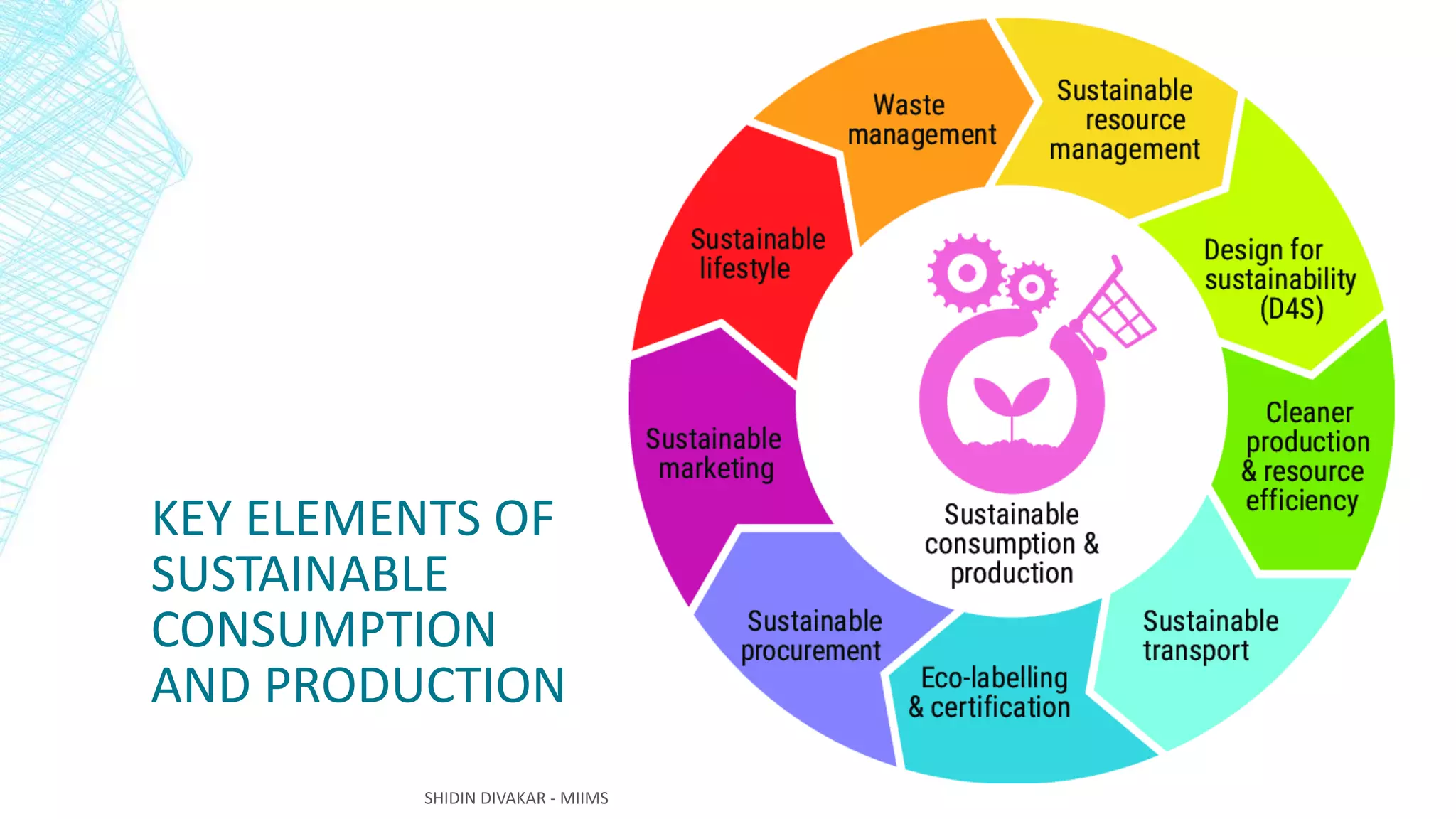
The document discusses sustainable development as the balanced use of resources to meet current needs without compromising future availability, emphasizing the integration of economic, social, and environmental aspects. It highlights the importance of good governance and cultural diversity, while outlining principles for improving quality of life and narrowing gaps between rich and poor. Additionally, it addresses the relationship between climate change and sustainable development, stressing the need for active involvement from all societal stakeholders.