The document provides information about ISO 22301, which is an international standard for business continuity management systems (BCMS). Some key points covered include:
- ISO 22301 helps organizations implement a BCMS to meet stakeholder requirements and be resilient during disruptions.
- A BCMS aims to establish, implement, maintain and improve business continuity processes. It specifies requirements around preparing for, responding to and recovering from disruptions.
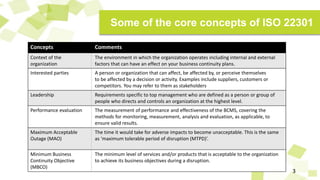
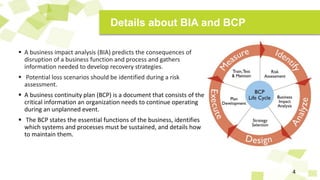
- Other concepts discussed include business impact analysis, business continuity plans, maximum acceptable outage times, and residual risks after risk reduction efforts.
- Two case studies are presented about data center outages - one from cooling failures during a heat wave, and another from an electrical explosion that injured