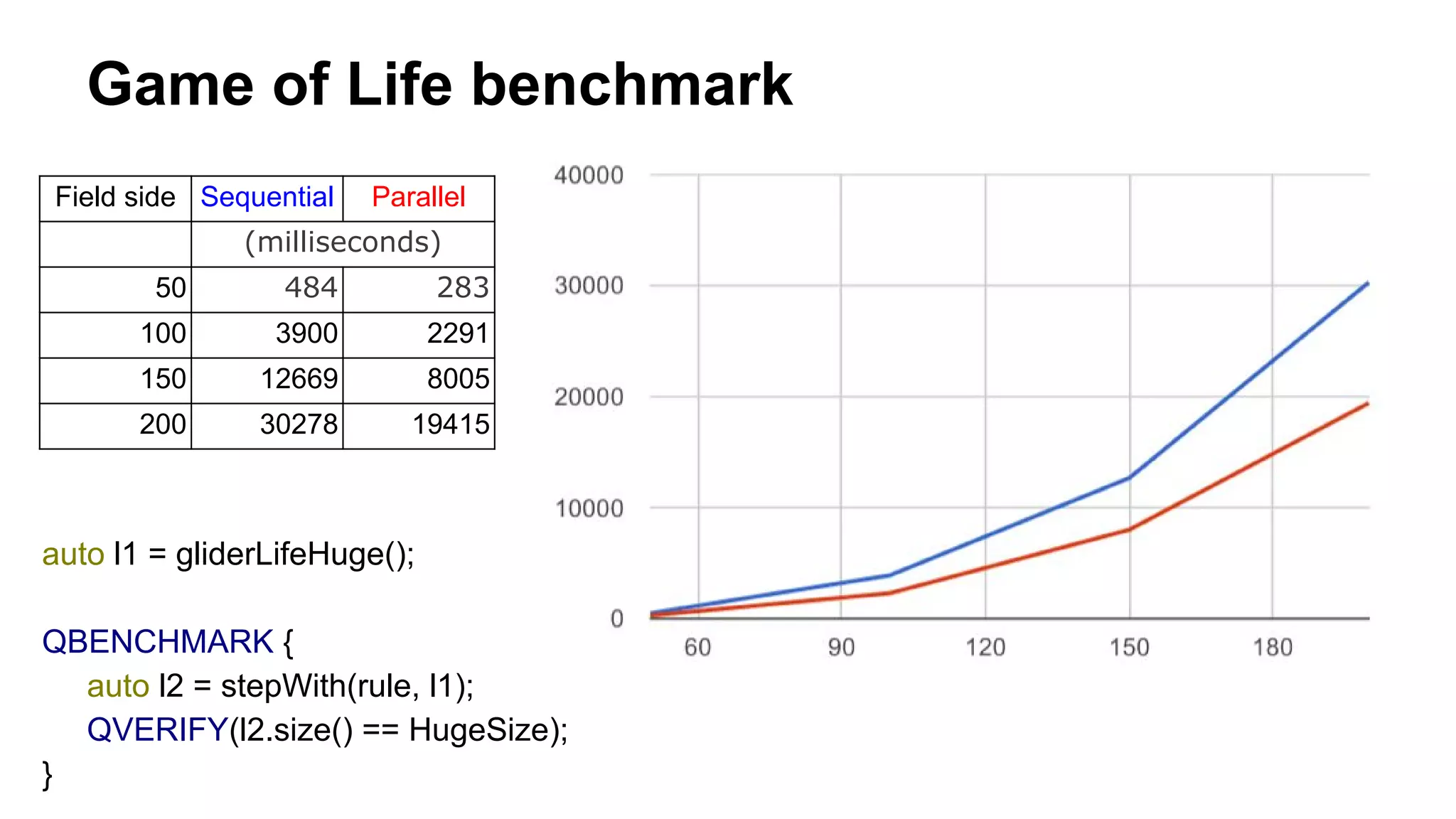
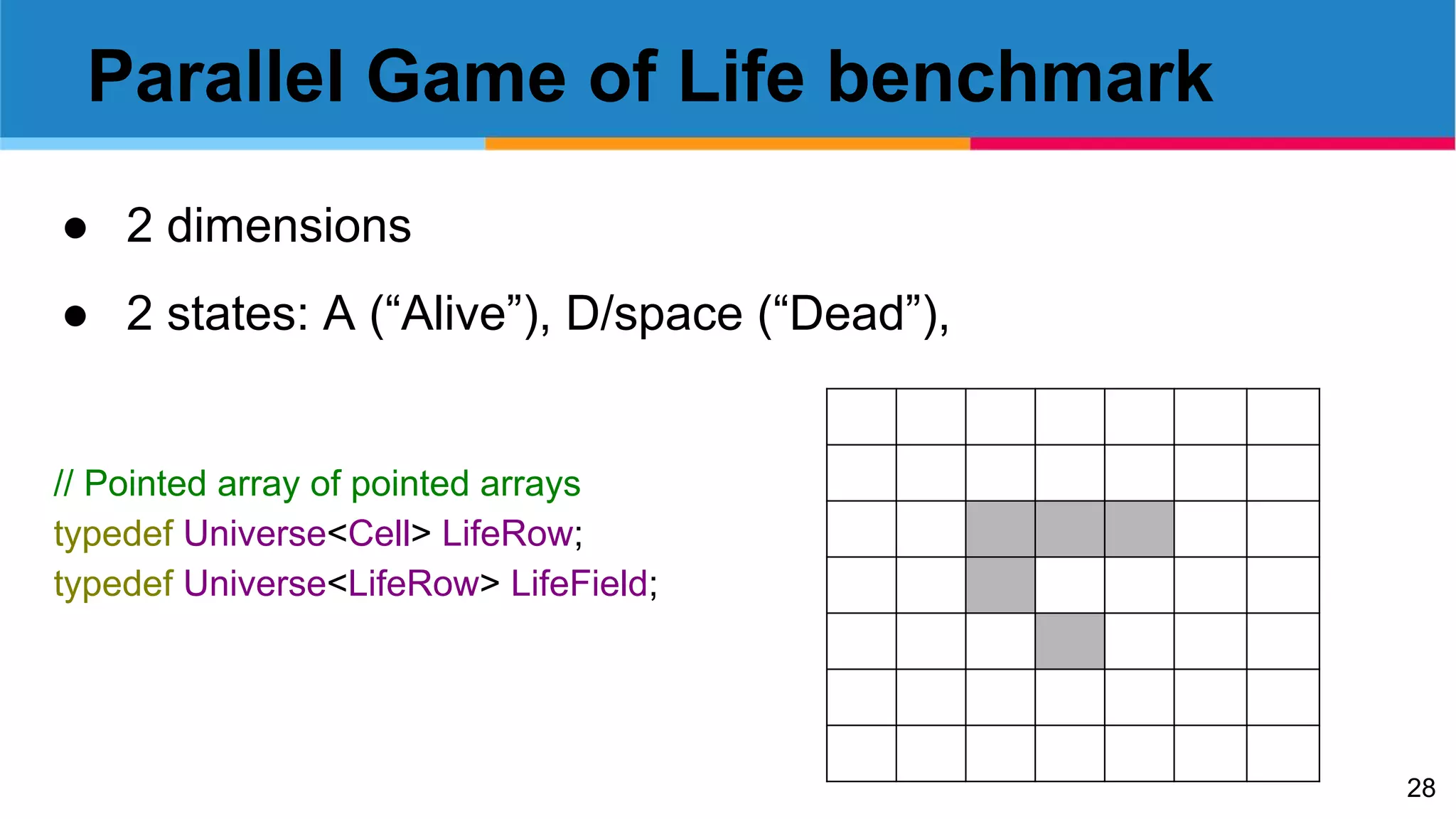
The document presents an exploration of functional programming concepts within C++, focusing on parallel cellular automata and comonads. It includes code examples, theoretical constructs, and benchmarks for implementing a Game of Life simulator using a functional design approach. The work highlights the implementation of functional techniques and their applications to parallel computation in C++, along with performance comparisons of sequential versus parallel execution.



 { return old + 6; };
Account account3 = over(lens, account2, modifier);
// account3.person.address.house == 26
Lens 2 Lens 3Lens 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionallife-160312060222/75/Functional-Life-parallel-cellular-automata-and-comonads-7-2048.jpg)

![Observing: shift and extract
A A A A
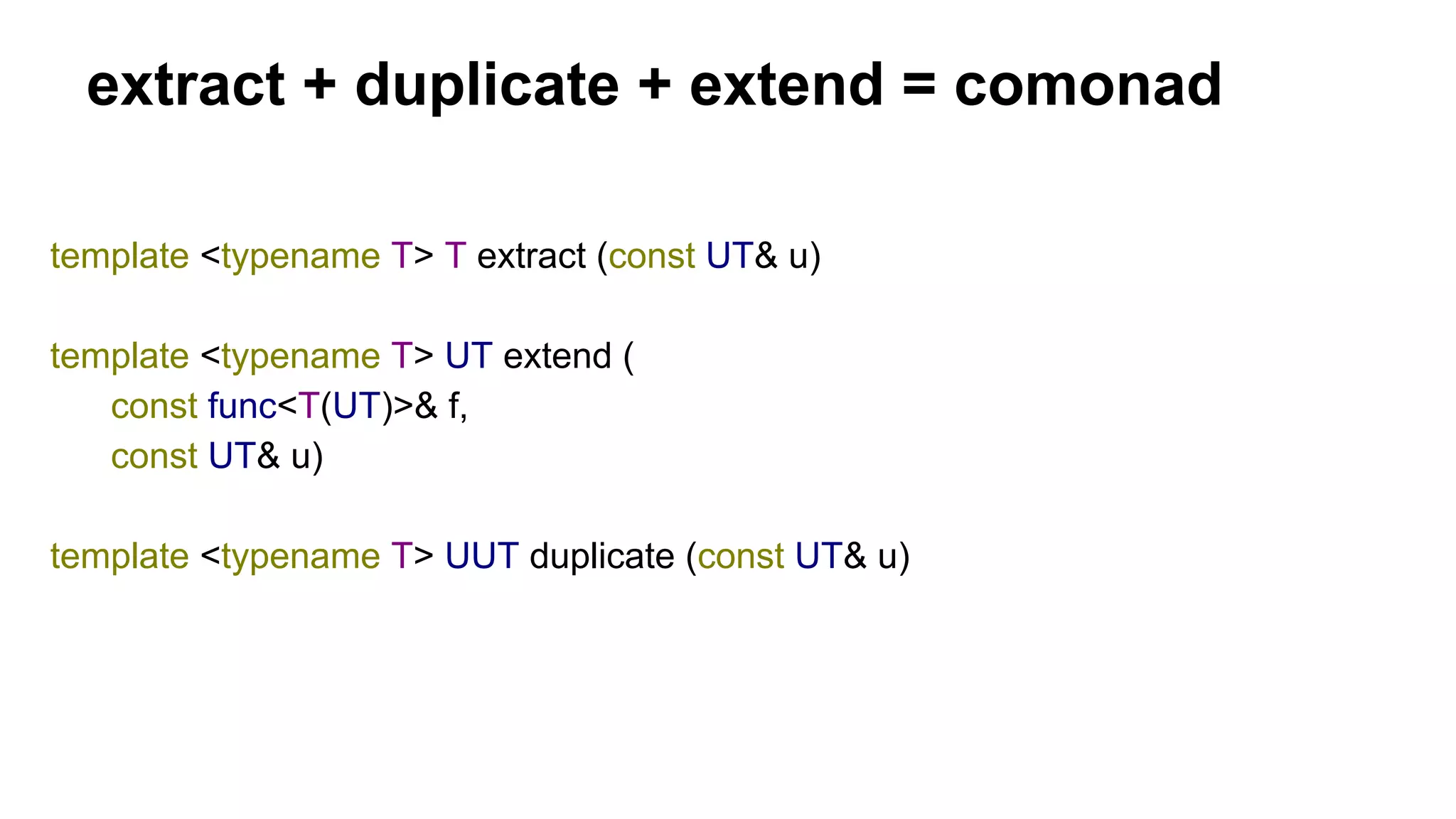
Cell extract(const Universe<Cell>& u) {
return u.field[u.position];
}
Universe<Cell> u = {...};
Cell cur = extract (u);
Cell r = extract (right (u));
Cell rr = extract (right (right (u)));
Cell l = extract (left (u));
Cell ll = extract (left (left (u)));
D
A A A A
shift to left
shift to left
extract](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionallife-160312060222/75/Functional-Life-parallel-cellular-automata-and-comonads-12-2048.jpg)



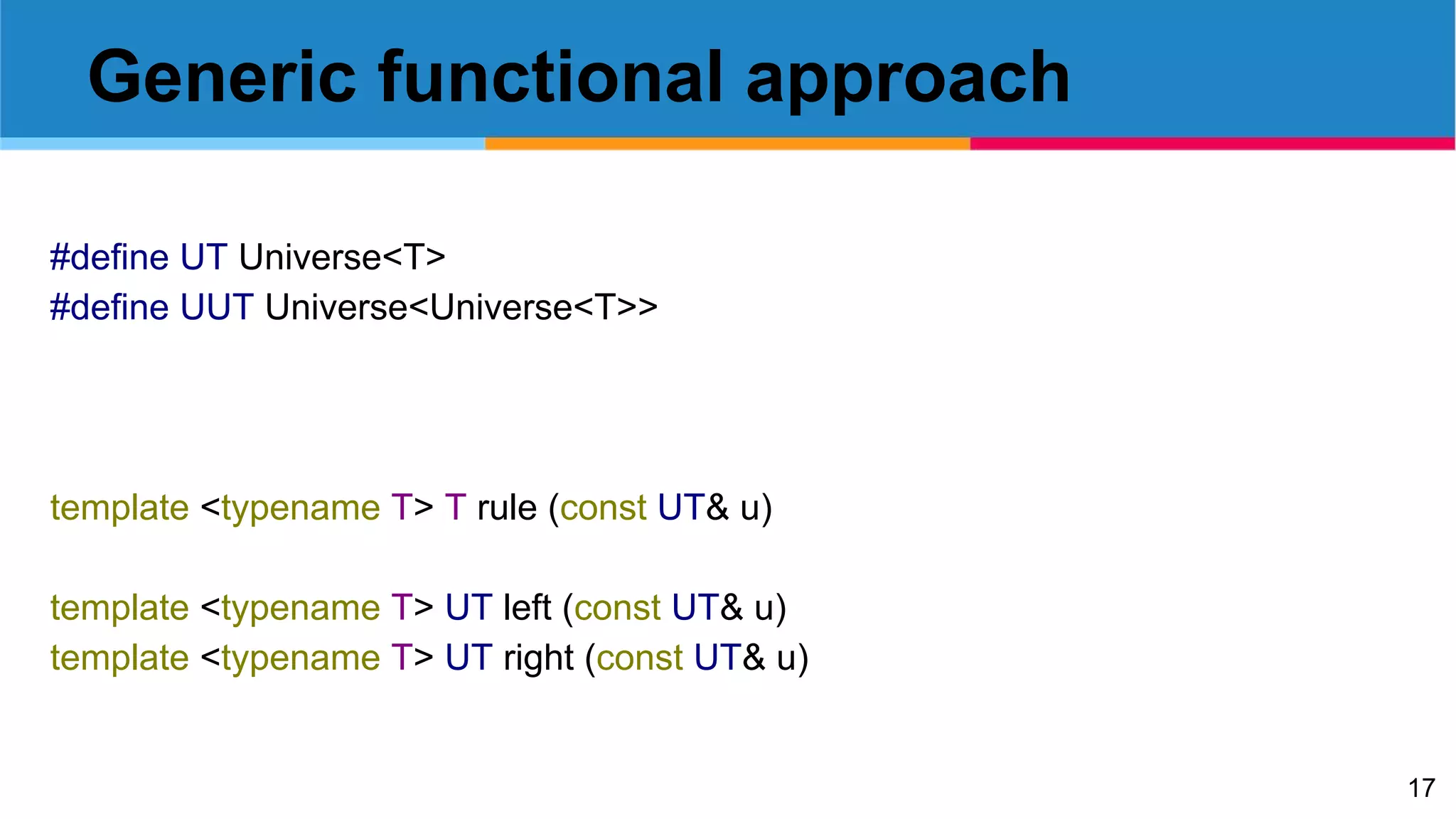
![Generic extract
template <typename T> T extract(const UT& u)
{
return u.field[u.position];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionallife-160312060222/75/Functional-Life-parallel-cellular-automata-and-comonads-18-2048.jpg)

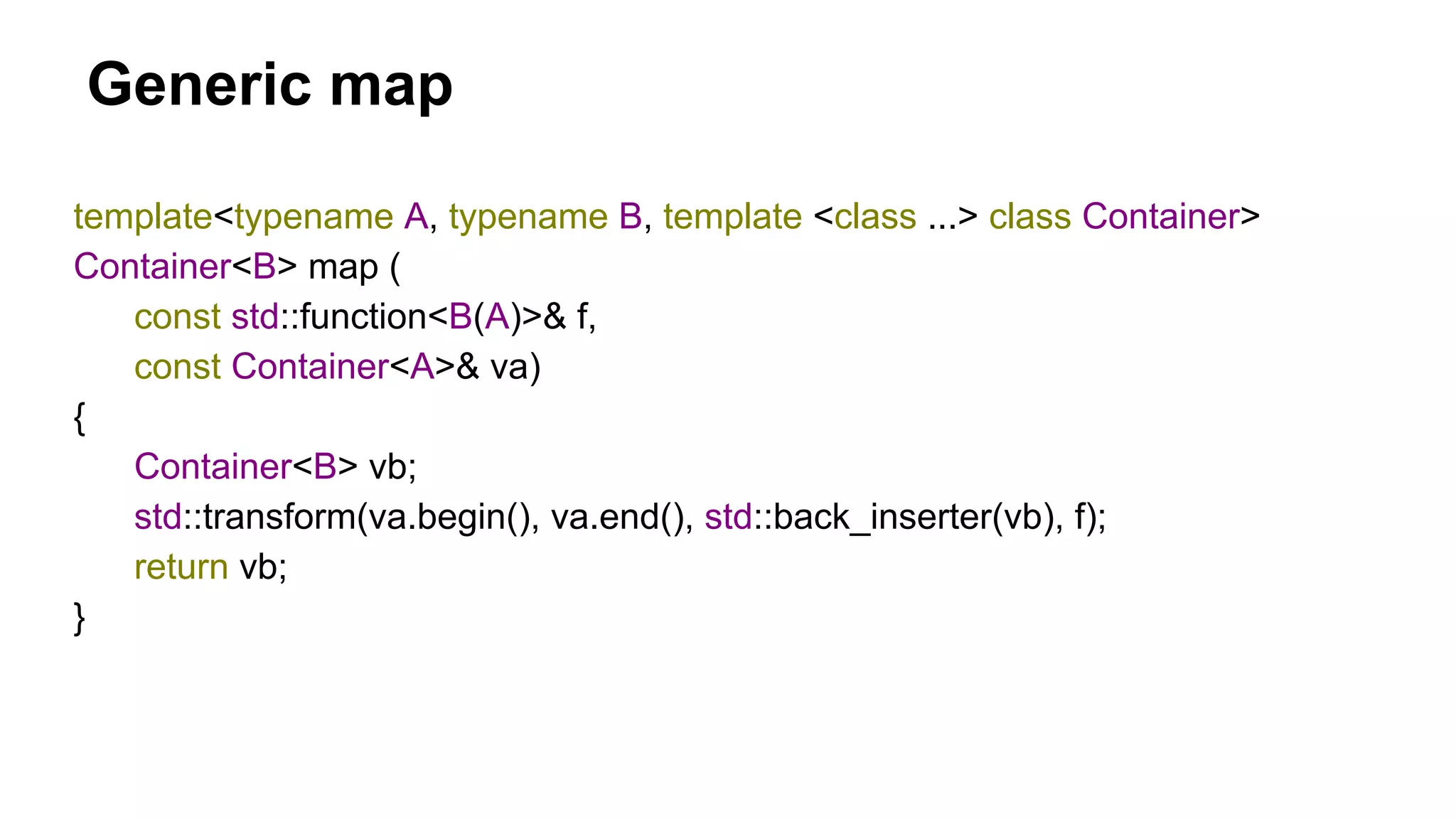
 {return left(u); };
const std::function<UT(UT)> rightCreator = [](const UT& u) {return right(u); };
template <typename T> UUT duplicate (const UT& u)
{
return makeUniverse (leftCreator, rightCreator, u);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionallife-160312060222/75/Functional-Life-parallel-cellular-automata-and-comonads-21-2048.jpg)



{
return std::async(std::launch::async, [=]() { return f(a); } );
};
}
par](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionallife-160312060222/75/Functional-Life-parallel-cellular-automata-and-comonads-26-2048.jpg)
![template <typename B> std::future<std::vector<B>> joinPars(
std::vector<std::future<B>>& pars)
{
return std::async(std::launch::async, [&]() {
std::vector<B> bs;
bs.reserve(pars.size());
for (auto& it : pars)
bs.push_back(it.get());
return bs;
});
}
joinPars](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionallife-160312060222/75/Functional-Life-parallel-cellular-automata-and-comonads-27-2048.jpg)


 {
UT newUt;
newUt.position = uuut2.position;
newUt.field = map (f, uuut2.field);
return newUt;
};
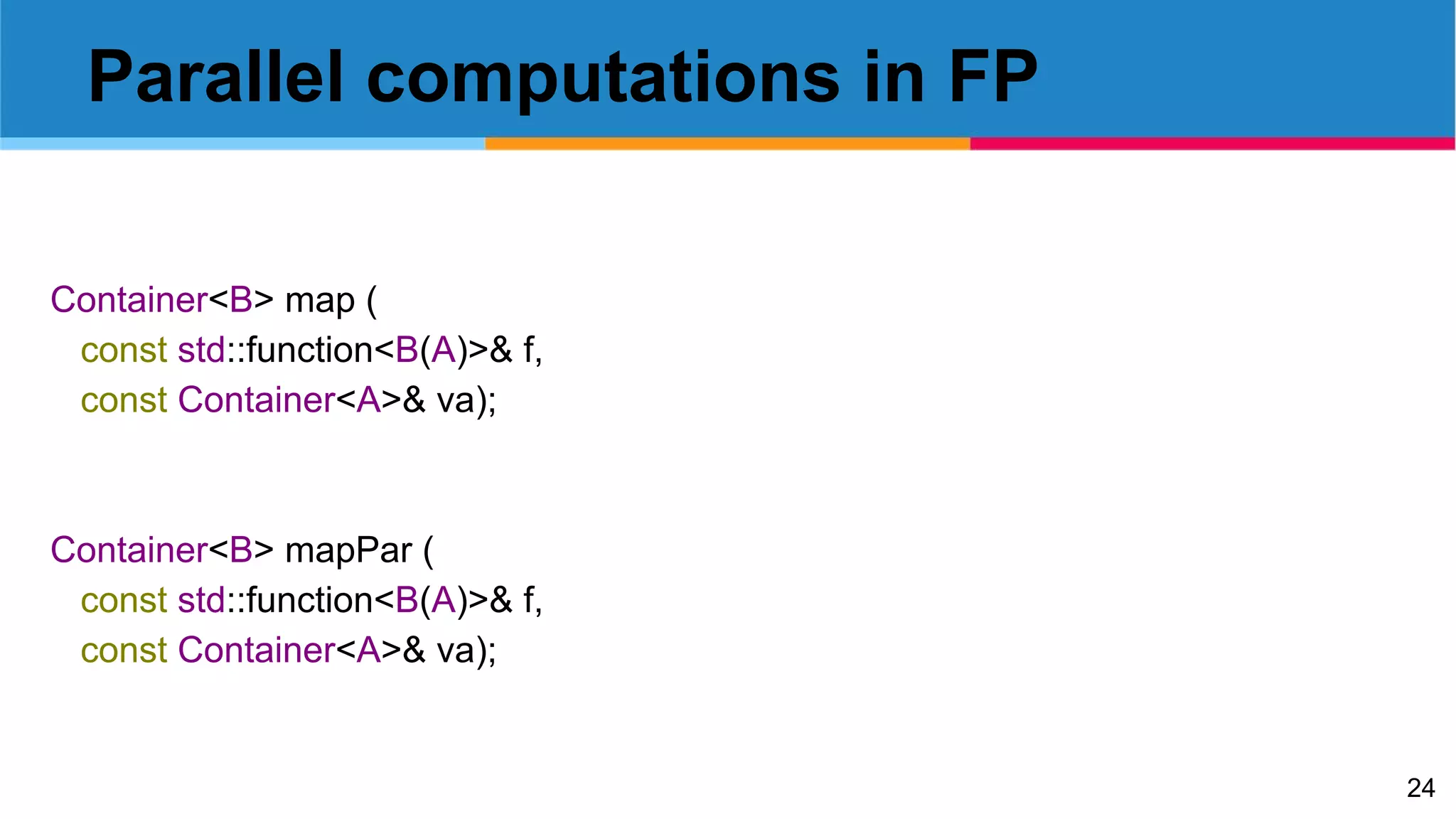
return { map (f2, uuut.field), uuut.position }; // parallelization: map -> mapPar
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionallife-160312060222/75/Functional-Life-parallel-cellular-automata-and-comonads-31-2048.jpg)