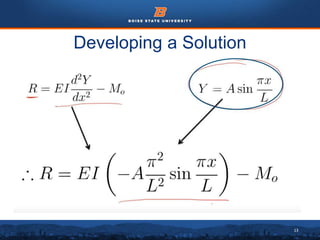
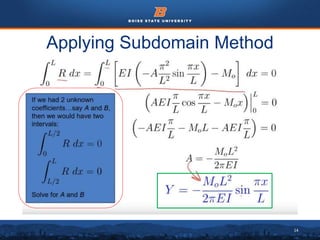
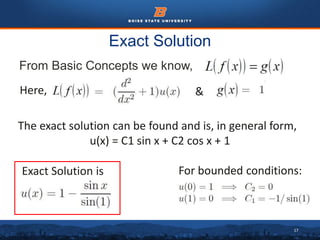
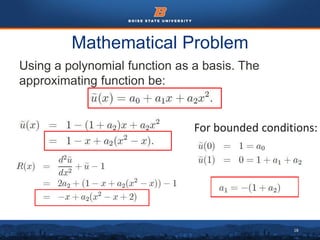
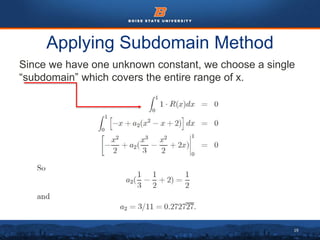
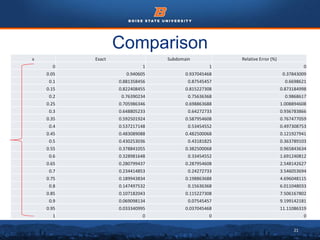
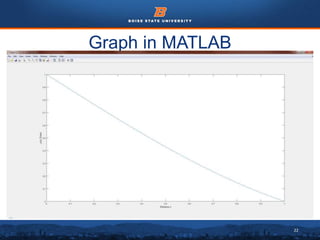
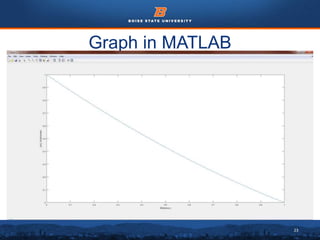
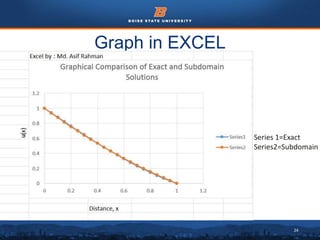
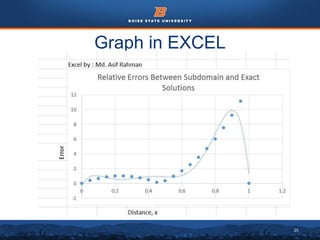
This document discusses the subdomain method for solving differential equations using finite element analysis. The subdomain method approximates solutions by forcing the integral of the residual to equal zero over subintervals, or subdomains, of the total domain. It provides an example problem of using the subdomain method to solve a second order differential equation. The exact solution is compared to the approximate subdomain solution, showing good accuracy with less than 12% relative error. The subdomain method is simple to formulate but works best for problems involving a single governing equation.