Embed presentation
Download to read offline



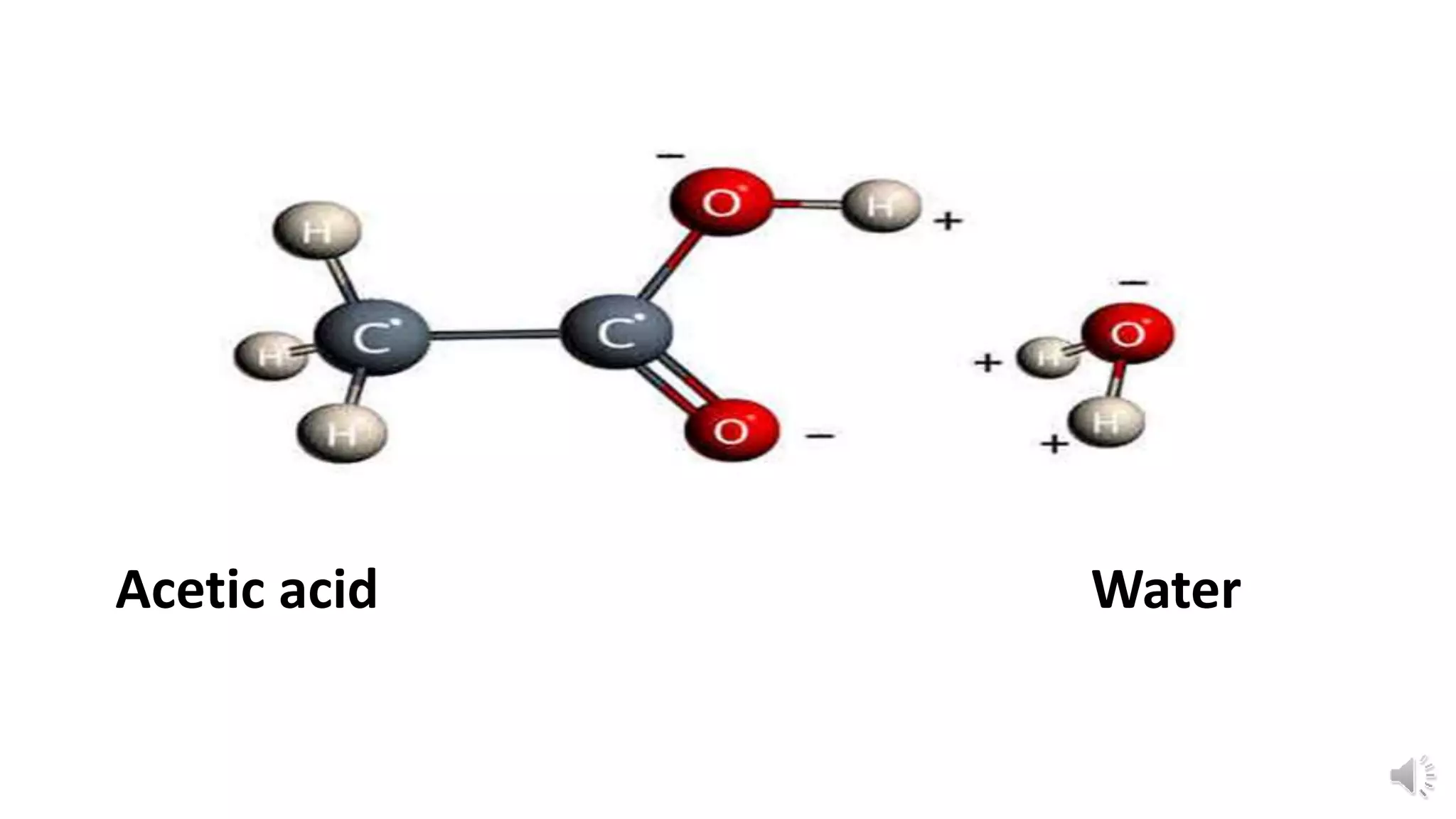
Polarity refers to a molecule having positive and negative ends due to an uneven distribution of electrons. The polarity of a bond depends on two main factors: 1) the relative electronegativity of the bonded atoms, with more electronegative atoms attracting electrons more strongly, and 2) the spatial arrangement of bonds in the molecule, as this influences how electron pairs are pulled by other atoms. For example, the O-H bond in acetic acid has different polarity than in water due to differences in their molecular structures.




