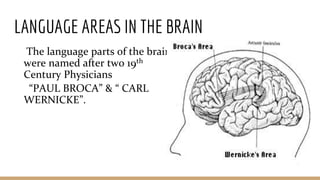
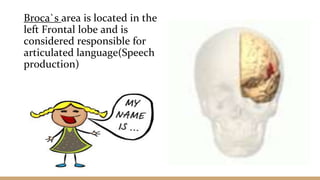
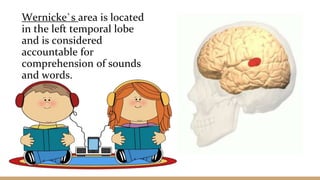
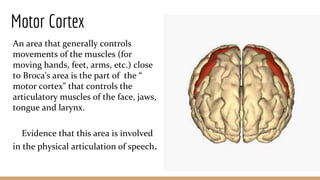
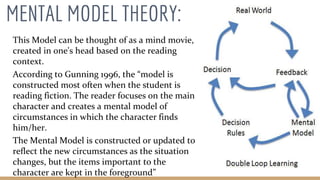
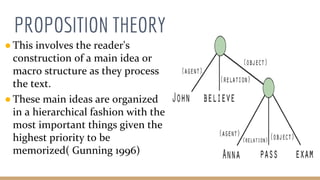
This document discusses language comprehension and the brain areas involved. It describes how comprehending language is a complex process that utilizes various skills and knowledge. Two key brain areas are Broca's area in the frontal lobe, involved in speech production, and Wernicke's area in the temporal lobe, involved in comprehending sounds and words. It also outlines three main theories of language comprehension: schema theory involving background knowledge, mental model theory creating a mind movie based on context, and proposition theory constructing a hierarchical structure of main ideas.