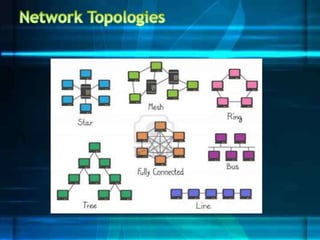
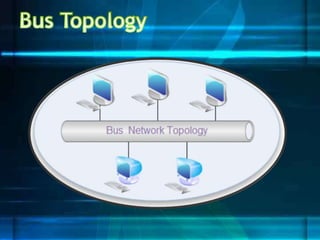
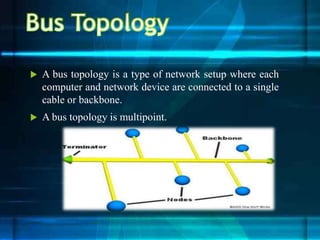
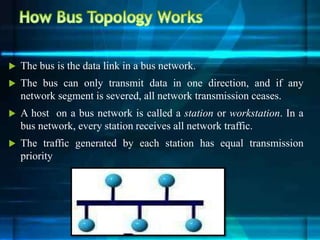
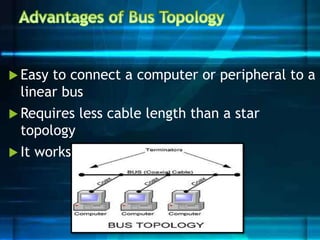
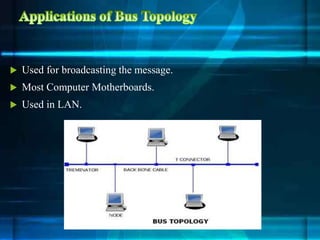
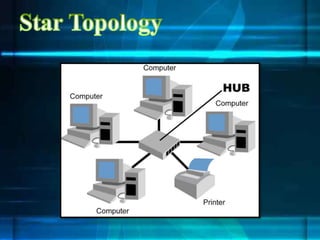
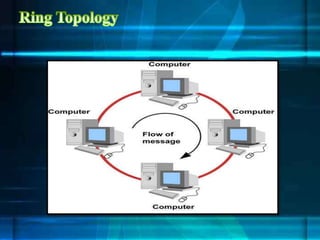
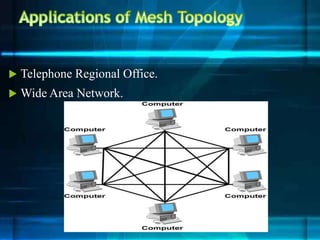
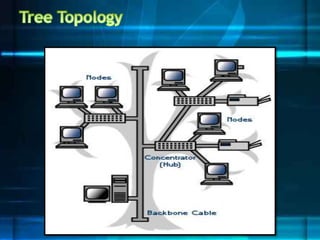
The document discusses different network topologies including bus, ring, star, tree, and mesh. It provides details on the structure and characteristics of each topology. A bus topology uses a single cable to connect all devices. A ring topology connects devices in a circular shape to pass data around the ring. A star topology connects all devices to a central hub. A tree topology combines star and bus topologies by connecting multiple star networks with a backbone bus. A mesh topology allows all devices to connect and transmit data to each other simultaneously.