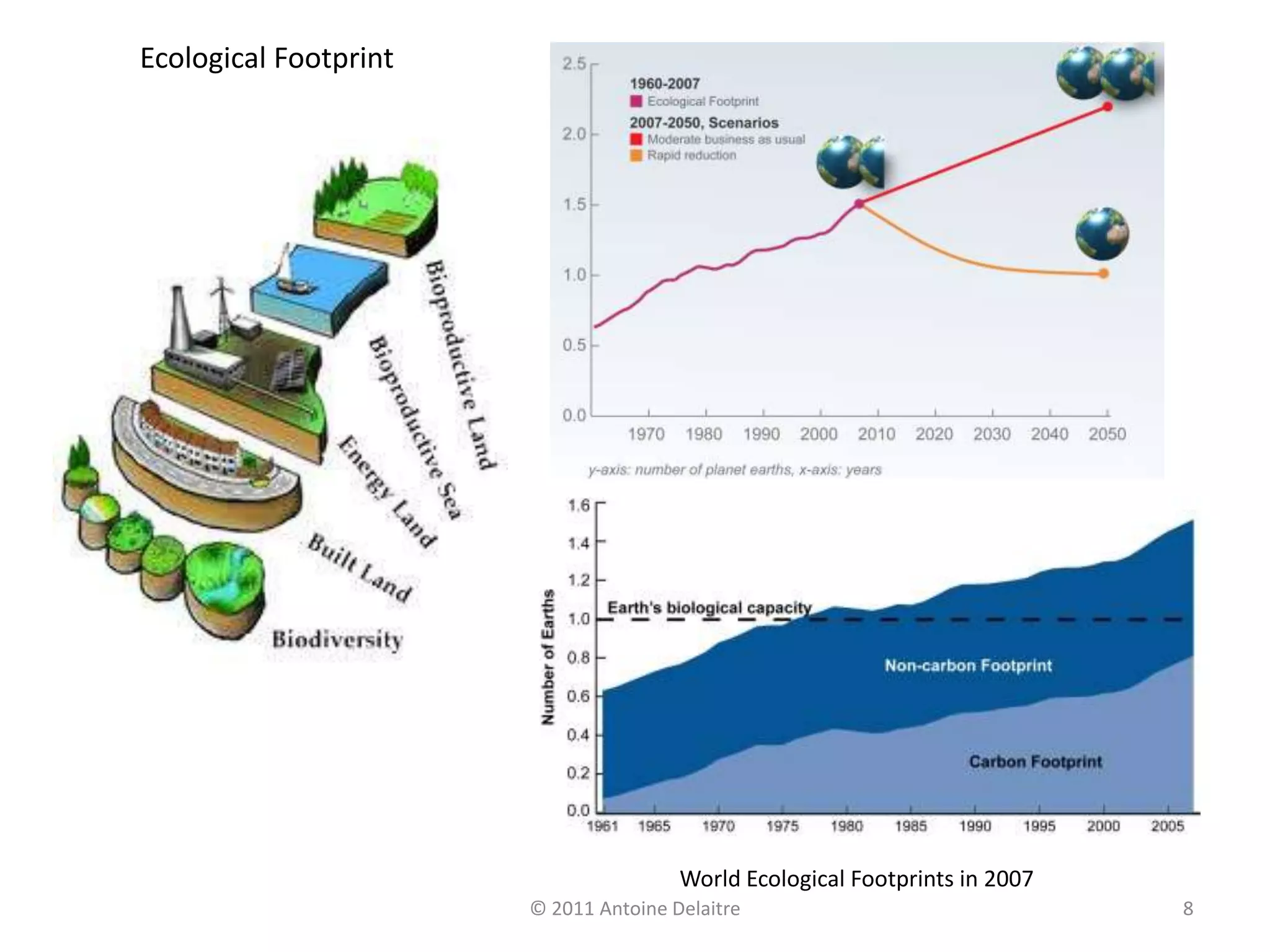
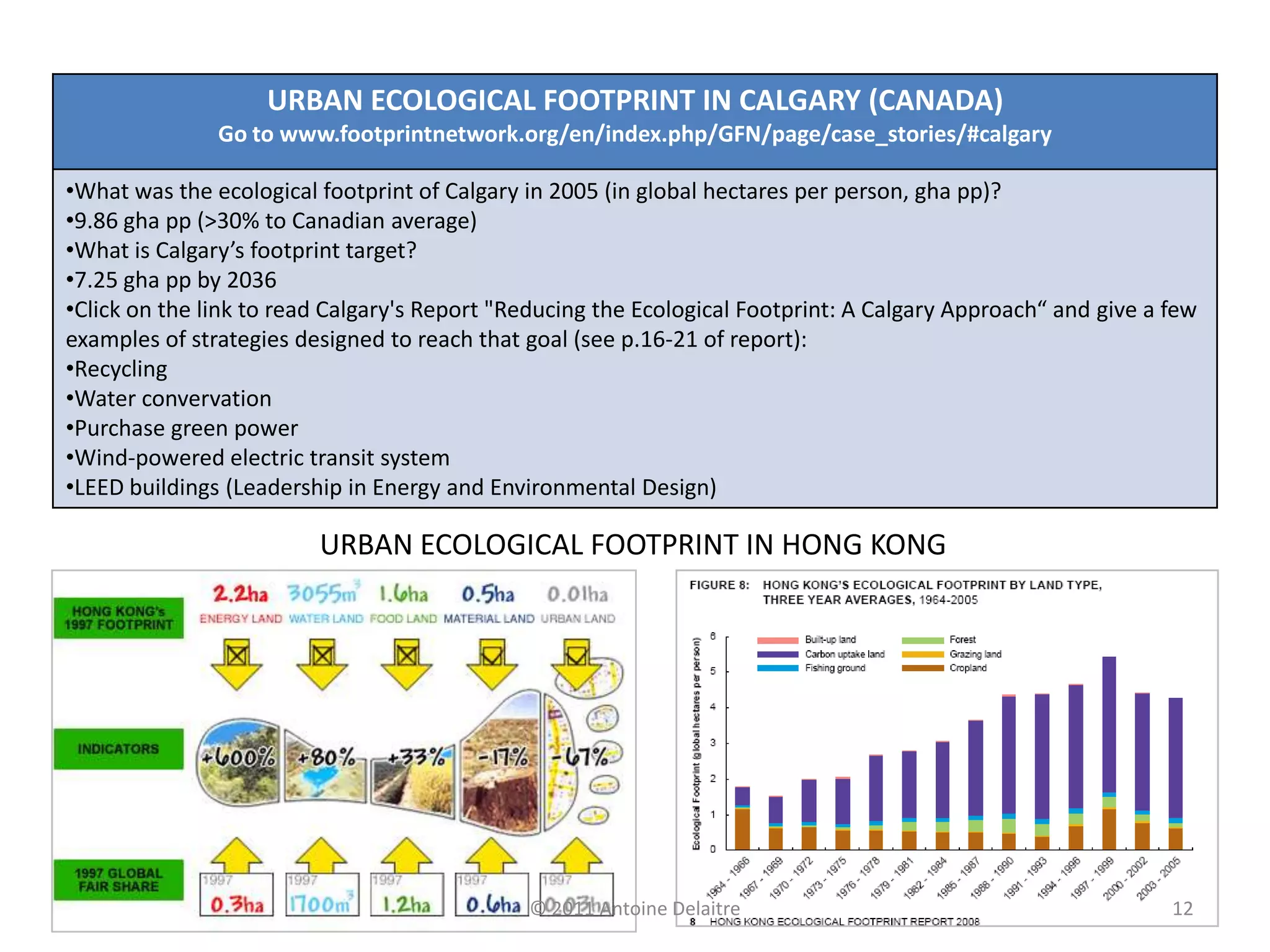
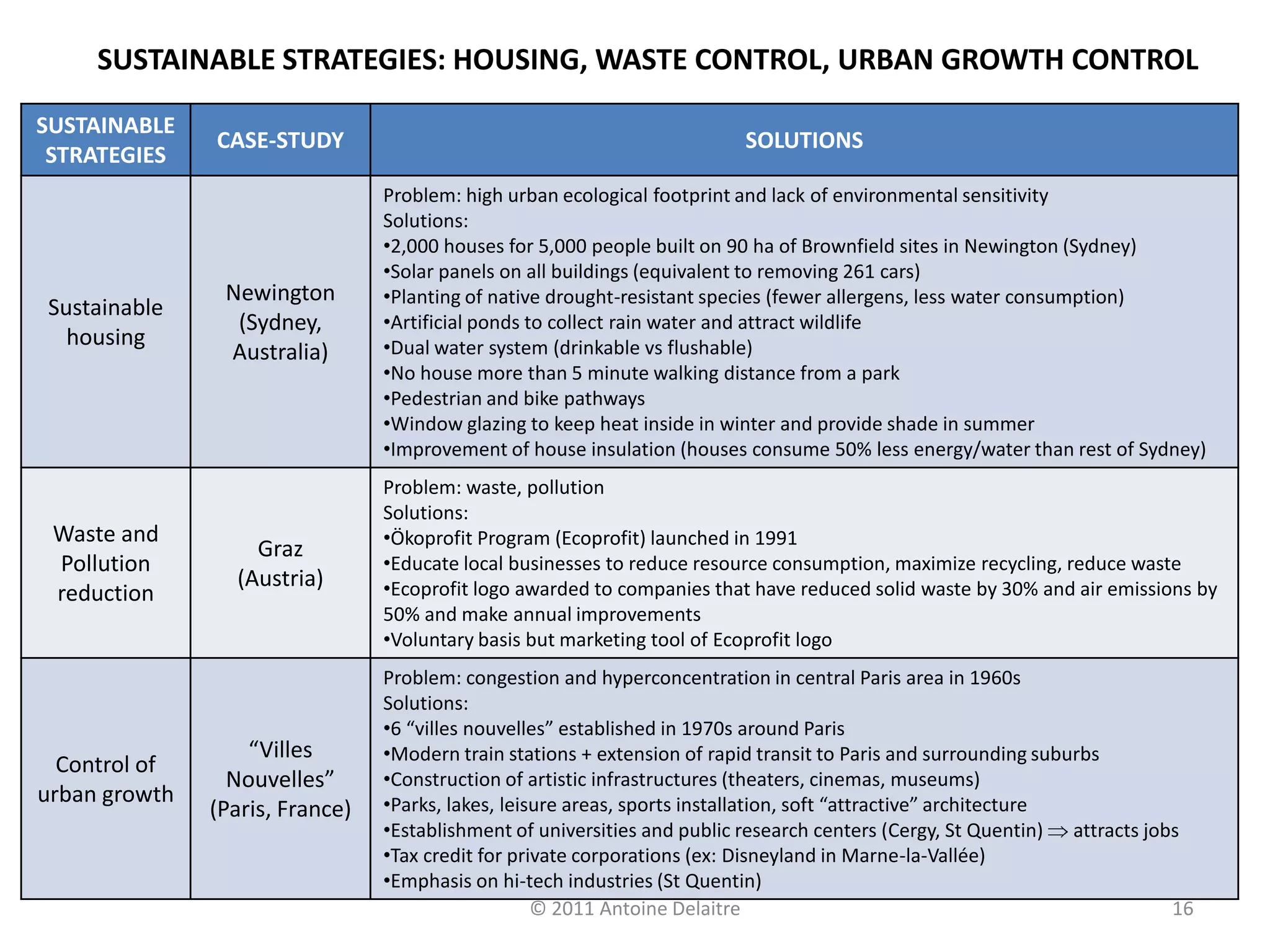
The document describes Rogers' models of sustainable and unsustainable city systems. It then provides examples of sustainable city management strategies in various cities. Some key points:
- Rogers outlines linear "unsustainable" and circular "sustainable" city models in terms of inputs, throughputs, and outputs.
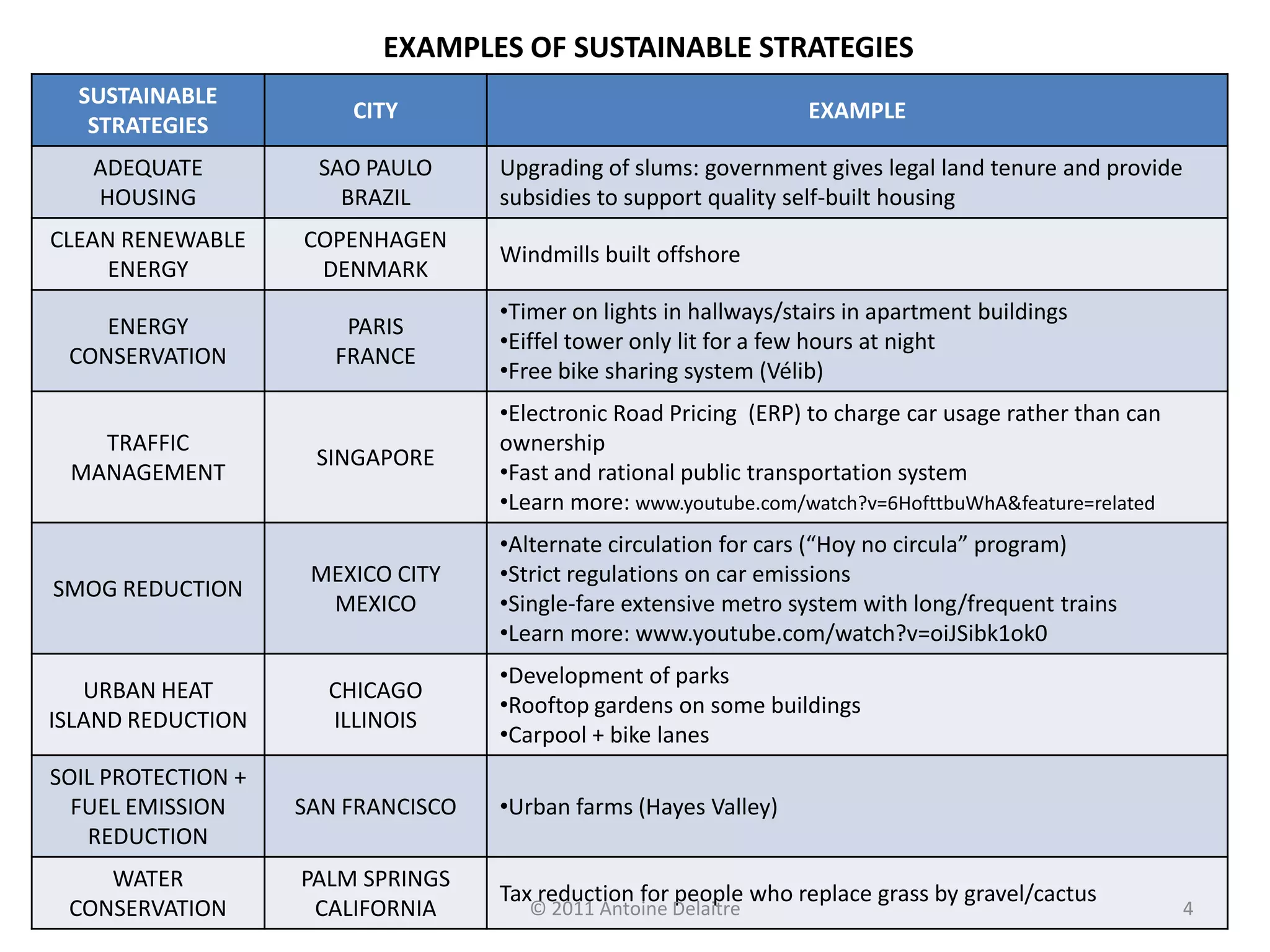
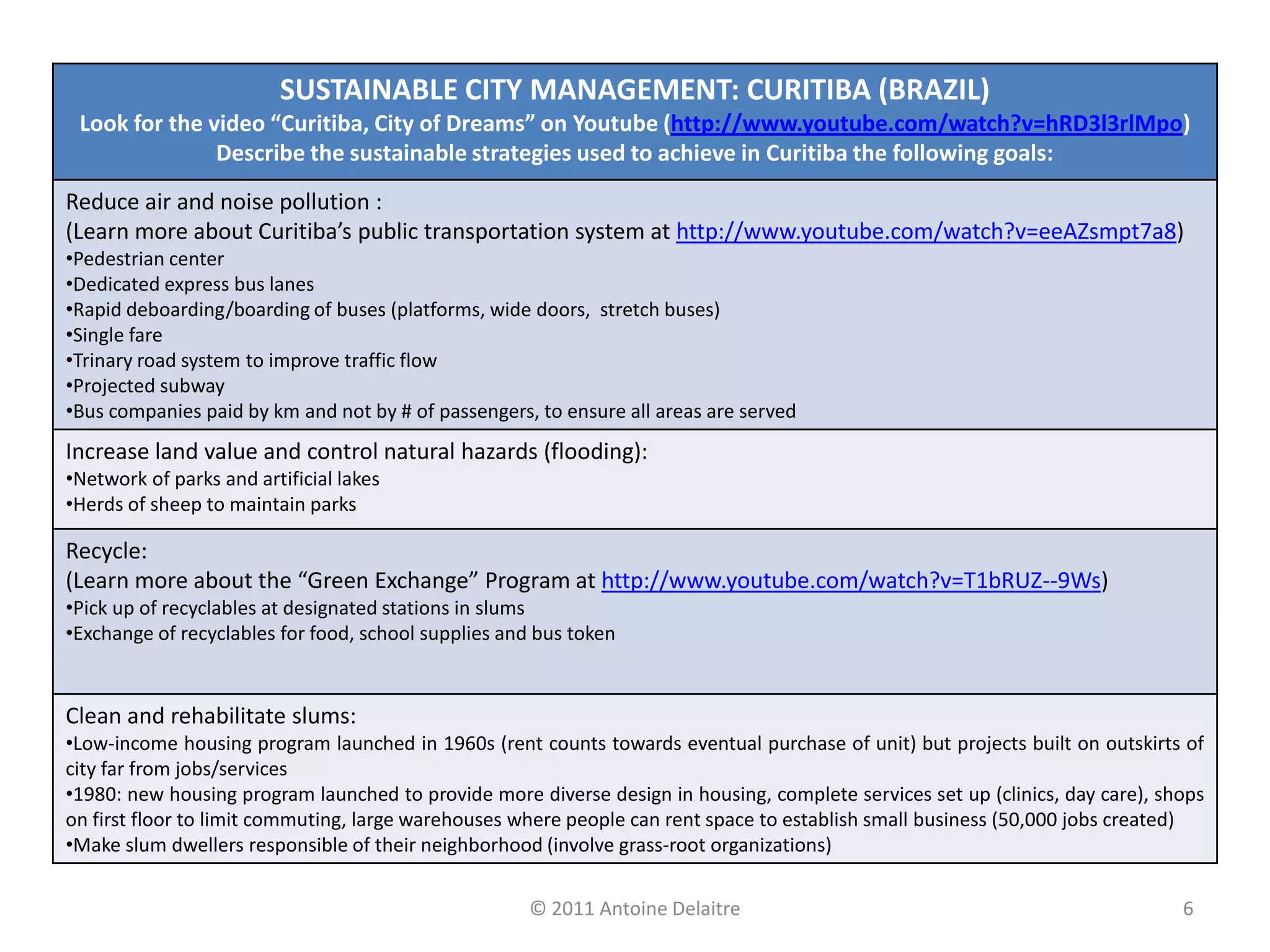
- Examples are given of sustainable strategies around housing, energy, transportation, and environment in cities like Curitiba, Copenhagen, Paris, Singapore, and Mexico City.
- Curitiba's strategies are summarized, including its bus rapid transit system, parks/lakes for flooding control, and slum upgrading paired with recycling programs.