Bioenergetic
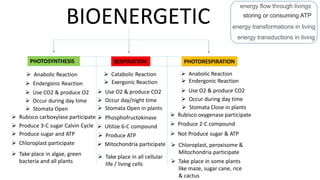
- 1. BIOENERGETIC energy flow through livings storing or consuming ATP energy transformations in living energy transductions in living PHOTOSYNTHESIS RESPIRATION PHOTORESPIRATION Anabolic Reaction Anabolic Reaction Catabolic Reaction Endergonic Reaction Endergonic Reaction Exergonic Reaction Use CO2 & produce O2 Use O2 & produce CO2 Use O2 & produce CO2 Occur during day time Occur during day time Occur day/night time Stomata Open Stomata Open in plants Stomata Close in plants Rubisco carboxylase participate Rubisco oxygenase participate Phosphofructokinase Produce 3-C sugar Calvin Cycle Produce 2-C compound Utilize 6-C compound Produce sugar and ATP Produce ATP Not Produce sugar & ATP Chloroplast participate Mitochondria participate Chloroplast, peroxisome & Mitochondria participate Take place in algae, green bacteria and all plants Take place in all cellular life / living cells Take place in some plants like maze, sugar cane, rice & cactus
- 2. PHOTOSYNTHESIS Plants Stem Leaf Mesophyll Palisade Chloroplast Grana Thylakoid Thylakoid Membrane PhotosystemAntenna Complex CarotenoidChlorophyll bChlorophyll aMg Mg ++ Photolysis Light Reaction ATP, NADH STROMADark Reaction CO2 Triose Triose GLUCOSE O2 Mg Sun Photon P e - e - H2O
- 3. Chloroplast Grana Thylakoid Thylakoid Space Thylakoid Lumen Thylakoid Membrane Photosystem Reaction Centre Antenna complex Primary e acceptor Photosystem I Reaction Centre Antenna complex Primary e acceptor Photosystem II Reaction Centre Antenna complex Primary e acceptor P 680 P 700Carotenoid Ch b Ch a SUN Stroma SUN P 680 P 700 Hillreaction is the light-driven transfer of electrons from water to Hill reagents (non-physiological oxidants) in a direction against the chemical potential gradient in photosynthesis. Robin Hill discovered in 1937. ee ee ee SOLARIZATION
- 4. Thylakoid Space PS II PS I PQ Cyt PC Fd NADP ase NADPH H2O H+ O Stroma H+ ATP ase ATP Cyclic Phosphorylation Non-Cyclic Photo-Phosphorylation Chemiosmosis LIGHT REACTION Pyrrole PHYTOL PORPHYRIN (Basic Structure) Mg Mg++ e e H2O 2H+ e e + O OXIDATION Photolysis Oxidizing Agent O2 Photolysis LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION Z-Scheme PHOTOPHOSPHORYLATION OXIDATION PHASE ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN ee ee ee ee ee ee ee eeee ee ee ee REDUCED LIGHT PHASE Source of e
- 5. 3-C 3-C 3-C 3-C 3-C 6-C 9-C 5-C 4-C 7-C 10-C 5-C 5-C 5-C 3(5-C) + 3 CO2 3 (6 C) 6 (3 C) 5 (3 C) (3 C) (3 C) (6 – C) Glucose 1st Calvin Cycle RuBP Rubisco Carboxylase 3 C Calvin Cycle C 3 Cycle Reduction Phase Light Independent Light Reaction Dependent Dark Phase REGENERATION REDUCED OXIDIZED CARBOXYLATION
- 6. FIRST CALVIN CYCLE SECOND CALVIN CYCLE TotalRequired CO2 3 3 6 RuBP 3 3(5-C) 15 - C 3 3(5-C) 15 - C 6, 6(5-C), 30 C 6 C 3 3(6-C) 18 - C 3 3(6-C) 18 - C 6, 3(6-C), 36 C 3 C 6 6(3-C) 18 - C 6 6(3-C) 18 - C 12, 6(3-C), 36 C 3 C Recycle 5 5(3-C) 15 - C 5 5(3-C) 15 - C 10, 10(3-C), 30 C ATP 6 + 3 = 9 6 + 3 = 9 18 NADPH 6 6 12 ENERGY BALANCE SHEET OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS Light Required Water used = 12 Light Reactions = 12 O atoms produce = 12 Non – Cyclic reactions = 12 NADH produced = 12 PS II participate = 12 Plastoquinone participate = 12 Photolysis = 12 680 Participate = 12 ETC (respiration)of NADH will be = 12 Cyclic Photophosphorylation = 6 CO2 required = 3+3 = 6 For 1 CO2 water required = 2For 1 Glucose Molecule Calvin Cycles = 2 Triose required = 2 ATP required = 6+3 = 9 x 2 = 18 NADH required = 6+6 = 12 Designed by Dr. Tahir Abbas Baloch H2O : CO2 1: 2 H2O : Calvin cycle 2: 1 12 : 6 O2 : CO2 1: 1 I Glucose Require Total ATP = 2 (6+3) + 2 (6NADH) = 18 + 36 = 54 ATP Glucose : RuBP 1: 6 H2O : CO2: NADPH: ATP 12 : 6 : 12 : 18 6 : 3 : 6 : 9 CO2: NADPH: ATP 1 : 2 : 3
- 7. Triose Triose GLUCOSE ATP, NADH Light Required Water used = 12 Light Reactions = 12 O atoms produce = 12 Non – Cyclic reactions = 12 NADH produced = 12 PS II participate = 12 Plastoquinone participate = 12 Photolysis = 12 680 Participate = 12 ETC (respiration) of will be = 12 Cyclic reaction = 6 CO2 required = 3+3 = 6 For 1 CO2 water required = 2 Net Yield of H2O in Photosynthesis = 0 Aerobic Product of Glucose = 10 NADH 2 FADH, 6 CO2, 2 ATP, 2GTP
- 8. PS II PS I ETC Calvin Cycle Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH GLUCOSE Pyruvic Acid Pyruvic Acid Kreb‘s Cycle Kreb‘s Cycle NADH ETC CHLOROPLAST MITOCHONDRIA CYTOPLASM GLYCOLYSIS CYTOCHROME ENDOSYMBIOSIS
- 9. Glucose To the electron transport chain Glycolysis: 2 Pyruvic acid • Where Cytoplasm • NO O2 required • Energy Yield net gain of 2 ATP at expense of 2 ATP • 6-C glucose 2 molecule of 3-C pyruvates • Free e- and H+ combine with NAD+ NADH + H+ (nicotinamide dinucleotide) • Out 2 pyruvate; 2(3-C) 2NADH ETC = 2 ATP by ETC = 6 net gain ATP = 2 Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP) pathway
- 10. ATP use ATP use 2 NADH 2 ATP 2 ATP PREPARATORY PHASE PAYOFFPHASE 2 E T C 6 ATP Mitochondria 2 ATP2 ATP 4 ATP Without O2 10 ATP Total ATP = 10-2= 8 ATP Net ATP = 2 SUBSTRATE PHOSPHORYLATION
- 11. • Intermediate in mitochondria • Pyruvate (3-C) Acetic acid (2-C) • 3rd C forms CO2 • Acetic acid combines with Coenzyme A to form ACETYL-CoA • Out CO2 (as waste) = 1 x 2 = 2 NADH = 1x2 = 2 ETC = 1 x 2 = 2 ATP by ETC = 6 Acetyl-CoA = 1x 2 = 2OXIDATIVE DECARBOXYLATION
- 12. Kreb’s Cycle Citric Acid Cycle TCA Cycle SUBSTRATE PHOSPHORYLATION
- 13. Decarboxylase Dehydrogenase Decarboxylase Fumarase Citric Acid Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle TCA Cycle
- 14. 1 Glucose 2 Triose 2 Pyruvic Acid 2 Acetyl Co A 2 Kreb’s Cycle 12 ETC GLYCOLYSIS PYRUVATE OXIDATION KREBS CYCLE ETCPARAMETERS ATP use 2 0 0 0 Total ATP -2 ATP Produce 4 0 1 x 2 0 4 + 2 = 6 Net gain ATP 2 ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION, FERMENTATION 2 NADH 2 1x 2 = 2 3x 2 = 6 10 10x3=30 FADH 0 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 2x2 = 4 CO2 0 1x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 Acetyl Oxidize = 3 NADH or Citrate Oxidize 1 FADH 1 GTP = 1 ATP 4 ATP by ETC 11 12 ketoglutarate Oxidize = 2 NADH, 1 FADH, 1 ATP 3 ATP 8 9 Succinate Oxidize = 1 NADH, 1 FADH 2 5 Fumarase, Malate Oxidize = 1 NADH 1 3 Designed by Dr. Tahir Abbas Baloch Pyruvate Oxidize = 4 NADH 1 FADH 1 GTP = 1 ATP ETC = 5 times ATP produce = 12+2+1 = 15 ATP by ETC = 12 + 2 = 14 Total ETC = 2 + 2 + 3x2 + 1x2 =12 Total ATP by ETC = 34
- 15. Where inner membrane of mitochondria Energy Yield Total of 34 ATP O2 combines with 2 H+ to form H2O Electron Transport Chain Section 9-2 Electron Transport Hydrogen Ion Movement ATP Production ATP synthase Channel Inner Membrane Matrix Intermembrane Space Mitochondrion • Glycolysis 2 Times • Intermediate2 Times • Krebs Cycle 4x2 Time • Total ETC 12 Time • ETC 34 ATP • Total 38 ATP NADH = 10 FADH = 2 OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION
- 16. ATP ATP ATP3 ATP 2 ATP Glycolysis = 2 NADH, Pyruvate Oxidation 1x2 NADH, Krebs cycle = 3 x2 NADH, Total NADH = 2+2+6=10 NADH x 3 ATP = 30 ATP FADH = 1 x 2 = 2 ATP = 2 x 2 = 4 ATP TOTAL ETC = 12 1 x2 FADH = 4 ATP e acceptor Terminal Oxidation OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION
- 17. Intermediate Reaction NADH = 1 x 2 = 2 x 3 = 6 ATP CO2 = 1 x2 = 2 CO2 Krebs Cycle NADH = 3 x 2 = 6 x 3 = 18 ATP FADH = 1 x 2 = 2 x 2 = 4 ATP CO2 = 2 x2 = 4 CO2 Glycolysis NADH = 1 x 2 = 2 x 3 = 6 ATP ATP = 2 Total ATP 2 + 6 + 4 + 18 + 6 = 36 ATP GTP = ATP = 2 direct from Krebs Cycle ETC = 2 + 6 + 2 + 2 = 12 ATP from ETC = 6 + 18 + 4 + 6 = 34 For 1 Glucose Molecule: GLYCOLYSIS = 1 Phosphorylation = 4 Dephosphorylation = 2 Dehydration = 2 Dehydrogenation = 12 INTERMEDIATE STEP = 2 Oxidation = 12 KREB’s CYCLE = 2 ETC = 12 For 1 Glucose Molecule: Light Reaction = 12 Water use = 12 Photolysis = 12 O atom produce = 12 ATP produce non cyclic = 12 NADPH produce = 12 Dark Reaction = 2 or 6 CO2 use = 6 REDUCTION = 6
- 18. 2 NADH ENERGY BALANCE SHEET RESPIRATION Glycolysis ATP use = 2 ATP produce = 4 NADH ‘’ = 2 Intermediate Step Oxidation of Pyruvate NADH produce = 1x2 = 2 CO2 produce = 1 x2 = 2 Kreb’s Cycle NADH produced = 3x2 = 6 FADH produce = 1x2 = 2 CO2 produced = 2x2 = 4 GTP produce = 1x2= 2 ATP ETC for Aerobic Respiration 2+2+6+2=12 From NADH = 10x3= 30 ATP From FADH = 2x2 = 4 ATP Total ATP = 30+4+2= 36ATP
- 19. Process Step No ATP use Direct ATP Produced NADH FADH ETC CO2 produce H2O Total ATP GLYCOLYSIS 1 ATP GLYCOLYSIS 3 ATP GLYCOLYSIS 6 2 NADH 6 ATP GLYCOLYSIS 7 2 ATP 4- 2=2 GLYCOLYSIS 9 2 H2O produce GLYCOLYSIS 10 2 ATP INTERMEDIATE 1 2 NADH 6 ATP 2CO2 KREB’s CYCLE 2 2 H2O use KREB’s CYCLE 5 2 NADH 6 ATP 2CO2 KREB’s CYCLE 6 2 NADH 6 ATP 2CO2 KREB’s CYCLE 7 2 GTP KREB’s CYCLE 8 2FADH 4 ATP KREB’s CYCLE 9 2 H2O use KREB’s CYCLE 10 2 NADH 6 ATP TOTAL 2 use ATP 6 ATP produce 10 ETC Cristae 2 ETC Cristae 34 ATP 6 produce 38 ATP Designed by Dr. Tahir Abbas Baloch
- 20. Plants have adaptations to limit the effects of photorespiration: 1. C4 plants 2. CAM plants Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) plants plants adaptation to arid conditions. 15% of plants (grasses,corn,sugarcane) 5% of plants (cactus and ice plants) Stomates closed during day Stomates open during the night Light reaction - during the day Calvin Cycle - when CO2 is present Photorespiration, C2 Cycle, Glycolate Pathway C2 cycle have consumption of ATP There is no net conservation of energy in C2 cycle. Photorespiration is wasteful process occurs due to oxygenase RuBisCo enzyme in plants. Major Part
- 22. C4 Plants Mesophyll Cell CO2 C-C-C PEP C-C-C-C Malate-4C sugar ATP Bundle Sheath Cell C-C-C Pyruvic Acid C-C-C-C CO2 C3 Malate Transported glucose Vascular Tissue C₄ carbon fixation or the Hatch–Slack pathway is a photosynthetic process in some plants. It is the first step in extracting carbon from carbon dioxide to be able to use it in sugar and other biomolecules. It is one of three known processes for carbon fixation.
- 23. CAM Plants Night (Stomates Open) Day (Stomates Closed) Vacuole C-C-C-C Malate C-C-C-C Malate Malate C-C-C-C CO2 CO2 C3 C-C-C Pyruvic acid ATP C-C-C PEP glucose • Cam plants close their stomata in the hottest part of the day to conserve water CAM plants close their stomata during the day and take up CO2 at night, when the air temperature is lower. Water loss can be lowered by an order of magnitude. CAM photosynthesis, is a carbon fixation pathway that evolved in some plants as an adaptation to arid conditions
- 34. Aerobic 38x5 = 190 ATP Anaerobic 2x5 = 10 ATP CO2 Aerobic 6 x5 = 30 CO2 Anaerobic 2x5=10
- 35. 12 3 4 5 6 7 10x3 + H2O 1 g sugar = 4 cal (38 ATP) 1 g Protein = 4 cal 1 g fat = 9 cal 1 ATP = 7.3 Kcal
- 36. ATP Compensation Point Fuel of Cell= Glucose NADH
- 37. Kreb’s cycle 1 NADH = 3ATPc Phosphoenol Pyruvic Acid Kreb’sCycle = 3 CO2 Removal of H2O
- 38. Kreb’s Cycle =3 NADH + FADH + GTP Pyruvate Oxidize = 4 NADH 1 FADH 1 GTP = 1 ATP ETC = 5 times ATP produce = 12+2+1 = 15 Total ETC = 2 + 2 + 3x2 + 1x2 =12 Total ATP by ETC = 34, 34 + 2 GTP Total ATP by ETC = 34
- 40. When 1 g of glucose respires 38 ATP molecules are generated. The terminal group of ATP has 10 kcal, 38 ATP yield 380 kcal energy. 380 kcal Under standard conditions, E react = -686 kcal/mol stored in the chemical bonds of the 38 ATP .
- 41. The mass of a biological sample after water removed, used to measure biomass .
- 42. limiting factors for photosynthesis are light, temperature, and carbon dioxide Sun is the Ultimate Source of Energy, bringing light and heat to the earth, we rarely spare a thought for that bright object in the sky. Cori cycle (lactic acid cycle), is a metabolic pathway; lactate produced by anaerobic muscles is converted to glucose in liver. 38 ATP glucose : 2 NADH in glycolysis (3 ATP) + 8 NADH in Krebs cycle (3 ATP) + 2 FADH2 (2 ATP) + 2 ATP Krebs cycle + 2 ATP in glycolysis = 6 + 24 + 4 + 2 + 2 = 38 ATP
- 43. 38 ATP produced from a single glucose molecule: 2 NADH produced in glycolysis (3 ATP each) 8 NADH produced in Krebs cycle (3 ATP each) + 2 FADH2 produced (2 ATP each) + 2 ATP produced in the Krebs cycle + 2 ATP produced in glycolysis = 6 + 24 + 4 + 2 + 2 = 38 ATP Cytochromes proteins have heme as a cofactor. ratio of CO2 evolved & O2 consumed by cell in a given time.
- 44. Annual plant that completes its life cycle, within one growing season, and then dies Biennial plant that takes two years to complete its biological life cycle. Perennial plant is a plant that lives more than two years. ATP is a reservoir of potential chemical energy as a common intermediate in metabolism, linking energy. ATP has two high-energy phosphate bonds and is the main form of energy currency in the cell Organic fuel, glucose, a biofuel cell and directly generates bioelectricity.
- 48. DAP, Diammonium phosphate, used as a fertilizer and flame retardant THANKS Glycolysis: The net ATP yield is 2 ATP. NADH+H shuttles its electrons and protons to produce 3 ATP in the ETC.