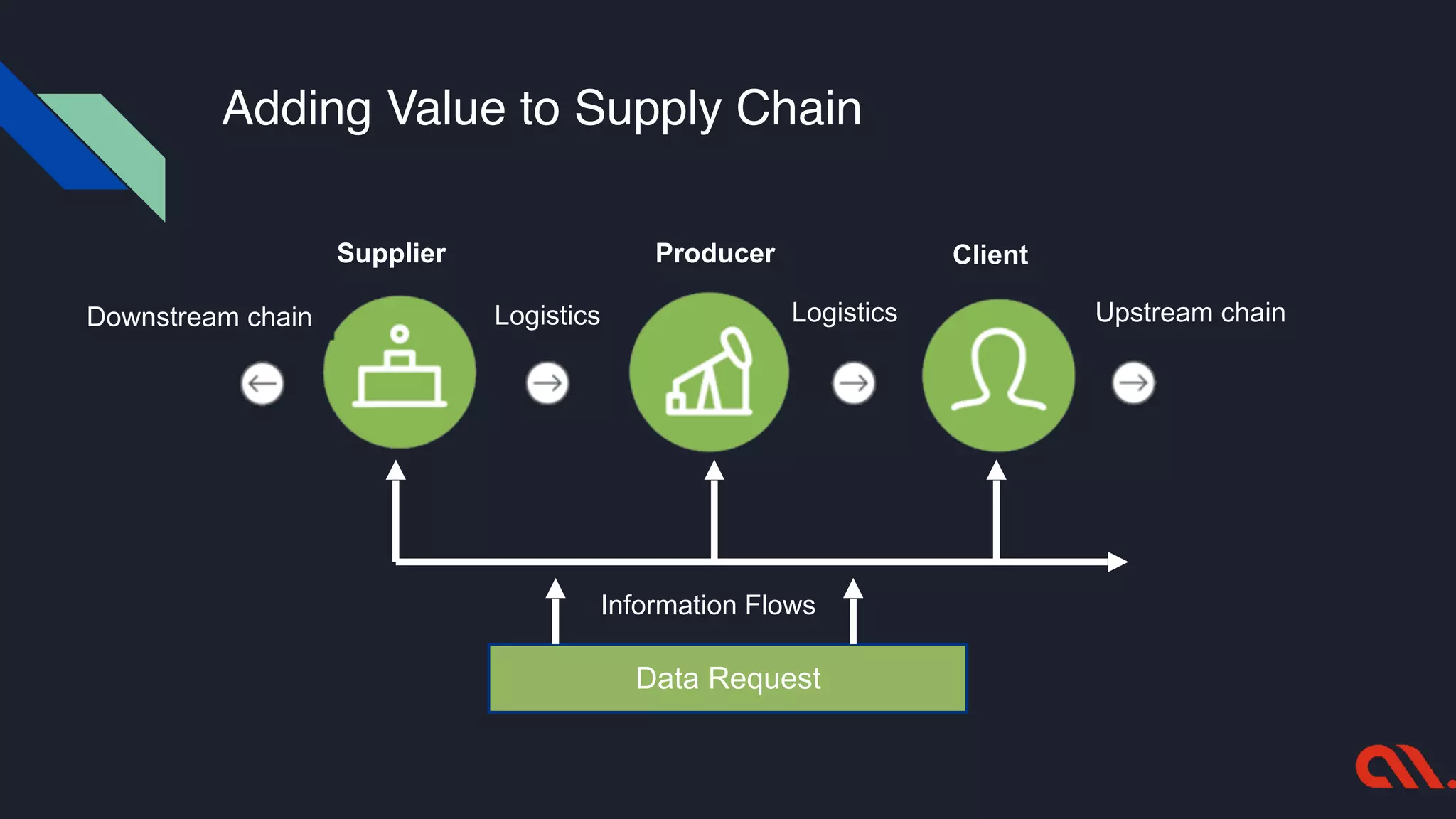
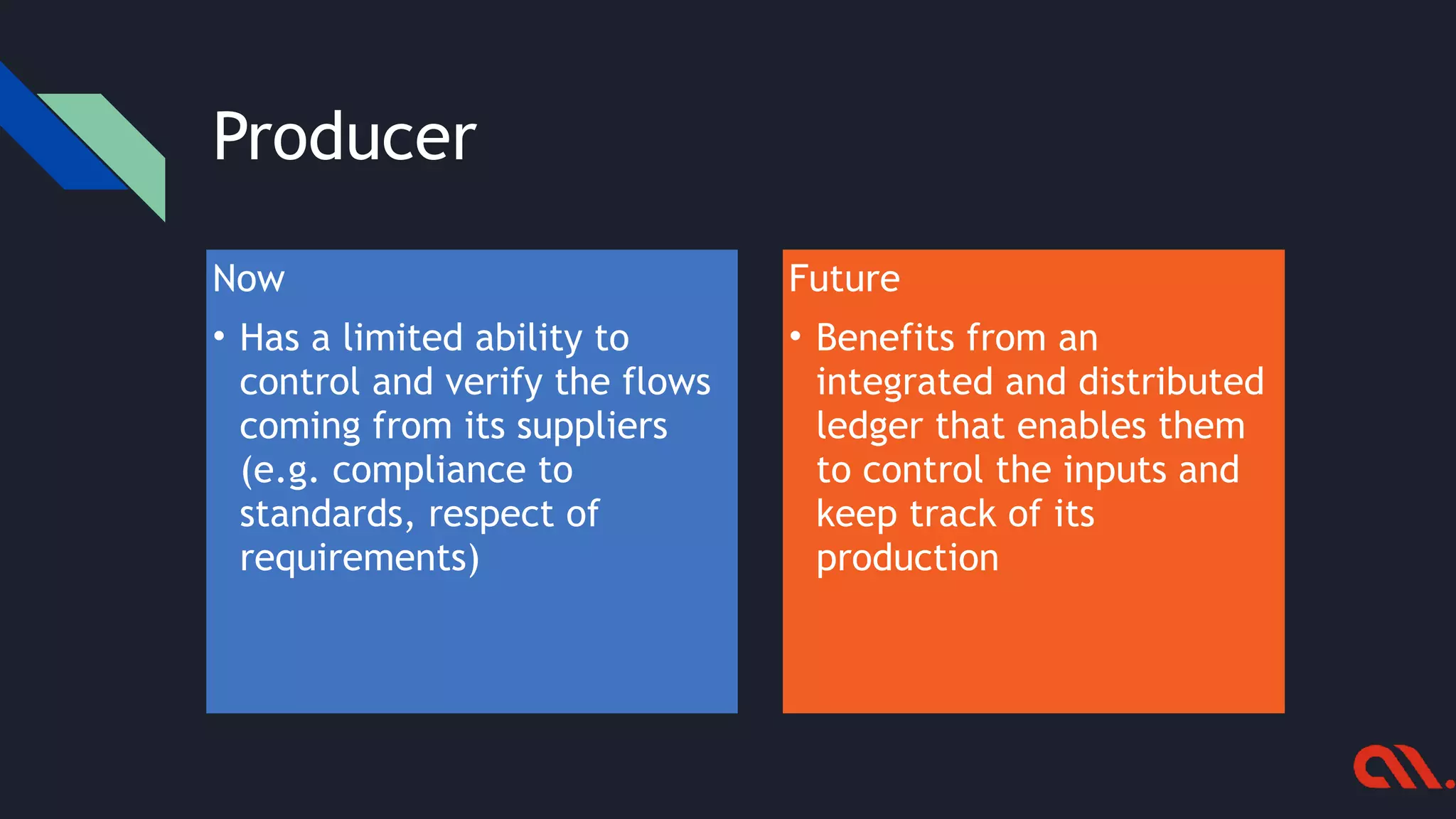
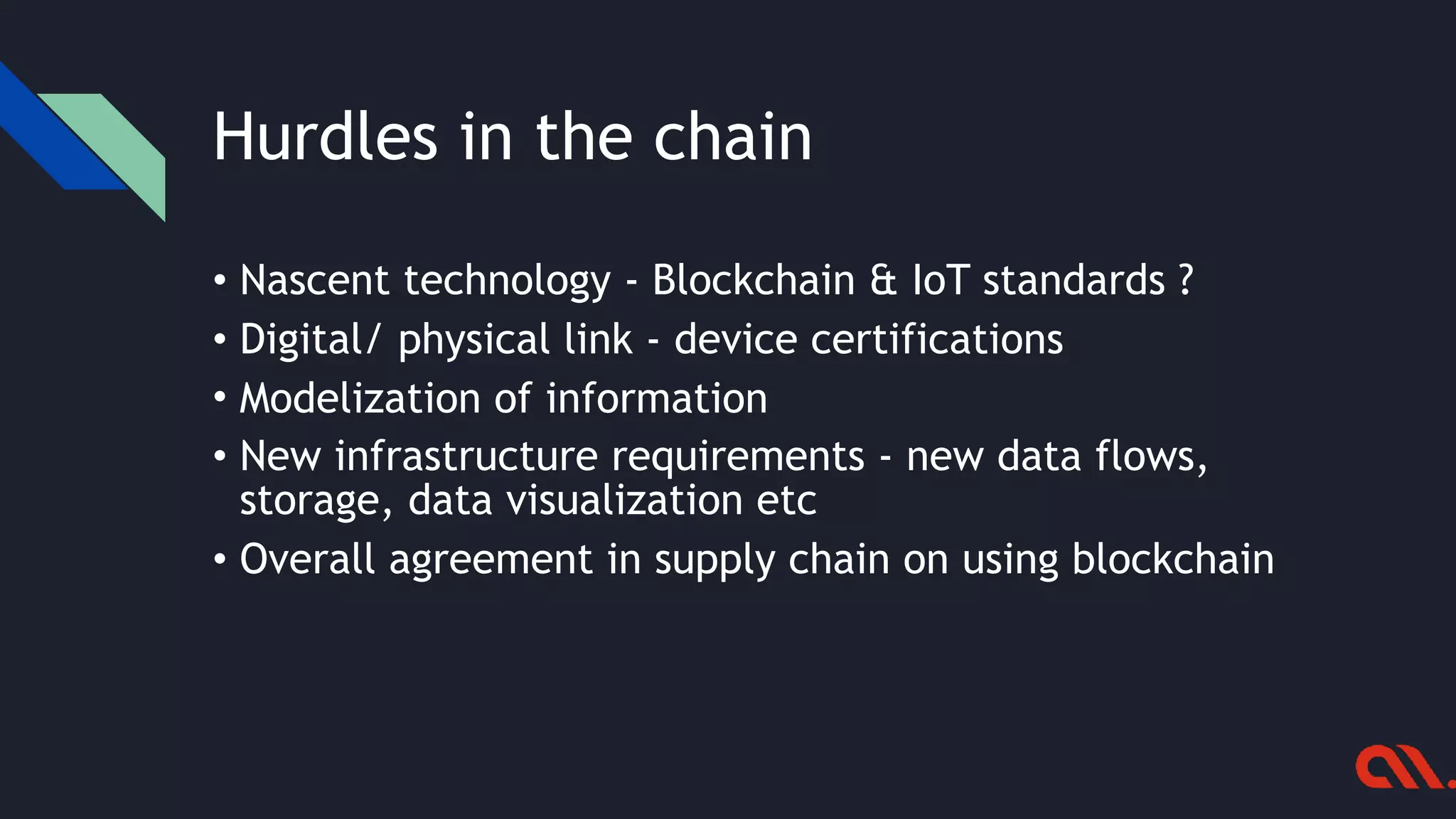
The document highlights the challenges in supply chain management and how blockchain and IoT technologies can address issues like traceability, fraud, and inefficiencies. It outlines the current limitations faced by various stakeholders and the potential benefits of adopting an integrated blockchain system for improved visibility, trust, and compliance. The text also discusses implementation strategies for organizations looking to enhance their supply chain operations.