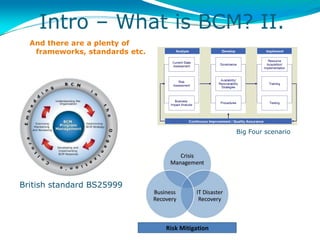
BCM, or business continuity management, involves identifying risks, analyzing the impact of disruptions on business processes, and developing recovery strategies and plans. It is important for organizations because 2 out of 5 enterprises that experience a disaster go out of business within 5 years. BCM ensures business viability during crisis situations like fires, floods, or technology failures. The most important aspects of effective BCM are planning, training employees, and regularly testing plans. While technology plays a role, BCM is not primarily about IT - it requires support from top management and focuses on protecting critical business processes.