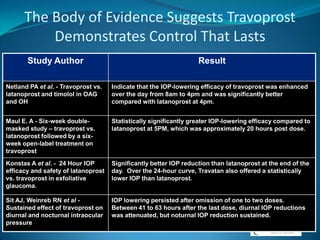
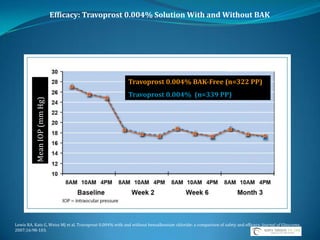
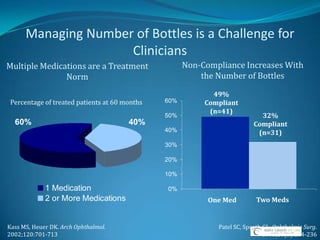
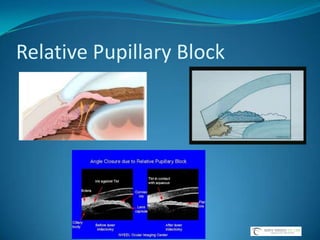
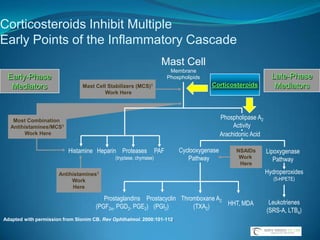
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases characterized by optic nerve damage often associated with elevated intraocular pressure (IOP). Risk factors include increased IOP, age, family history, race, and diabetes. Goals of treatment are to lower IOP, control IOP fluctuation over 24 hours, and preserve vision while balancing medication efficacy and side effects. Common glaucoma drug classes lower IOP by decreasing aqueous humor production or increasing outflow, and are dosed 1-3 times daily with possible side effects like redness, fatigue, and drowsiness. Plateau iris syndrome is when the iris remains occluded after iridotomy due to anteriorly positioned ciliary processes; argon laser peripheral iridoplasty








































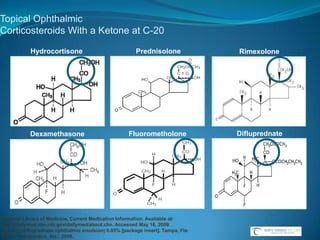











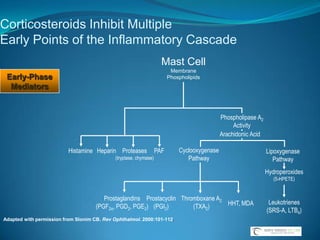
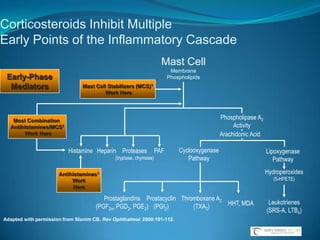
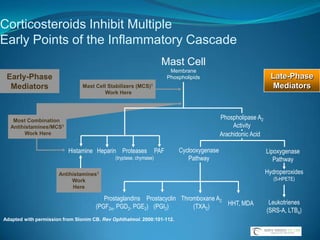
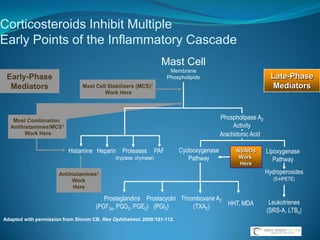




![Topical Ophthalmic Corticosteroids With a Ketone at C-20Hydrocortisone PrednisoloneRimexoloneDifluprednateFluorometholoneDexamethasoneNational Library of Medicine, Current Medication Information. Available at: http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/about.cfm. Accessed May 16, 2009. Durezol (difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion) 0.05% [package insert]. Tampa, Fla: Sirion Therapeutics, Inc.; 2008.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/narrowangles-111001162625-phpapp01/85/Narrow-angles-71-320.jpg)


