PPT_CLOUD COMPUTING_UNIT 1.pptx.pdf
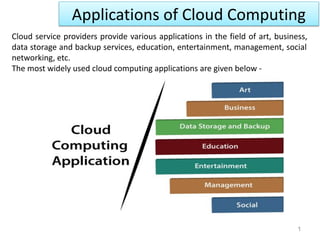
- 1. Applications of Cloud Computing 1 Cloud service providers provide various applications in the field of art, business, data storage and backup services, education, entertainment, management, social networking, etc. The most widely used cloud computing applications are given below -
- 2. 2 • The objective of this course is to provide the comprehensive knowledge of Cloud Computing concepts, technologies, and applications by introducing and researching state-of-the-art in Cloud Computing fundamental issues, technologies, applications and implementations. • Introduce the concepts of Cloud Computing to understand the Services &Storage. Gain knowledge of Resource Management and Security in Cloud. • Another objective is to expose the students to frontier areas of Cloud Computing and information systems, while providing sufficient foundations to enable further study and research. Course Objective
- 3. 3 • The student should have basic knowledge of fundamental of networking, distributed computing system. • Web technology, web services and server concept and knowledge of information and cyber security Prerequisite and Recap
- 4. Brief Introduction about the Subject with Videos 13/11/21 4 Cloud Computing is the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, intelligence, and more, over the Cloud (Internet). Cloud Computing provides an alternative to the on-premises datacentre. With an on-premises datacentre, we have to manage everything, such as purchasing and installing hardware, virtualization, installing the operating system, and any other required applications, setting up the network, configuring the firewall, and setting up storage for data. After doing all the set-up, we become responsible for maintaining it through its entire lifecycle. But if we choose Cloud Computing, a cloud vendor is responsible for the hardware purchase and maintenance. They also provide a wide variety of software and platform as a service. We can take any required services on rent. The cloud computing services will be charged based on usage. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M988_fsOSWo&t=4s https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JYq1AQkMdhE https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iSG_72VNBVs&t=55s
- 5. 13/11/21 5 • Introduction to cloud computing • Evolution of cloud computing – Desktop computing – client server computing – cluster computing – grid computing – cloud computing • Underlying Principles of Parallel Computing • Distributed Computing • Characteristics of cloud computing – Elasticity in Cloud – On Demand Provisioning • EC2 Instances and its types • Cloud Economics Unit Content
- 6. 13/11/21 6 Topic Objective Cloud computing To Understand the cloud computing and why is it required Evolution of cloud computing Study about evolution of various computing techniques Parallel and distributed computing Knowledge about parallel and distributed computing Characteristics Analysis of importance of cloud computing Topic Objective
- 7. What Happened Before the Cloud Technology Emerged? ✔ What was the approach to run an IT application or business projects in traditional model of computing? Buy stacks of servers and other hardware components Maintain and upgrade the servers Recruit network professional Major Disadvantages of Traditional Computing: ✔ Increase in expenditure cost. ✔ Poor scalability and flexibility based on varying traffic. ✔ Resources underutilization because most of the time servers are idle. ✔ Maintenance overhead. 13/11/21
- 8. ▪ In the simplest terms, “cloud computing makes IT resources as subscription oriented services wherein from third party service providers you simply rent the computing capability whatever you need for how long you need and pay for what you have consumed”. ▪ Real-time Example of Cloud Computing: For Backup and recovery Google provides Dropbox, Google Drive and Amazon provides S3. 5 13/11/21 Concept of Cloud Computing
- 9. 13/11/21 9 • Cloud computing is the on demand delivery of compute power database storage, application and other IT resources through a cloud service platform via internet with pay as you go. • Cloud Computing provides us a means by which we can access the applications as utilities, over the Internet. • It allows us to create, configure, and customize applications online. Example- cloud service platform • Amazon web service • Microsoft Azure • Alibaba • Google • oracle Introduction to cloud computing(CO1)
- 10. 13/11/21 10 • The term Cloud refers to a Network or Internet. • - In other words, we can say that Cloud is something, which is present at remote location. • - Cloud can provide services over network, i.e., on public networks or on private networks, i.e., WAN, LAN or VPN. • - Applications such as e-mail, web conferencing, customer relationship management (CRM),all run in cloud. Cloud(CO1..)
- 11. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has a more comprehensive definition of cloud computing. It describes cloud computing as "a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction." Cloud Computing Definition 13/11/21 11
- 12. Why cloud computing(CO1) 13/11/21 12 • Small as well as large IT companies, follow the traditional methods to provide the IT infrastructure. That means for any IT company, we need a Server Room that is the basic need of IT companies. • In that server room, there should be a database server, mail server, networking, firewalls, routers, modem, switches, QPS (Query Per Second means how much queries or load will be handled by the server), configurable system, high net speed, and the maintenance engineers. • To establish such IT infrastructure, we need to spend lots of money. To overcome all these problems and to reduce the IT infrastructure cost, Cloud Computing comes into existence.
- 13. • Traditional Computing – Buy & Own • Hardware, System Software, Applications often to meet peak needs. – Install, Configure, Test, Verify – Manage – Finally, use it • Cloud Computing – Subscribe – Use – $ - pay for what you use, based on QoS 13/11/21 13 Why cloud computing(CO1)
- 14. Parallel Computing (CO1) 13/11/21 14 • Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or the execution of processes are carried out simultaneously. • Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. • It saves time and money as many resources working together will reduce the time.
- 15. Evolution of cloud computing (CO1..) 13/11/21 15 Distributed Systems: • It is a composition of multiple independent systems but all of them together are depicted as a single entity to the users. • The purpose of distributed systems is to share resources and also use them effectively and efficiently. • Distributed systems possess characteristics such as scalability, concurrency, continuous availability, heterogeneity, and independence in failures.
- 16. Distributed Computing (CO1) 13/11/21 16 • A distributed computer system consists of multiple software components that are on multiple computers, but run as a single system. • The computers that are in a distributed system can be physically close together and connected by a local network, or they can be geographically distant and connected by a wide area network • Such systems are independent of the underlying software
- 17. Client/Server computing (CO1) 13/11/21 17 • In client/server computing, a server takes requests from client computers and shares its resources, applications and/or data with the clients on the network • a client is a computing device that initiates contact with a server in order to make use of a shareable resource. • A server may serve multiple clients at the same time while a client is in contact with only one server. • Both the client and server usually communicate via a computer network but sometimes they may reside in the same system.
- 19. Client/Server computing (CO1) 13/11/21 19 Characteristics of Client Server Computing: • The client server computing works with a system of request and response. The client sends a request to the server and the server responds with the desired information. • The client and server should follow a common communication protocol so they can easily interact with each other. All the communication protocols are available at the application layer. • A server can only accommodate a limited number of client requests at a time. So it uses a system based to priority to respond to the requests. • An example of a client server computing system is a web server. It returns the web pages to the clients that requested them.
- 20. Parallel vs Distributed Computing 13/11/21 Roshan Jameel Unit -3 20 Parallel Computing Distributed Computing Many operations are performed simultaneously. System components are located at different locations. Single computer is required. Uses multiple computers. Multiple processors perform multiple operations. Multiple computers perform multiple operations. It may have shared or distributed memory It only supports distributed memory Improves the system performance. Improves system scalability, fault tolerance and resource sharing capabilities. Processors communicate with each other through bus. Computer communicate with each other through message passing.
- 21. 13/11/21 21 Parallel vs Distributed Computing
- 22. Evolution of cloud computing (CO1..) 13/11/21 22 Mainframe computing: • Mainframes which first came into existence in 1951 are highly powerful and reliable computing machines. • These are responsible for handling large data such as massive input-output operations. • Even today these are used for bulk processing tasks such as online transactions etc. • These systems have almost no downtime with high fault tolerance. • After distributed computing, these increased the processing capabilities of the system. But these were very expensive.
- 24. Cluster vs Grid Computing 13/11/21 24 Cluster Computing A cluster computer refers to a network of same type of computers whose target is to work as a same unit. Such a network is used when a resource hungry task requires high computing power or memory. Two or more same types of computers are clubbed together to make a cluster and perform the task. Grid Computing Grid computing refers to a network of same or different types of computers whose target is to provide a environment where a task can be performed by multiple computers together on need basis. Each computer can work independently as well.
- 25. 13/11/21 25 Key Cluster Computing Grid Computing Type Nodes or computers has to be of same type, like same CPU, same OS. Cluster computing needs a homogeneous network Nodes or computers can be of same or different types. Grid computer can have homogeneous or heterogeneous network. Task Computers of Cluster Computing are dedicated to single task and they cannot be used to perform any other task. Computers of Grid Computing can leverage the unused computing resources to do other tasks. Location Computers of Cluster computing are co-located and are connected by high speed network bus cables. Computers of Grid Computing can be present at different locations and are usually connected by internet or a low speed network bus. Topology Cluster computing network is prepared using a centralized network topology. Grid computing network is distributed and have a de-centralized network topology. Cluster vs Grid Computing
- 26. 13/11/21 26 Key Cluster Computing Grid Computing Task Scheduling A centralized server controls the scheduling of tasks in cluster computing. In Grid Computing, multiple servers can exist. Each node behaves independently without need of any centralized scheduling server. Resource Manager Cluster Computing network has a dedicated centralized resource manager, managing the resources of all the nodes connected. In Grid Computing, each node is independently managing each own resources. Autonomy In Cluster computing network, whole system works as a unit. In Grid computing network, each node is independent and can be taken down or can be up at any time without impacting other nodes. Cluster vs Grid Computing
- 27. Utility Computing 13/11/21 27 • Utility computing is a service provisioning model. This service provisioning modeling provides computing resources and infrastructure management to the customer as per their demand. • The customers are charged for them as you go basis without any upfront cost. The utility model maximizes the efficient use of resources while minimizing the associated cost. • Utility computing has an advantage that there will be a low initial cost to acquire computer resources. • The customer can access the infinite amount of computing solution with the help of the internet or a virtual private network. The provider will perform the backend infrastructure and computing resources management.
- 28. Continue 13/11/21 28 • On the basis of above computing, there was emerged of cloud computing concepts that later implemented. • At around in 1961, John MacCharty suggested in a speech at MIT that computing can be sold like a utility, just like a water or electricity • In 1999, Salesforce.com started delivering of applications to users using a simple website. • The applications were delivered to enterprises over the Internet, and this way the dream of computing sold as utility were true.
- 29. Cloud Service Providers 13/11/21 29 • 2002- Amazon launched Amazon Web Services (AWS) providing services like storage, computation and even human intelligence. • 2006- Amazon launched Amazon Web Services (AWS) with Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) which allows users to launch computing resources on pay-per-use. • 2008- Google launched its Google App Engine (GAE) Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), allowing developers to host web applications in its managed data centers. • 2010- Microsoft, entered the cloud market with the launch of its cloud computing platform Azure. • 2011- IBM launched Smart Cloud then renamed it as IBM's Bluemix and launched in 2014 for the academic organizations concerning to PaaS services. • 2011- IIT Delhi launched Baadal cloud for Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) services. • 2013- C-DAC Chennai launched Meghdoot cloud platform for IaaS services
- 30. Characteristics of cloud computing(CO1) 13/11/21 30
- 31. 13/11/21 31 Characteristics of cloud computing(CO1) • On-demand self-service: Cloud computing resources can be provisioned without human interaction from the service provider. In other words, the user can provision additional computing resources (storage space, virtual machine instances, database instances etc.) as needed without going through the cloud service provider. • Broad network access: Cloud computing resources are available over the network and can be accessed by diverse customer platforms. It other words, cloud services are available over a network—ideally high broadband communication link—such as the internet, or in the case of a private clouds it could be a local area network (LAN).
- 32. 13/11/21 32 • Multi-tenancy and resource pooling: Cloud computing resources are designed to support a multi-tenant model. Multi-tenancy allows multiple customers to share the same applications or the same physical infrastructure while retaining privacy and security over their information. Resource pooling means that multiple customers are serviced from the same physical resources. Providers’ resource pool should be very large and flexible enough to service multiple client requirements and to provide for economy of scale. When it comes to resource pooling, resource allocation must not impact performances of critical applications. Characteristics of cloud computing(CO1)
- 33. 13/11/21 Roshan Jameel Unit -3 33 Characteristics of cloud computing(CO1) • Rapid elasticity and scalability: One of the great things about cloud computing is the ability to quickly provision resources in the cloud as users need them. And then to remove them when they don’t need them. Cloud computing resources can scale up or down rapidly and, in some cases, automatically, in response to business demands. It is a key feature of cloud computing. The usage, capacity, and therefore cost, can be scaled up or down with no additional contract or penalties. • Measured service: Cloud computing resources usage is metered and users pay accordingly for what they have used. Resource utilization can be optimized by leveraging charge-per-use capabilities. This means that cloud resource usage—whether virtual server instances that are running or storage in the cloud—gets monitored, measured and reported by the cloud service provider. The cost model is based on “pay for what you use”—the payment is variable based on the actual consumption by the user.
- 34. 13/11/21 Roshan Jameel Unit -3 34 Cloud Elasticity Cloud Scalability Elasticity is used just to meet the sudden up and down in the workload for a small period of time. Scalability is used to meet the static increase in the workload. Elasticity is used to meet dynamic changes, where the resources need can increase or decrease. Scalability is always used to address the increase in workload in an organization. . Elasticity is commonly used by small companies whose workload and demand increases only for a specific period of time. Scalability is used by giant companies whose customer circle persistently grows in order to do the operations efficiently. It is a short term planning and adopted just to deal with an unexpected increase in demand or seasonal demands. Scalability is a long term planning and adopted just to deal with an expected increase in demand. Elasticity vs Scalability
- 35. Advantages of Cloud Computing 13/11/21 Roshan Jameel Unit -3 35 1. Cost efficiency: The biggest reason behind companies shifting to Cloud Computing is that it takes considerably lesser cost than any on-premise technology. Now, companies need not store data in disks anymore as the cloud offers enormous storage space, saving money and resources. 2. High speed: Cloud Computing lets us deploy the service quickly in fewer clicks. This quick deployment lets us get the resources required for our system within minutes. 3. Excellent accessibility: Storing information in the cloud allows us to access it anywhere and anytime regardless of the machine making it a highly accessible and flexible technology of the present times. 4. Back-up and restore data: Once data is stored in the cloud, it is easier to get its back-up and recovery, which is quite a time-consuming process in on-premise technology. 5. Manageability: Cloud Computing eliminates the need for IT infrastructure updates and maintenance since the service provider ensures timely, guaranteed, and seamless delivery of our services and also takes care of all the maintenance and management of our IT services according to the service-level agreement (SLA).
- 36. 1. Vulnerability to attacks: Storing data in the cloud may pose serious challenges of information theft since in the cloud every data of a company is online. Security breach is something that even the best organizations have suffered from and it’s a potential risk in the cloud as well. Although advanced security measures are deployed on the cloud, still storing confidential data in the cloud can be a risky affair. 2. Network connectivity dependency: Cloud Computing is entirely dependent on the Internet. This direct tie-up with the Internet means that a company needs to have reliable and consistent Internet service as well as a fast connection and bandwidth to reap the benefits of Cloud Computing. 3. Downtime: Downtime is considered as one of the biggest potential downsides of using Cloud Computing. The cloud providers may sometimes face technical outages that can happen due to various reasons, such as loss of power, low Internet connectivity, data centers going out of service for maintenance, etc. This can lead to a temporary downtime in the cloud service. 36/2 Disadvantages of Cloud Computing 13/11/21
- 37. • 4. Vendor lock-in: When in need to migrate from one cloud platform to another, a company might face some serious challenges because of the differences between vendor platforms. Hosting and running the applications of the current cloud platform on some other platform may cause support issues, configuration complexities, and additional expenses. The company data might also be left vulnerable to security attacks due to compromises that might have been made during migrations. • 5. Limited control: Cloud customers may face limited control over their deployments. Cloud services run on remote servers that are completely owned and managed by service providers, which makes it hard for the companies to have the level of control that they would want over their back-end infrastructure. 37/2 Disadvantages of Cloud Computing 13/11/21
- 38. 13/11/21 38 1. Which is/are true regarding cloud computing? (a) It does not provide ubiquitous access (b) It provides on-demand network access (c) Resources can not be used with no management effort (d) None of these Quiz
- 39. 13/11/21 39 2. Which of the following option is a service provided by AWS? (a) EC10 (b) EC2 (c) EC3 (d) None of the above Quiz
- 40. 13/11/21 40 3. Which is the biggest are of concern in cloud computing? (a) Security (b) Scalability (c) Elasticity (d) On Demand Provisioning Quiz
- 41. 13/11/21 41 Cloud provisioning means allocating a cloud service provider’s resources to a customer. It is a key feature of cloud computing. It refers to how a client gets cloud services and resources from a provider. 3 Cloud Provisioning Types • Advanced Cloud Provisioning Also known as “post-sales cloud provisioning,” customers get the resources upon contract or service signup. They sign formal contracts with the cloud service provider. The provider then prepares and delivers the agreed-upon resources or services. The customers are charged a flat fee or billed every month. • Dynamic Cloud Provisioning Also referred to as “on-demand cloud provisioning,” customers are provided with resources on runtime. In this delivery model, cloud resources are deployed to match customers’ fluctuating demands. Cloud Provisioning
- 42. 13/11/21 Roshan Jameel Unit -3 42 Deployments can scale up to accommodate spikes in usage and down when demands decrease. Customers are billed on a pay-per-use basis. When this model is used to create a hybrid cloud environment, it is sometimes called “cloud bursting.” • User Cloud Provisioning: In this delivery model, customers add a cloud device themselves. Also known as “cloud self-service,” clients buy resources from the cloud service provider through a web interface or portal. The model usually involves creating a user account and paying for resources with a credit card. The resources are quickly spun up and made available for use within hours, if not minutes. An example of this includes an employee purchasing cloud-based productivity applications via Microsoft 365 or G Suite. Cloud Provisioning
- 43. 13/11/21 43 Cloud provisioning has several benefits that are not available with traditional provisioning approaches, such as: Scalability: The traditional information technology (IT) provisioning model requires organizations to make large investments in their on-premises infrastructure. That needs extensive preparation and forecasting of infrastructure needs since on-premises infrastructures are often set up to last for many years. The cloud provisioning model, meanwhile, lets companies simply scale up and down their cloud resources depending on their short-term usage requirements. Speed: Organizations’ developers can quickly spin up several workloads on-demand, so the companies no longer require IT administrators to provide and manage computing resources. Cloud Provisioning Benefits
- 44. 13/11/21 44 Cost savings: While traditional on-premises technology requires large upfront investments, many cloud service providers let their customers pay for only what they consume. But the attractive economics of cloud services presents challenges, too, which may require organizations to develop a cloud management strategy. Cloud Provisioning Benefits
- 45. 13/11/21 45 Like any other technology, cloud provisioning also presents several challenges, including: Complex management and monitoring: Organizations may need several provisioning tools to customize their cloud resources. Many also deploy workloads on more than one cloud platform, making viewing everything on a central console more challenging. Resource and service dependencies: Cloud applications and workloads often tap into basic infrastructure resources, such as computing, networking, and storage. But public cloud service providers offer higher-level ancillary services like serverless functions and machine learning (ML) and big data capabilities. Such services may carry dependencies that can lead to unexpected overuse and surprise costs. Cloud Provisioning Challenges
- 46. 13/11/21 46 Policy enforcement: User cloud provisioning helps streamline requests and manage resources but requires strict rules to make sure unnecessary resources are not provided. That is time-consuming since different users require varying levels of access and frequency. Setting up rules to know who can provide which resources, for how long, and with what budgetary controls can be difficult. Cloud Provisioning Challenges
- 47. 13/11/21 47 4. Which of the following is not a cloud computing platform? (a) Microsoft Azure (b) Amazon EC2 (c) IBM Deep Blue (d) Google 101 Quiz
- 48. 13/11/21 Roshan Jameel Unit -3 48 5. Which are essential characteristics of cloud computing? (a) On-demand self service (b) Resource pooling (c) Rapid elasticity (d) None of these (e) All of the above Quiz
- 49. 13/11/21 49 6. What is Cloud Computing replacing? a) Corporate data centers b) Expensive personal computer hardware c) Expensive software upgrades d) All of the above Quiz
- 50. EC2 Instances 13/11/21 Roshan Jameel Unit -3 50 • An Amazon EC2 instance is a virtual server in Amazon's Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for running applications on the Amazon Web Services (AWS) infrastructure. • AWS is a comprehensive, evolving cloud computing platform; EC2 is a service that enables business subscribers to run application programs in the computing environment. It can serve as a practically unlimited set of virtual machines (VMs). • Amazon provides various types of instances with different configurations of CPU, memory, storage and networking resources to suit user needs. Each type is available in various sizes to address specific workload requirements.
- 51. 13/11/21 51 Instances are created from Amazon Machine Images (AMI). The machine images are like templates. They are configured with an operating system (OS) and other software, which determine the user's operating environment. Users can select an AMI provided by AWS, the user community or through the AWS Marketplace. Users also can create their own AMIs and share them. EC2 Instances
- 52. 13/11/21 52 • Operating system: EC2 supports many OSes, including Linux, Microsoft Windows Server, CentOS and Debian. • Persistent storage: Amazon's Elastic Block Storage (EBS) service enables block-level storage volumes to be attached to EC2 instances and be used as hard drives. With EBS, it is possible to increase or decrease the amount of storage available to an EC2 instance and attach EBS volumes to more than one instance at the same time. • Elastic IP addresses: Amazon's Elastic IP service lets IP addresses be associated with an instance. Elastic IP addresses can be moved from instance to instance without requiring a network administrator's help. This makes them ideal for use in failover clusters, for load balancing, or for other purposes where there are multiple servers running the same service. Features of EC2 Instances
- 53. 13/11/21 53 Features of EC2 Instances Amazon CloudWatch: This web service allows for the monitoring of AWS cloud services and the applications deployed on AWS. CloudWatch can be used to collect, store and analyze historical and real-time performance data. It can also proactively monitor applications, improve resource use, optimize costs and scale up or down based on changing workloads. Automated scaling: Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling automatically adds or removes capacity from Amazon EC2 virtual servers in response to application demand. Auto Scaling provides more capacity to handle temporary increases in traffic during a product launch or to increase or decrease capacity based on whether use is above or below certain thresholds. Bare-metal instances: These virtual server instances consist of the hardware resources, such as a processor, storage and network. They are not virtualized and do not run an OS, reducing their memory footprint, providing extra security and increasing their processing power.
- 54. 13/11/21 54 • Amazon EC2 Fleet: This service enables the deployment and management of instances as a single virtual server. The Fleet service makes it possible to launch, stop and terminate EC2 instances across EC2 instance types with one action. Amazon EC2 Fleet also provides programmatic access to fleet operations using an API. Fleet management can be integrated into existing management tools. With EC2 Fleet, policies can be scaled to automatically adjust the size of a fleet to match the workload. • Pause and resume instances: EC2 instances can be paused and resumed from the same state later on. For example, if an application uses too many resources, it can be paused without incurring charges for instance usage. Features of EC2 Instances
- 55. Types of EC2 Instances 13/11/21 55 Instance types are grouped into families based on target application profiles. These groups include the following: • General purpose: A general purpose instance is a VM that is designed to handle a variety of workloads. General purpose instances are optimized to have a high number of CPU cores, on-demand storage and memory. Some common use cases for general purpose instances include web server hosting and software development and testing.
- 56. 13/11/21 Roshan Jameel Unit -3 56 • Compute optimized: Compute optimized instances are used to run big data applications that require large amounts of processing power and memory on the AWS cloud. These instances are designed and optimized for running computational and data-intensive applications that require fast network performance, extensive availability and high input/output (I/O) operations per second (IOPS). Examples of types of applications includes scientific and financial modeling and simulation, machine learning, enterprise data warehousing and business intelligence. • Graphics processing unit (GPU):These instances provide a way to run graphics-intensive applications faster than with the standard EC2 instances. Systems that rely on GPUs include gaming and design work. For example, Linux distributions often take advantage of GPUs for rendering graphical user interfaces, improving compression speeds and speeding up database queries. Types of EC2 Instances
- 57. 13/11/21 57 • Memory optimized: Memory optimized instances use a high-speed, solid-state drive to provide ultra-fast access to data and deliver high performance. These instances are ideal for applications that require more memory and less CPU power, including open source databases, real-time big data analytics and in-memory caches. • Storage optimized: Storage optimized instances are ideal for applications that require high I/O performance, such as NoSQL databases that store and retrieve data in real time. They're also well suited for memory-intensive applications such as data processing, data warehousing, analytics workloads and log processing. • Micro: A micro instance is meant for applications with low throughput. The micro instance type can serve as a small database server, as a platform for software testing or as a web server that does not require high transaction rates. Types of EC2 Instances
- 58. Cloud Economics 13/11/21 58 Cloud economics is the study of the benefits, costs, and principles of cloud computing. It refers to the knowledge about the financial aspects of cloud computing. Cloud economics involves understanding: • The total cost of ownership for cloud computing • The benefits of cloud computing over on-premises models • Cost optimization strategies when operating in the cloud. Cloud economics is not just about costs in actual monetary terms, but also about the opportunity costs of the cloud and the peculiarities of managing costs in a highly dynamic environment.
- 59. 13/11/21 Roshan Jameel Unit -3 59 Cloud Economics: Key Areas Cloud total cost of ownership (TCO): TCO is the total cost of adopting, operating, and provisioning cloud infrastructure. TCO is helpful for understanding return on investment. Businesses have always performed TCO analysis for traditional IT infrastructure. However, performing TCO analysis for cloud computing can be challenging because the environment is inherently more complex and dynamic than on-premises environments. Getting an accurate TCO for cloud computing means capturing the purchase price of on-premises vs. cloud solutions as well as the intangible costs of either solution. In practice, this means: • Calculating the cost of your current IT infrastructure • Estimating the total cost of cloud adoption (including migration costs) • Quantifying the intangible benefits of the cloud The overall goal is to achieve a lower TCO compared to on-premises infrastructure, but it can also be about justifying a higher TCO by listing the intangible benefits associated with the cloud, such as agility and greater speed to market.
- 60. 13/11/21 60 CAPEX to OPEX switch Cloud computing uses a different pricing model from traditional computing and this affects how businesses account for cost. The move from capital expenses (CAPEX) to operating expenses (OPEX) is a key difference, and it affects how businesses gauge profitability in the cloud. In traditional IT environments, computing costs are predictable and relatively fixed. A business pays for the computing capacity it needs upfront and uses the capacity over time. Calculating the total cost of ownership in this setup is fairly straightforward. In contrast, cloud providers adopt a pay-as-you-go model and most services do not require any upfront commitment.
- 61. 13/11/21 61 The implication is that your business will have variable cloud computing bills that depend on the services you use and how they are consumed. While this model may save your business upfront capital expenditure, it can become a huge financial suck if resources are not managed properly. When moving to or operating in the cloud, it is important to develop and implement cloud cost optimization strategies that will help regulate your cloud costs. For example, CloudZero’s cost intelligence platform helps you track the cost of migrating to AWS and thereafter provides insights that help you reduce your AWS bill.
- 62. 13/11/21 62 Cloud Economics: Key Areas Elasticity: With on-premises systems and traditional IT environments, there’s a cost associated with anticipating demand. Traditional IT environments are built to anticipate peaks, which means you buy and maintain excess computing capacity in anticipation of those peak days. For most businesses, that’s a significant cost for something that’s rarely — if ever — used. Cloud computing eliminates the need for over-provisioning because you pay only for what you use. Cloud computing platforms, such as AWS, dynamically allocate resources to projects and processes, ensuring that a business has the right amount of resources it needs at any given time. This increases cost efficiency and allows businesses to optimize resource usage.
- 63. 13/11/21 63 Cloud Economics: Key Areas This elasticity is one of the most appealing aspects of cloud computing and a major selling point when making a case for switching to the cloud. On-demand pricing: On-demand pricing is a fundamentally different economic approach to computing power. Outside of the cloud, you’d buy a fixed amount of computing capacity or a physical server that you own. But in the cloud, you switch to on-demand pricing, so your costs become elastic. This means cloud costs can quickly spiral out of control if you are not monitoring them regularly and making data-driven decisions.
- 64. 13/11/21 64 7. Which of these companies is not a leader in cloud computing? a) Google b) Microsoft c) Amazon d) Blackboard Quiz
- 65. 13/11/21 65 8. Cloud" in cloud computing represents what? a)Internet b)Wireless c)Hard drives d)People Quiz
- 66. 13/11/21 66 9. What is the disadvantage of cloud computing? (a) It requires constant internet connection. (b) It does not support group collaboration. (c) It provides limited storage. (d) None of these Quiz
- 67. 13/11/21 67 10. Cloud computing is a distributed computing model. (a) True (b) False Quiz
- 68. 13/11/21 68 11. Which of the following a company must consider before moving towards cloud computing? (a) Employee Satisfaction (b) Potential cost reduction (c) Information Sensitivity (d) All of these Quiz
- 69. 13/11/21 69 12. What is Cloud computing? (a) Way to organize computers (b) Lightweight software (c) Computing resources that can be accessed on demand (d) World Wide Web Quiz
- 70. 13/11/21 70 Youtube/other Video Links: NPTEL/ Youtube/ Faculty Video Link: • https://acloud.guru/ • https://nptel.ac.in/courses/106/105/106105223/ • https://nptel.ac.in/courses/106/104/106104182/ • https://nptel.ac.in/courses/106/105/106105167/ • https://aws.amazon.com/ Faculty Video Links, Youtube & NPTEL Video Links and Online Courses Details
- 71. 13/11/21 71 1. Which of the following best describes cloud computing? (a) It is always going to be less expensive and more secure than traditional computing (b) The data can be accessed from any computer in the world using internet connection (c) Few companies are investing in the technology as it is very risky MCQs
- 72. 13/11/21 72 2. Which of the following computing resources are provided by the cloud computing model? (a) Servers (b) Storage (c) Applications (d) All of the above MCQs
- 73. 13/11/21 73 3. Which of the following is not true about distributed systems? (a) It is a composition of multiple independent systems (b) all the systems together are depicted as a single entity to the users. (c) The computers that are in a distributed system can be arranged physically close together and connected by a local network (d) Systems cannot be located at geographically distant locations MCQs
- 74. 13/11/21 74 4. Which of the following is true about client server systems? (a) a server is a computing device that initiates contact with a client in order to make use of a shareable resource. (b) In client/server computing, a server takes requests from client computers and shares its resources, applications and/or data with the clients on the network (c) A client may serve multiple servers at the same time while a server is in contact with only one client. MCQs
- 75. 13/11/21 75 5. Which of the following is not true about cluster computing? (a) Computers of Cluster Computing are dedicated to single task and they cannot be used to perform any other task. (b) Cluster computing network is prepared using a decentralized network topology. (c) Cluster Computing network has a dedicated centralized resource manager, managing the resources of all the nodes connected. MCQs
- 76. 13/11/21 76 6. Which of the following is true about grid computing? (a) Nodes or computers has to be of same type, like same CPU, same OS. (b) Distributed Computing network has a dedicated centralized resource manager, managing the resources of all the nodes connected. (c) Nodes or computers can be of same or different types. Grid computer can have homogeneous or heterogeneous network. MCQs
- 77. 13/11/21 77 7. Which of the following is not a characteristic of Cloud Computing? (a) On Demand Service (b) Resource Pooling (c) Rapid Elasticity (d) Offline Services (e) Measured Services MCQs
- 78. 13/11/21 78 8. Match the following (1) Advanced Cloud Provisioning (i) On Demand Cloud Provisioning (2) Dynamic Cloud Provisioning (ii) Cloud Self Service (3) User Cloud Provisioning (iii) Post sales Cloud Provisioning (a) (1)(i), (2)(ii) and (3)(iii) (b) (1)(iii), (2)(i) and (3)(ii) (c) (1)(ii), (2)(i) and (3)(iii) MCQs
- 79. 13/11/21 79 9. Which type of EC2 instance can be used in Real Time Applications? (a) Compute Optimized (b) Memory Optimized (c) Storage Optimized (d) Micro MCQs
- 80. 13/11/21 80 10. Which type of EC2 instance can be used for graphic intensive applications? (a) Compute Optimized (b) Memory Optimized (c) Storage Optimized (d) Graphical Processing Unit MCQs
- 81. 13/11/21 81 • Define cloud computing. • Write short notes on “on demand self service” and “elasticity of demand”. • Discriminate between cluster computing and grid computing. • List out essential characteristics of cloud computing. • Explain cloud computing evolution in terms of computing technique. • Identify the need of cloud computing with example. • Discuss the services of various cloud vendors. • Discuss advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing. Expected Questions for Exam
- 82. Unit Recap 13/11/21 82 • cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power over the internet. • there are number of vendors provide different services to the user over internet. • Amazon web service, Microsoft azure, oracle, salesforce, alibaba are the popular vendors. • cloud computing technique emerged after various computing techniques. • Cloud computing is a combination of grid and utility computing.
- 83. 13/11/21 Roshan Jameel Unit -3 83 • There are number of features of cloud computing like on demand self service, resource pooling, multi tenancy, rapid elasticity, security etc. • Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS), which allows users to launch computing resources on pay-per-use. • Various types of EC2 instances can be created as per the requirement e.g. general purpose, compute optimized, memory optimized, storage optimized, micro etc. • Cloud economics is the study of the benefits, costs, and principles of cloud computing. It refers to the knowledge about the financial aspects of cloud computing. Unit Recap