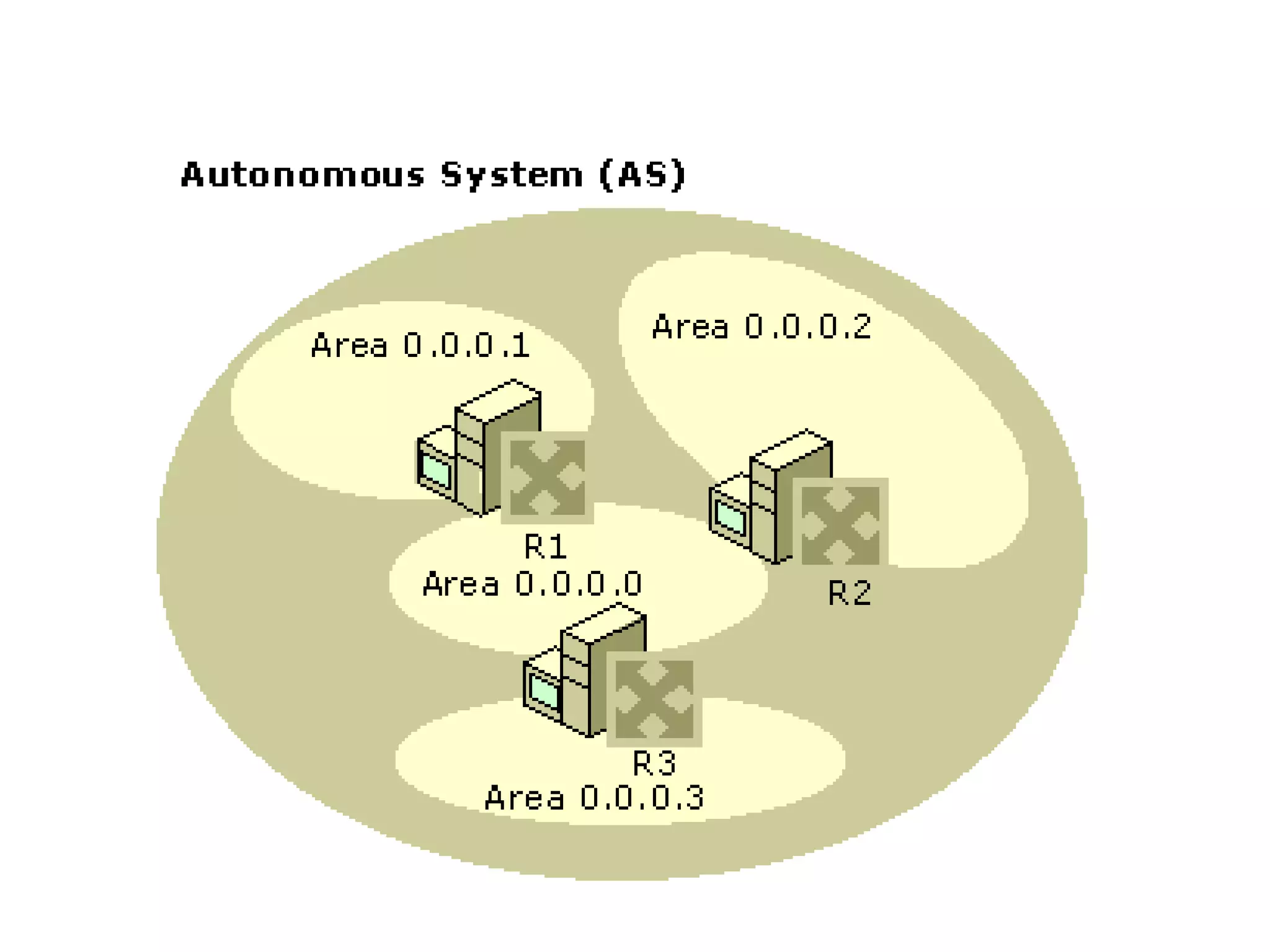
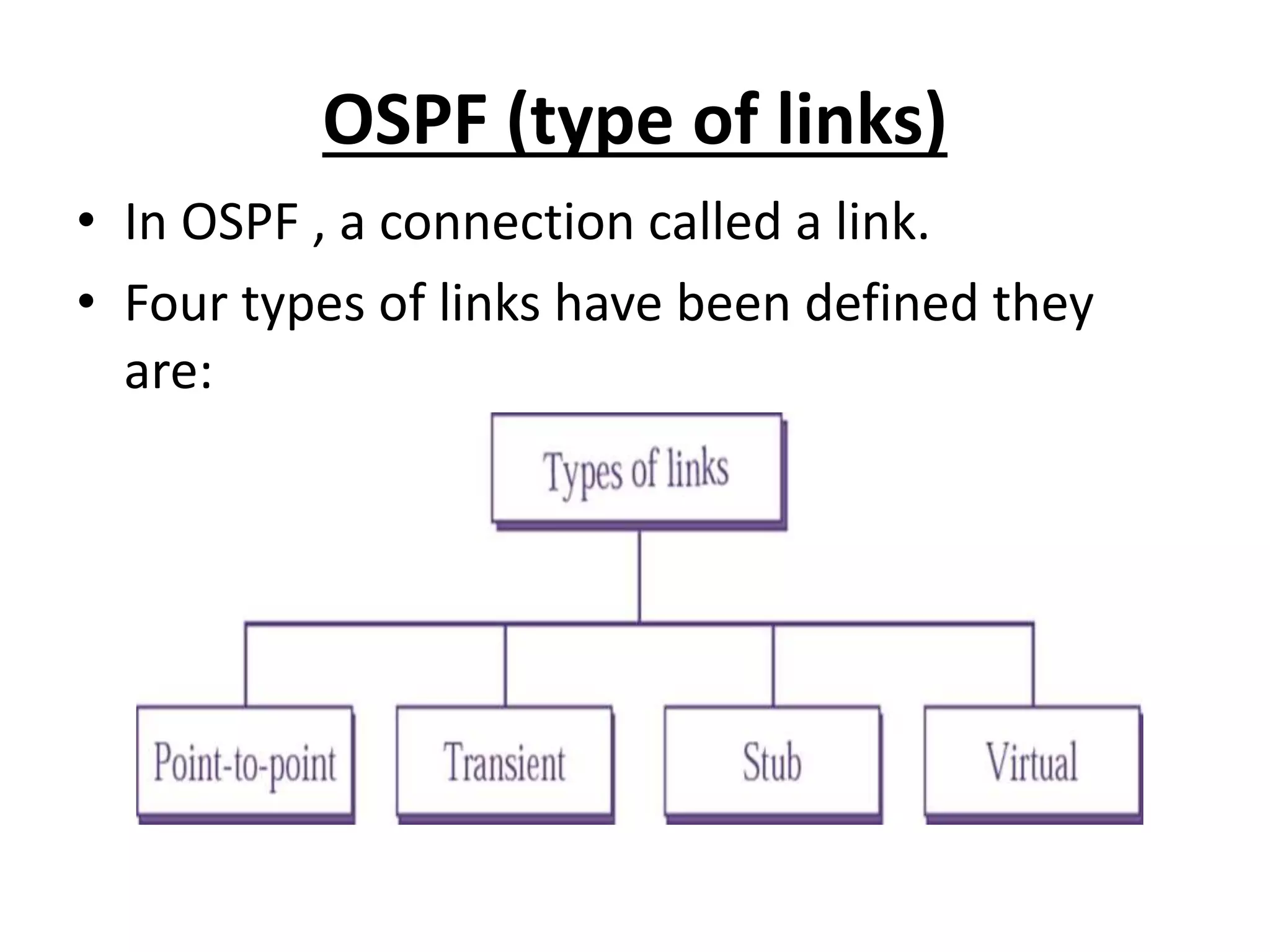
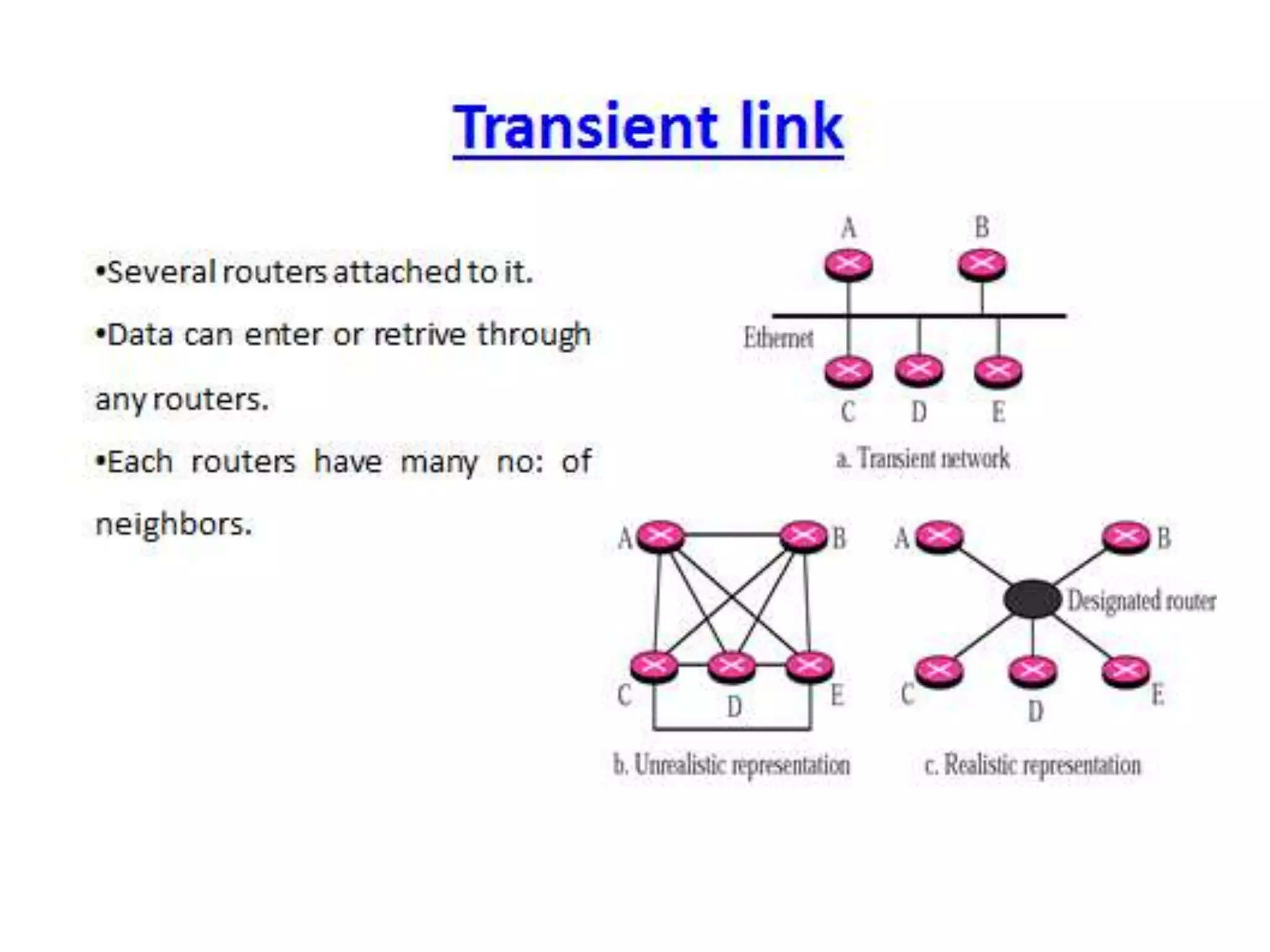
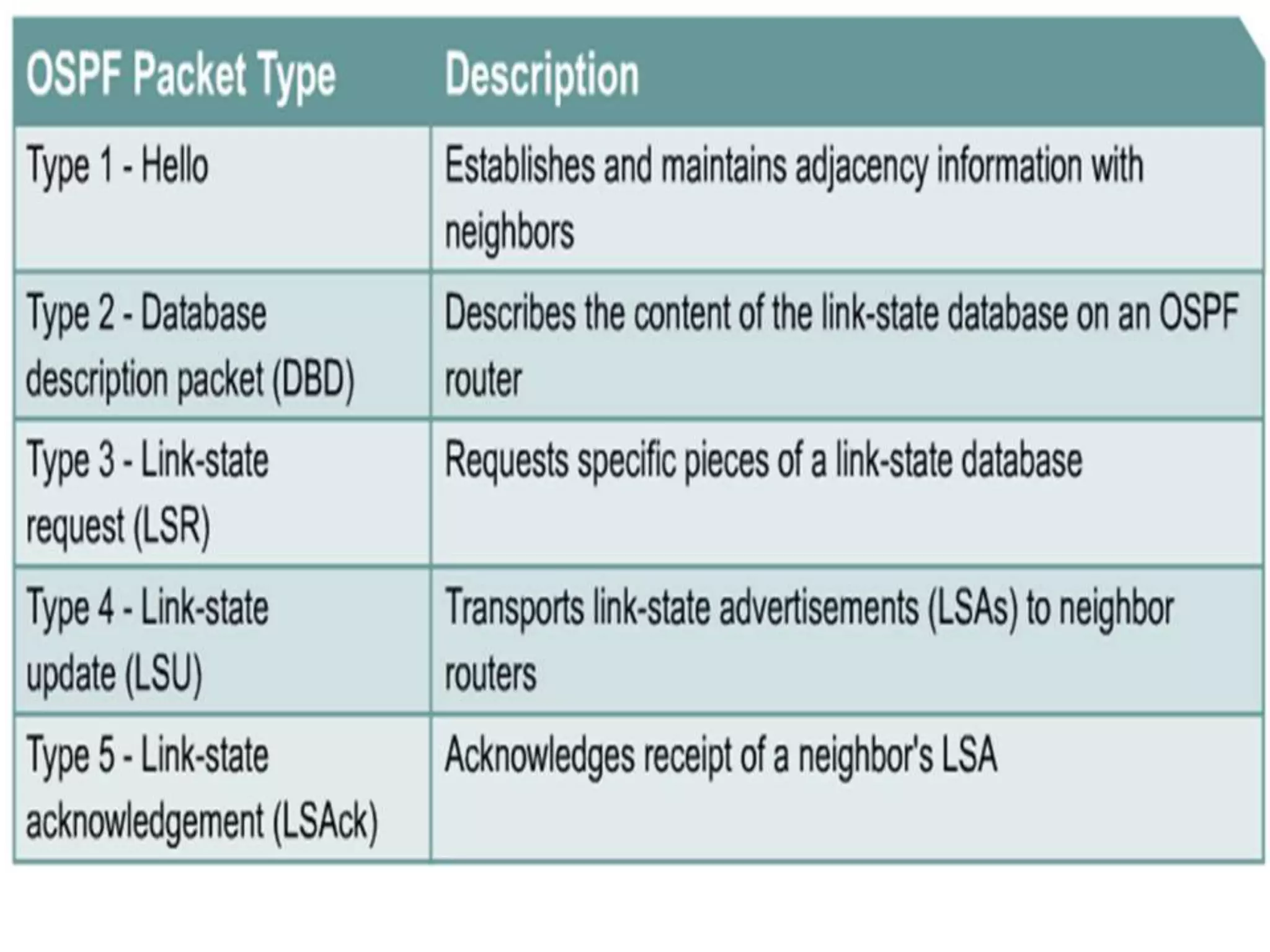
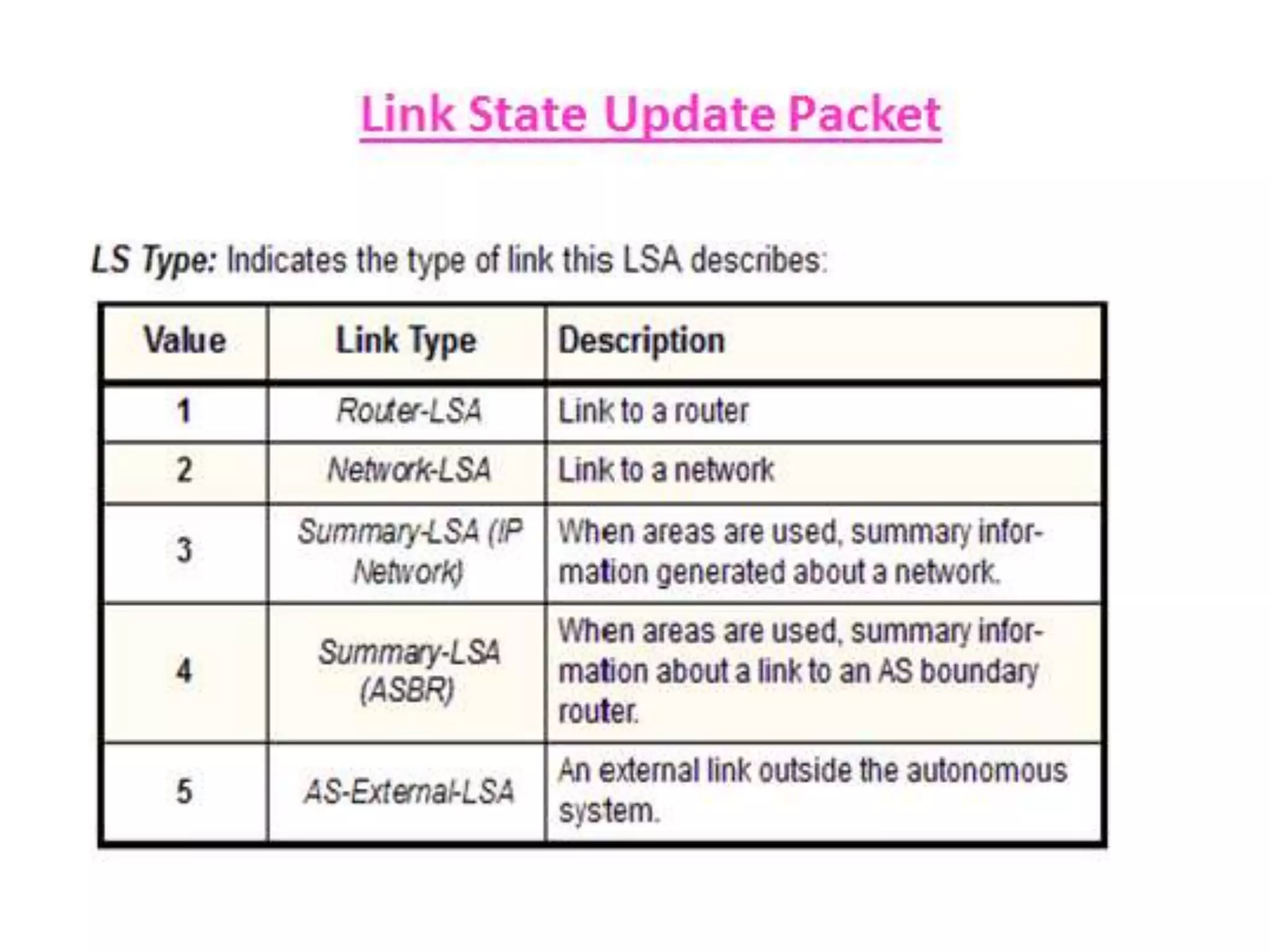
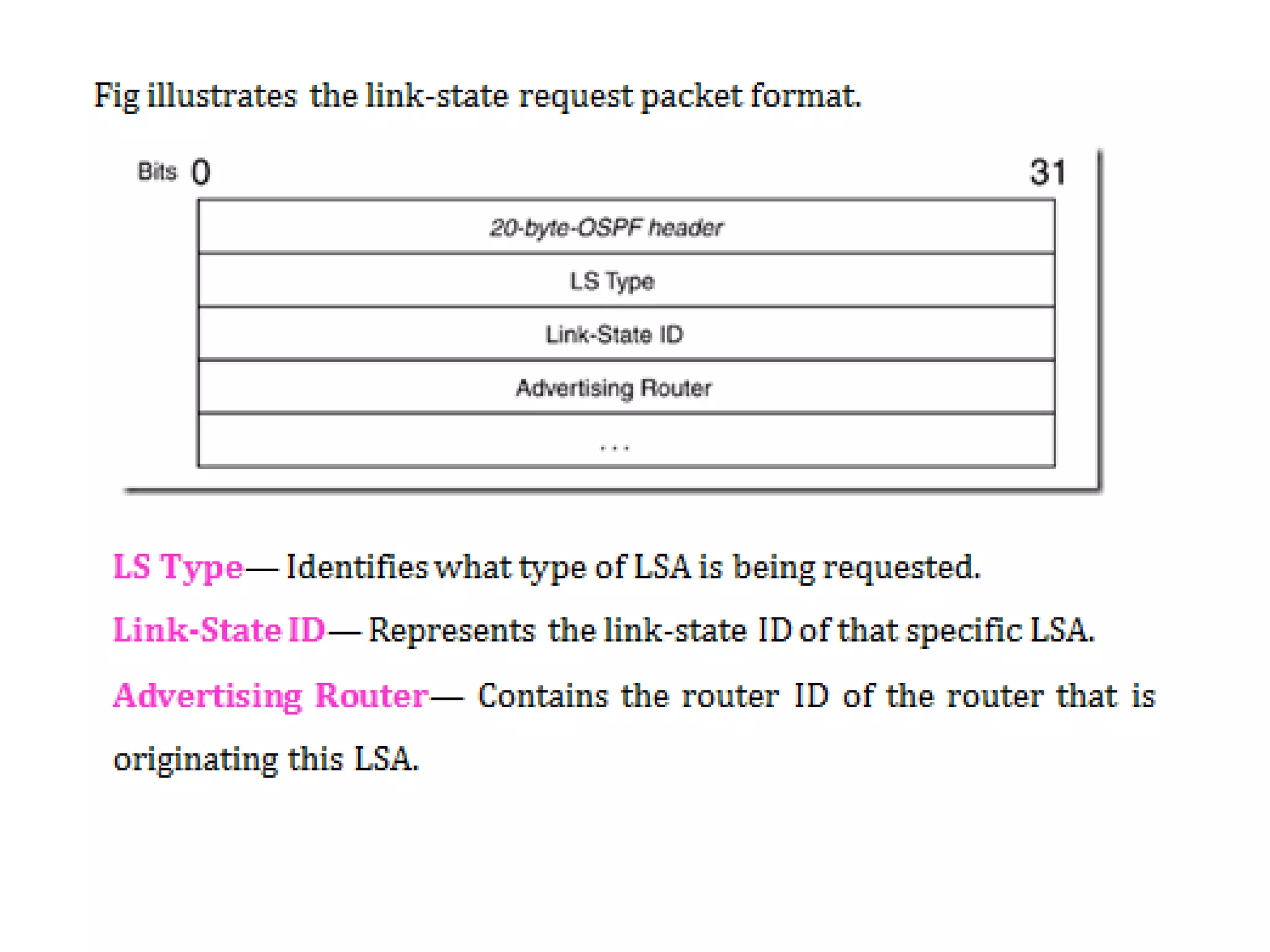
OSPF is an intra-domain routing protocol that uses a link-state algorithm to calculate the shortest path to destinations within an autonomous system. It divides an autonomous system into areas to limit routing updates and allows for route summarization between areas. OSPF uses hello packets to discover neighbors, database description packets to exchange routing information, link-state request packets to request updates, and link-state acknowledgment packets to acknowledge receipt of updates.