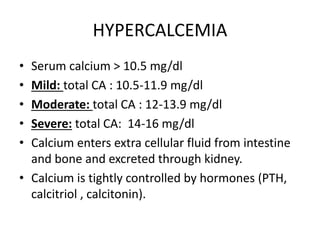
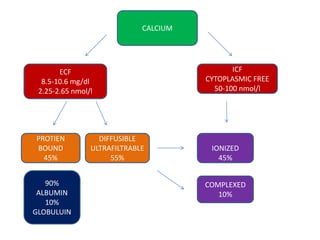
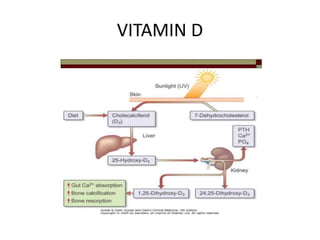
This document discusses hypercalcemia, which is defined as a serum calcium level above 10.5 mg/dl. It outlines the causes of hypercalcemia including primary hyperparathyroidism, certain cancers, and excessive vitamin D or calcium supplementation. Signs and symptoms are noted such as abdominal pain, nausea, weakness and cardiac issues. Diagnostic testing including PTH, calcium, and phosphate levels as well as imaging are covered. Treatment focuses on rehydration, bisphosphonates, glucocorticoids, calcitonin, surgery if needed, and addressing the underlying cause. Complications of untreated hypercalcemia include osteoporosis, kidney stones, and kidney failure.