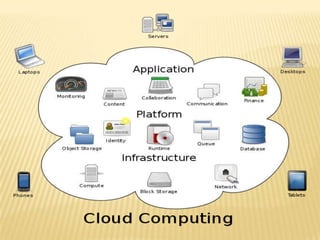
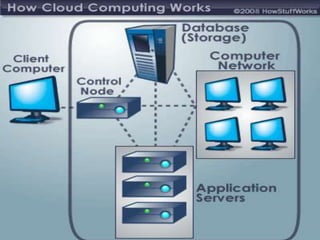
This document provides an overview of cloud computing. It begins by describing the disconnect between what businesses want from IT (e.g. fast experimentation) versus what IT wants (e.g. stability). Cloud computing is presented as filling this gap. The document defines cloud computing, discusses its characteristics such as pay-per-use and no long-term commitments. It also outlines the different types of cloud services (PaaS, IaaS, AaaS), common customers of cloud computing, and its advantages like economies of scale.