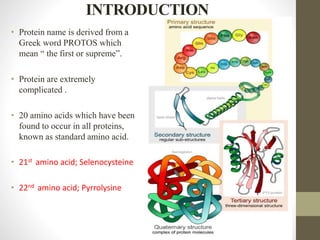
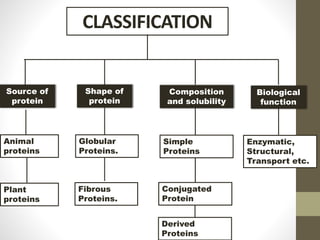
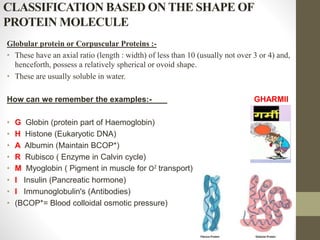
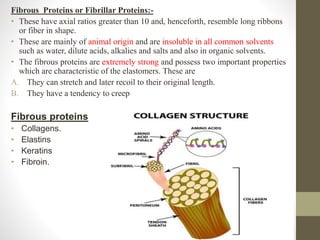
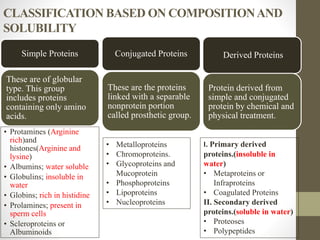
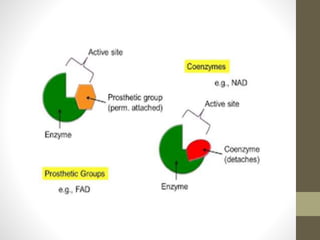
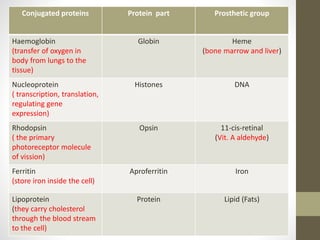
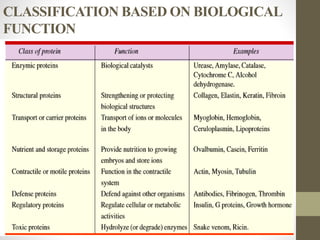
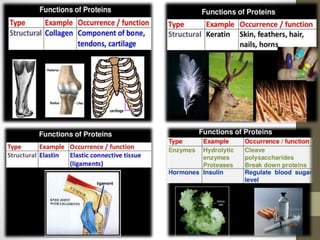
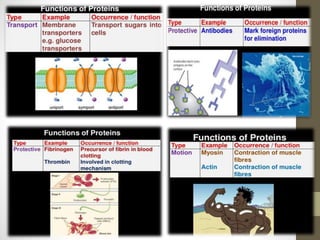
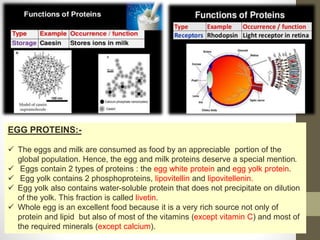
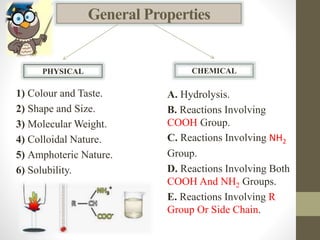
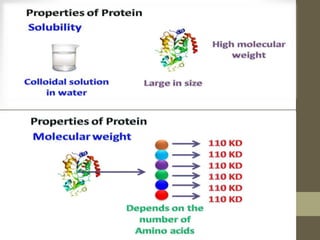
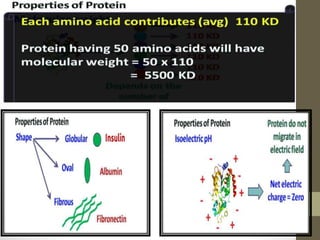
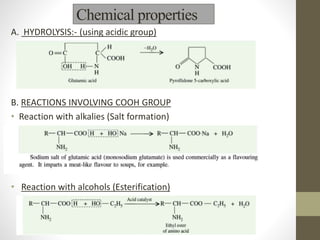
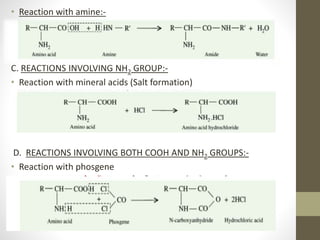
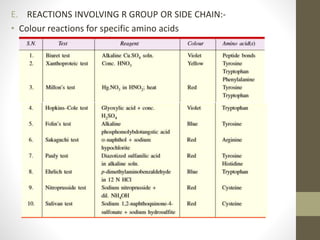
This document provides an introduction and overview of protein classification and properties. It discusses how proteins are classified based on their source, shape, composition and solubility, as well as their biological functions. Key points include that proteins are composed of amino acids and can have globular or fibrous shapes. Conjugated proteins are linked to non-protein groups. Insulin is an important protein hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and was the first to be fully sequenced. The document also examines general protein properties like molecular weight and reactions involving amino acid groups.