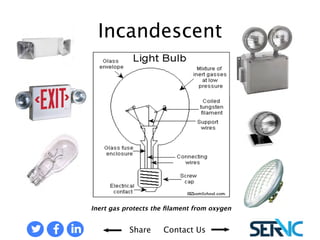
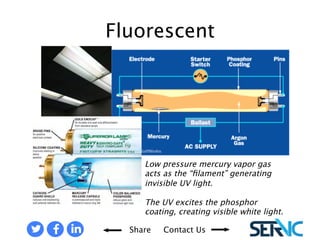
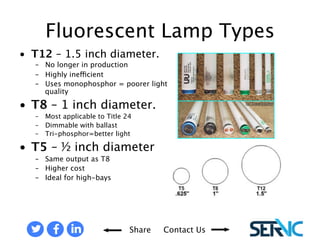
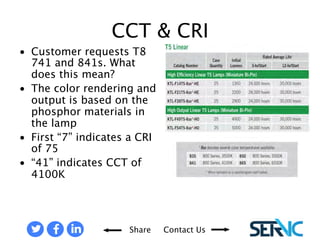
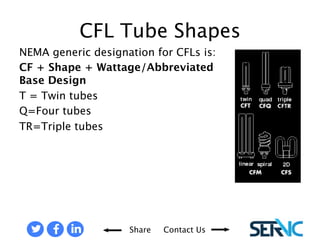
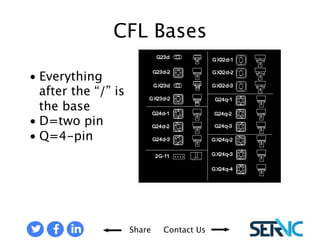
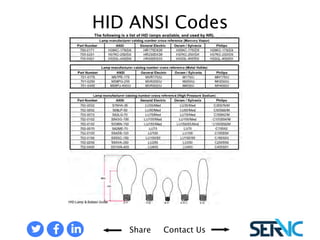
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various lamp technologies, including incandescent, fluorescent, halogen, high-pressure sodium, and metal halide lamps. It discusses their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and applications, as well as lamp codes and classifications for fluorescent lamps. Additionally, it features quizzes to assess understanding of the material covered regarding lighting systems and their compliance requirements.