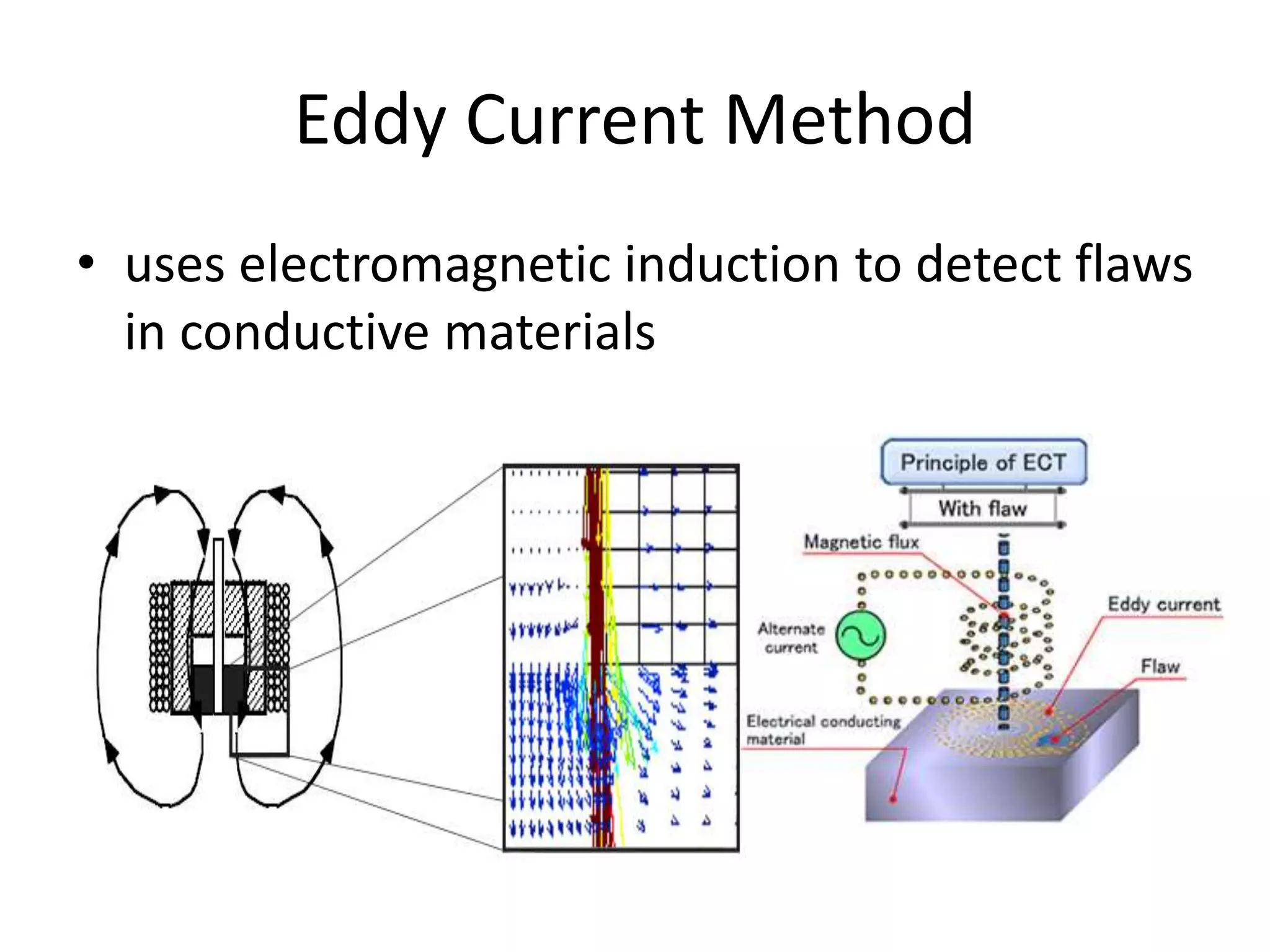
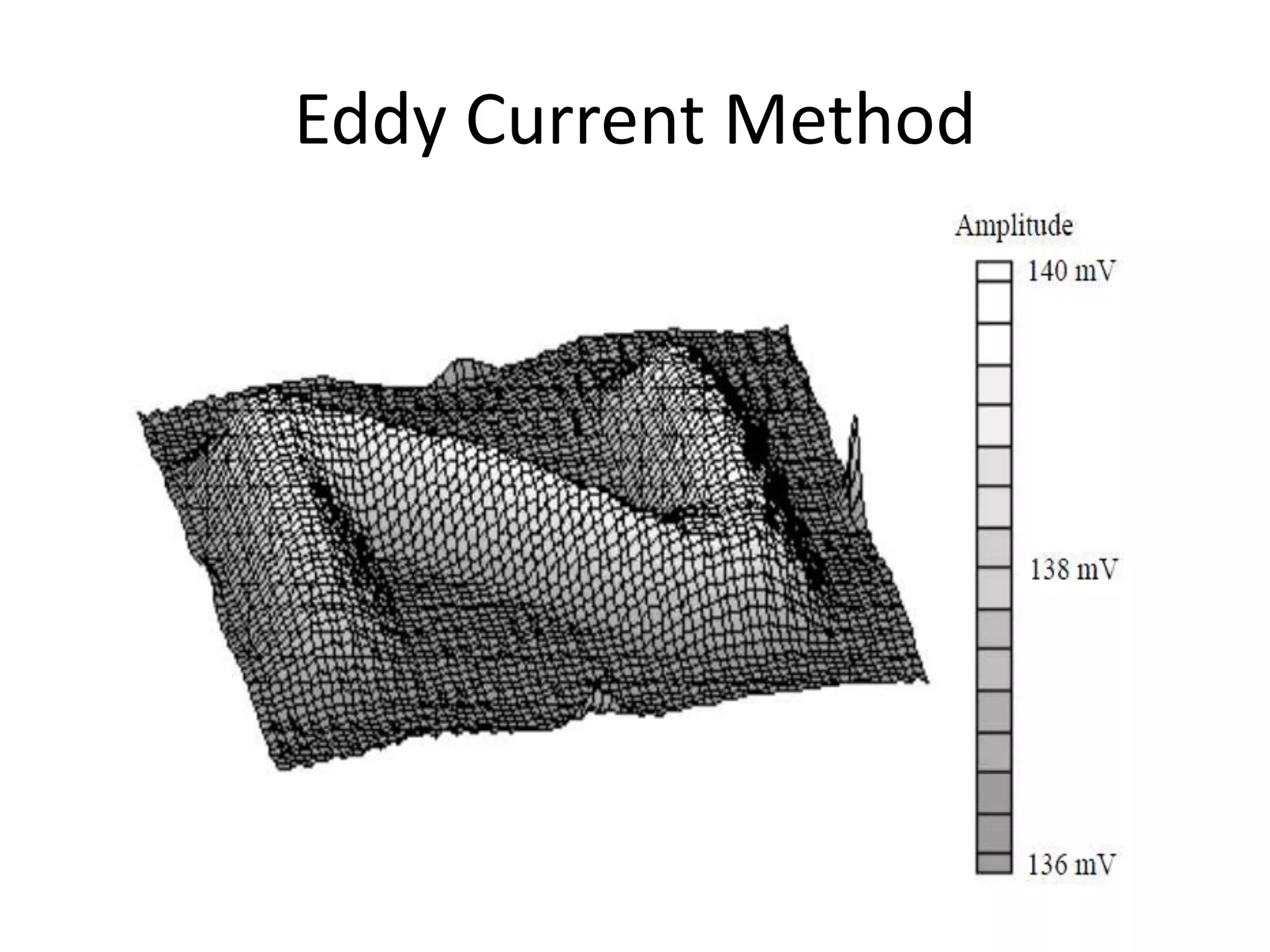
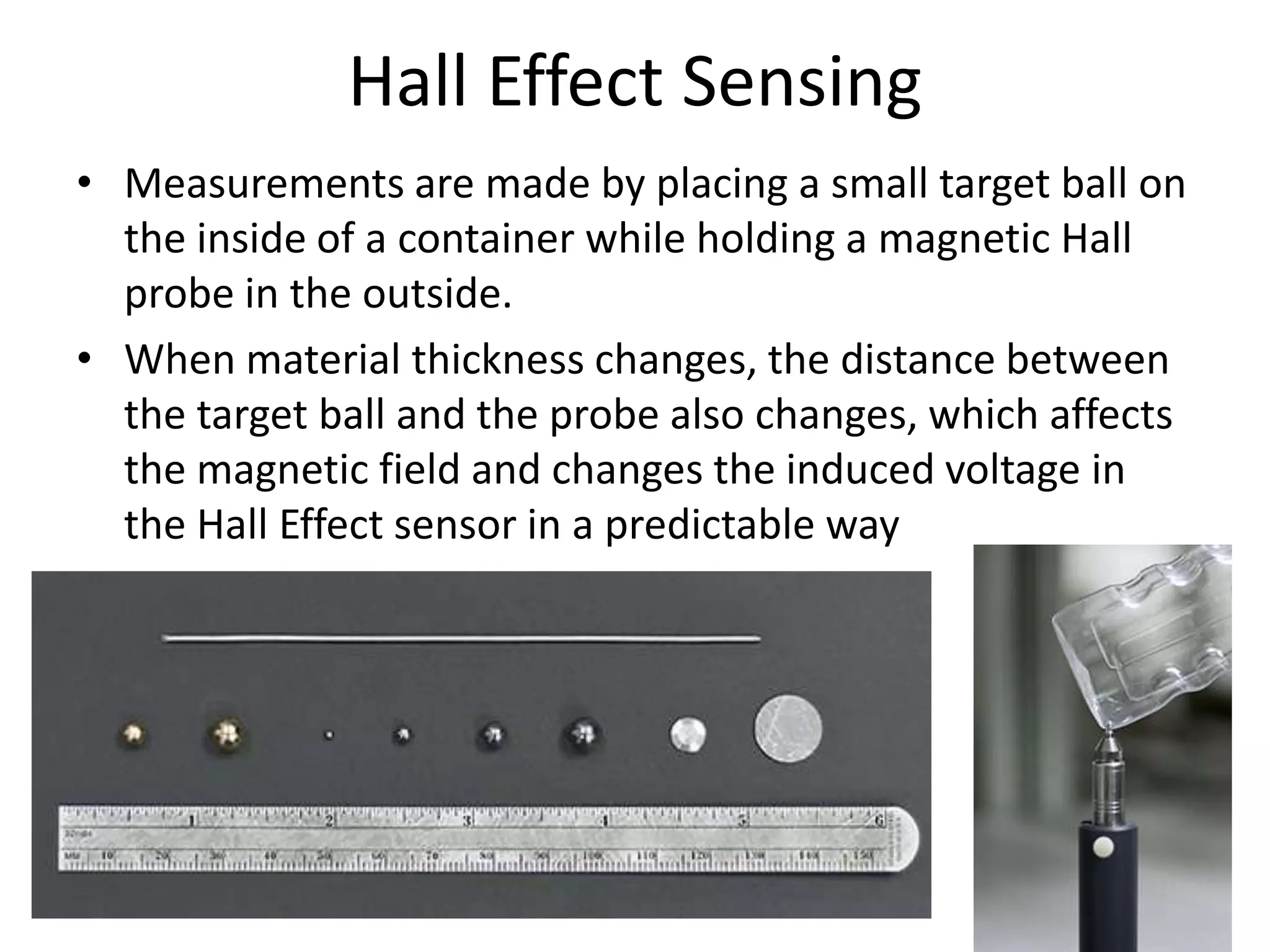
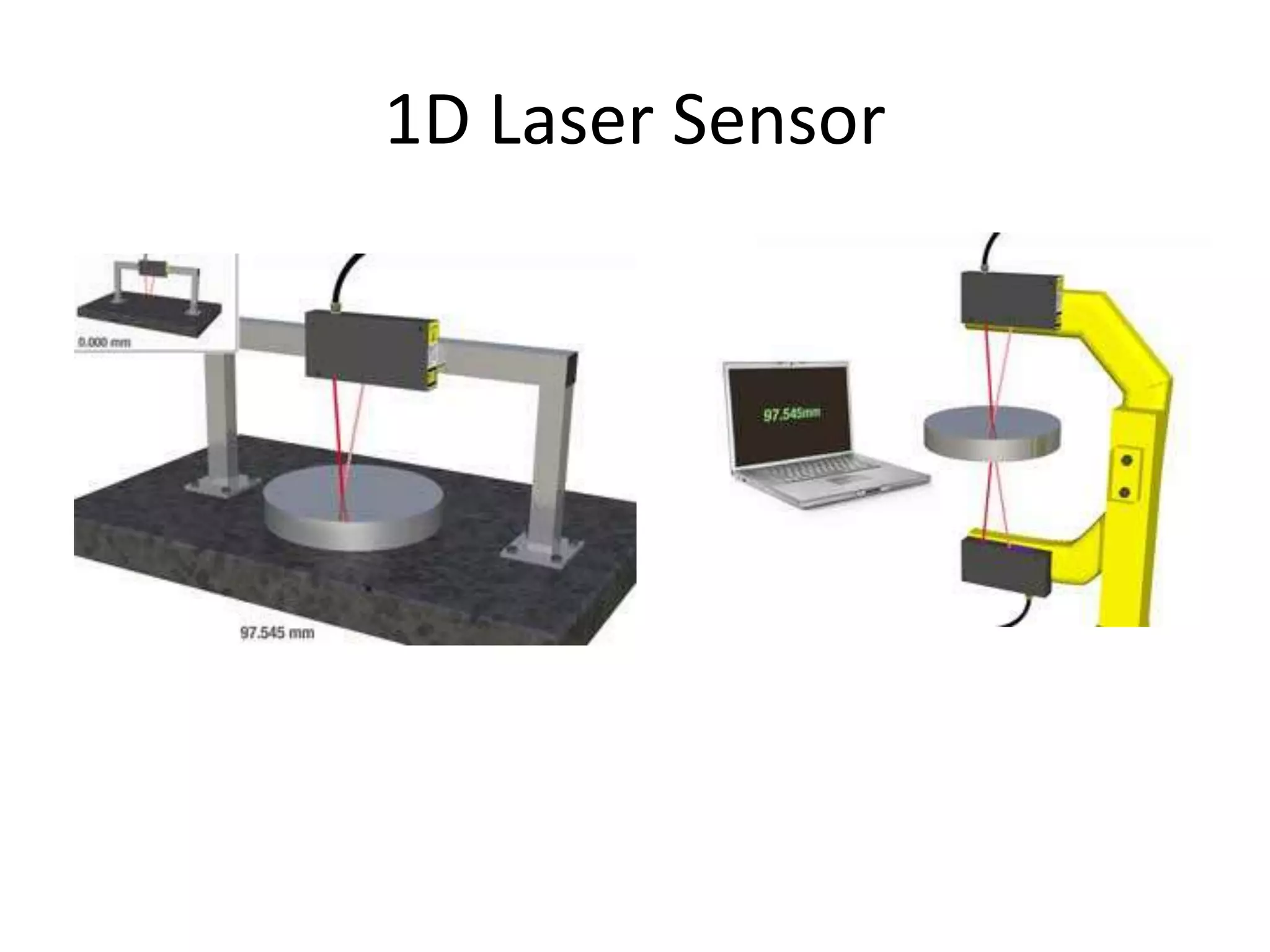
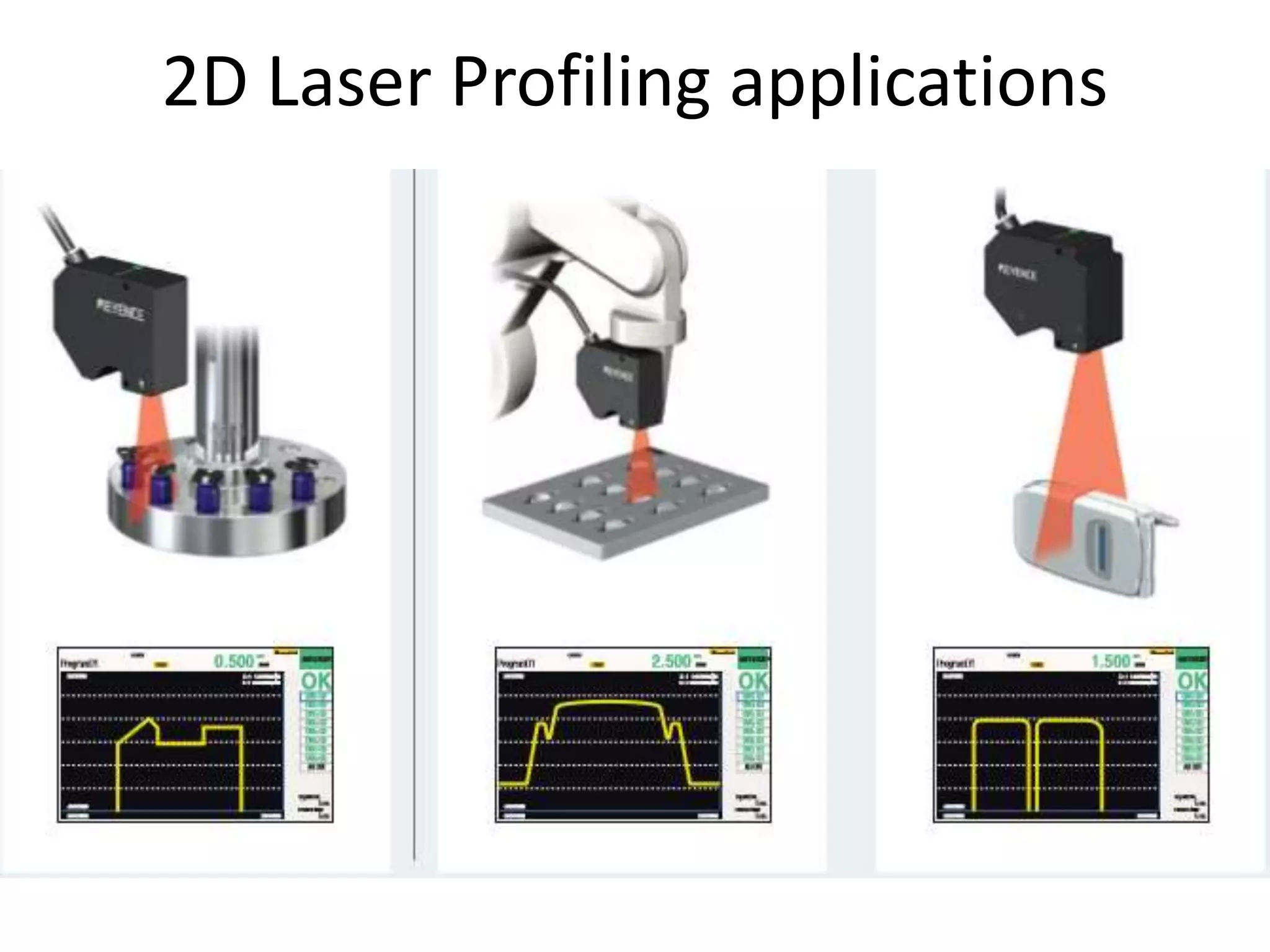
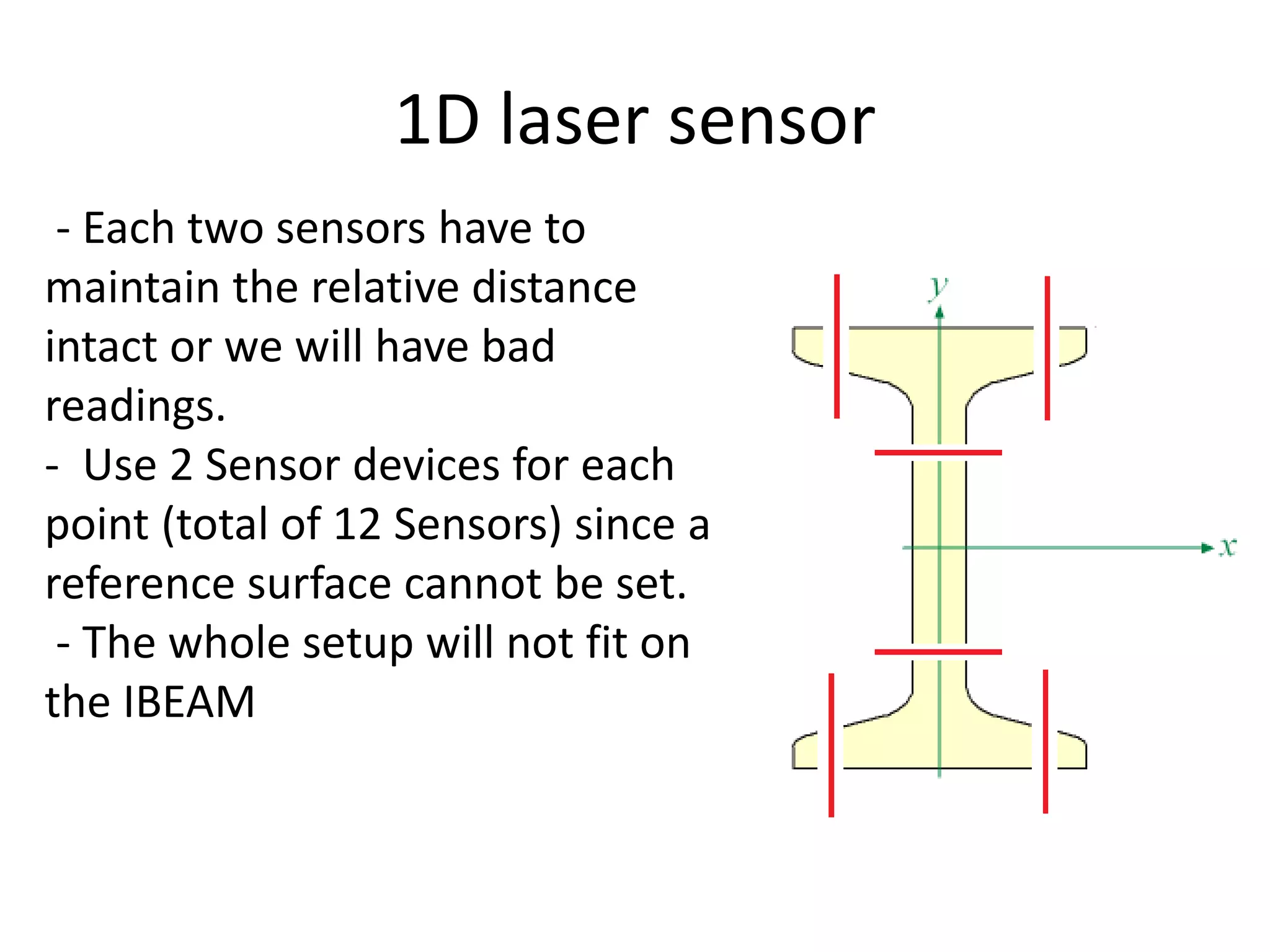
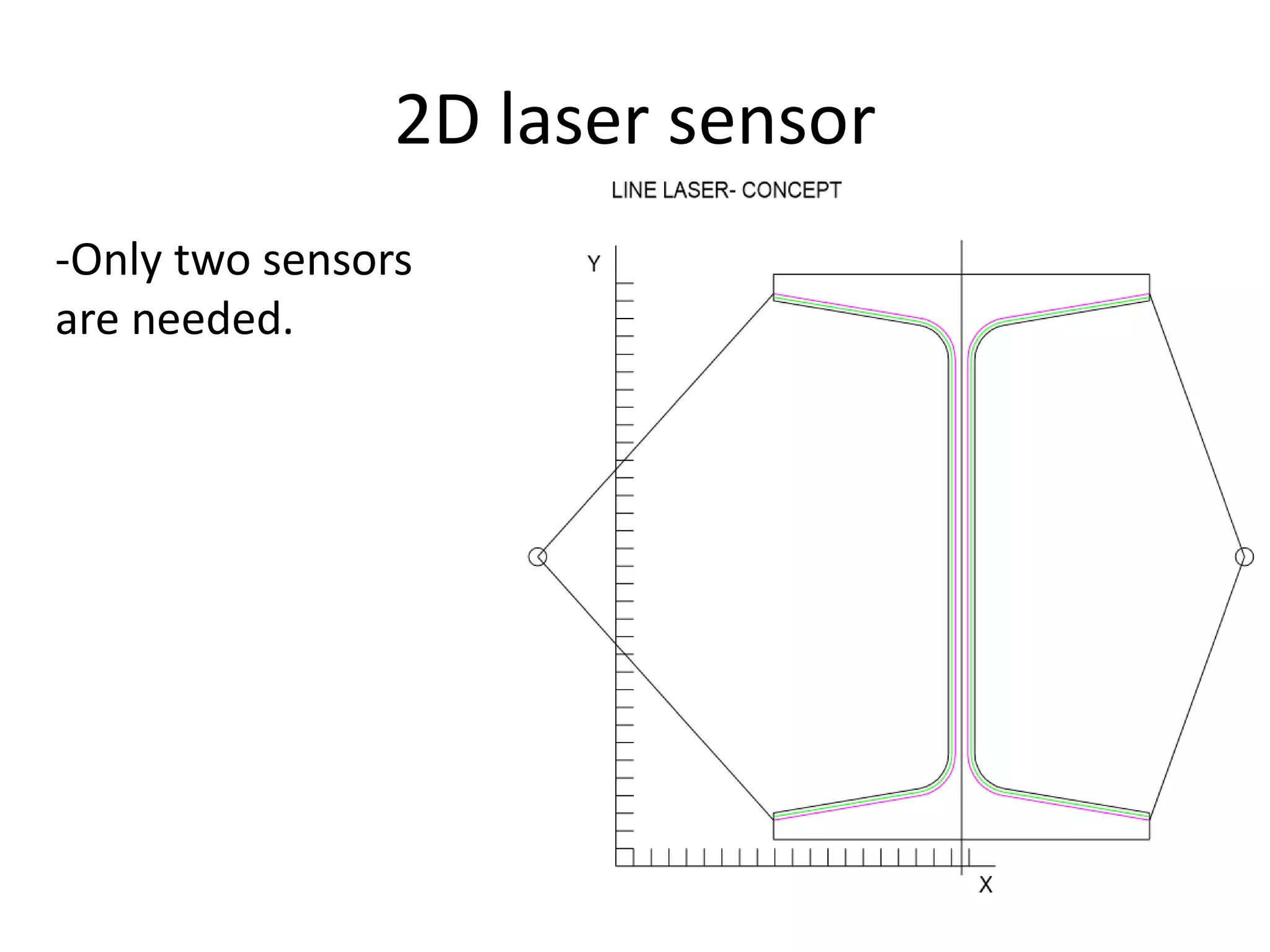
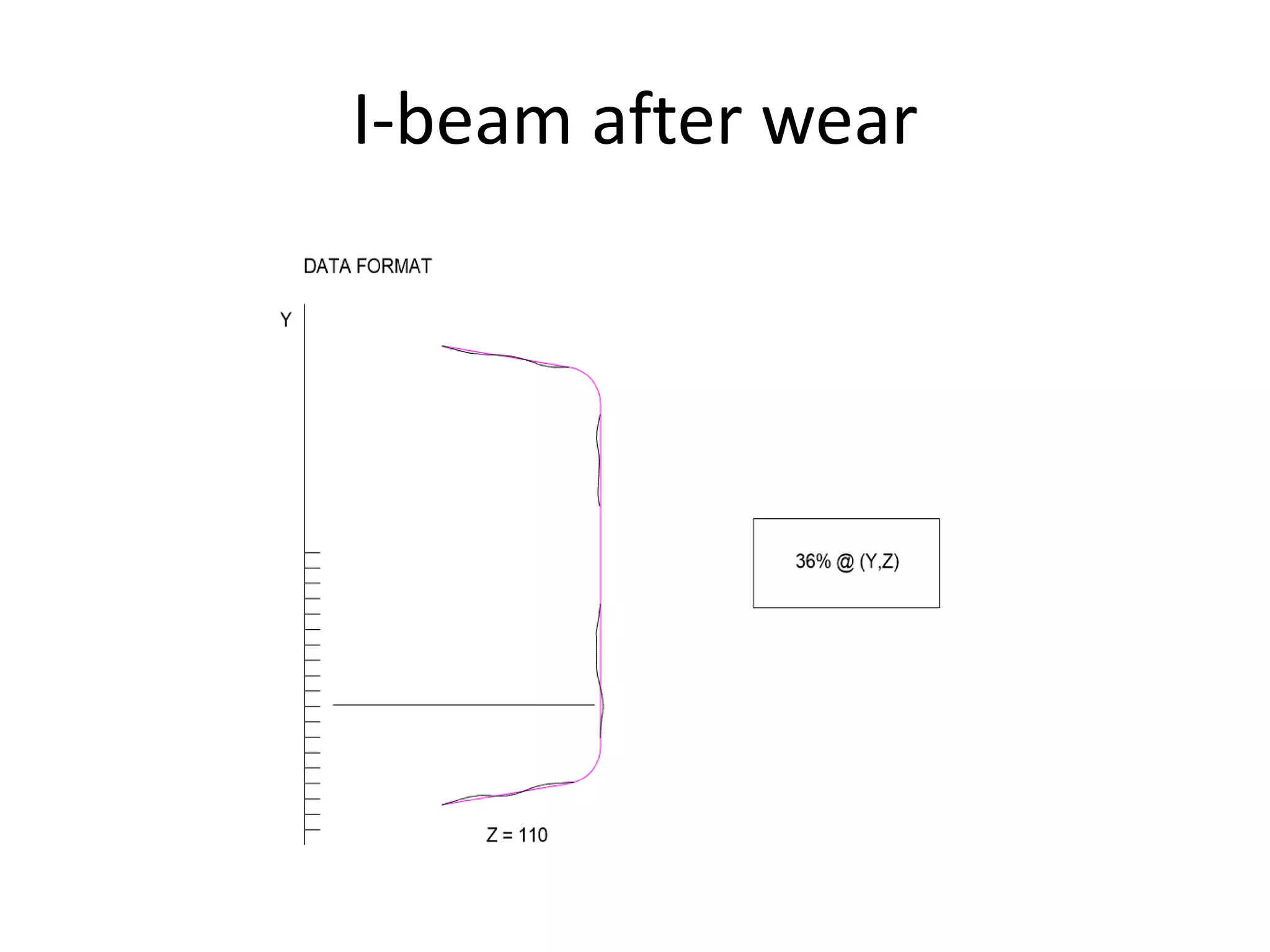
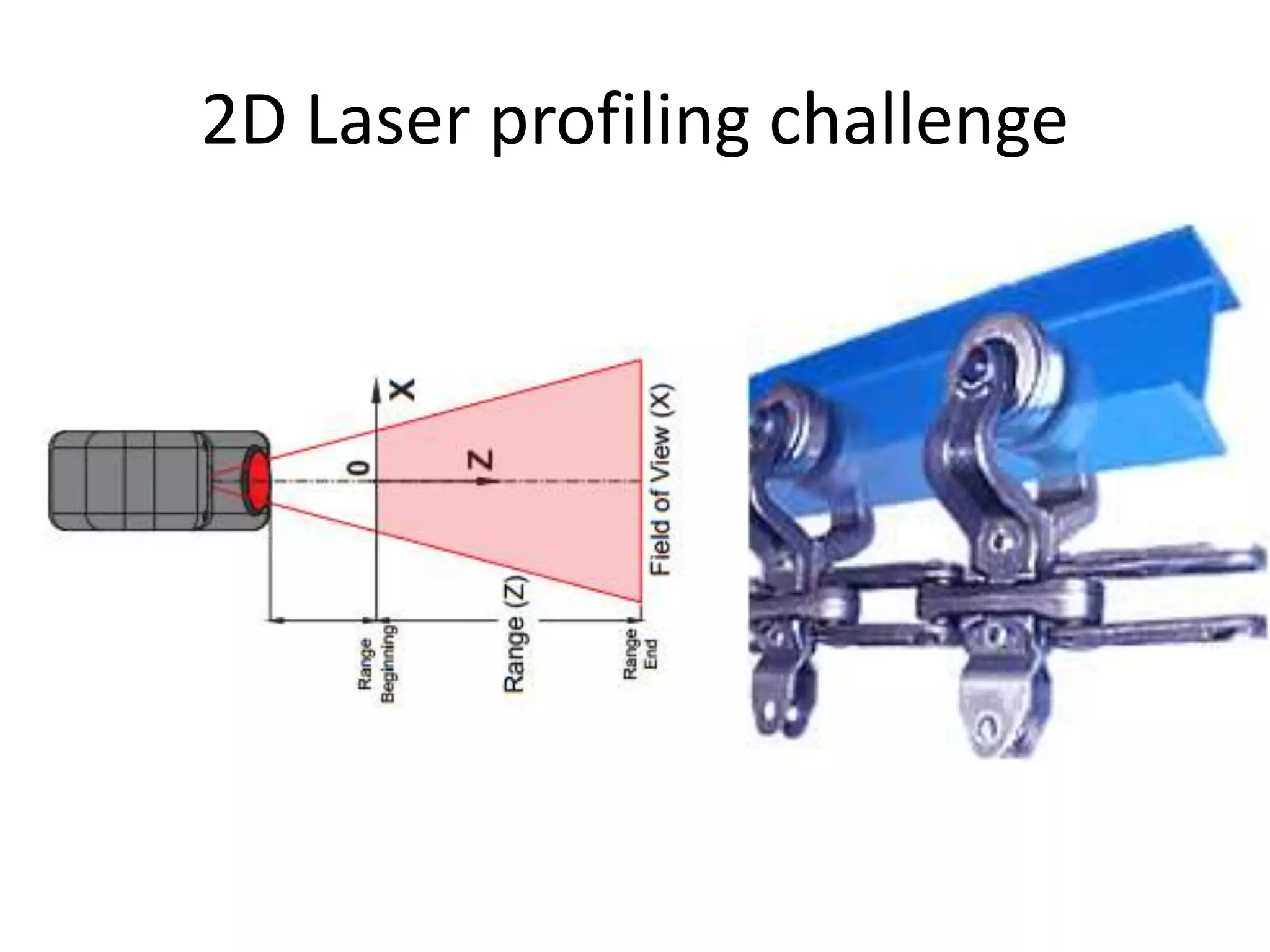
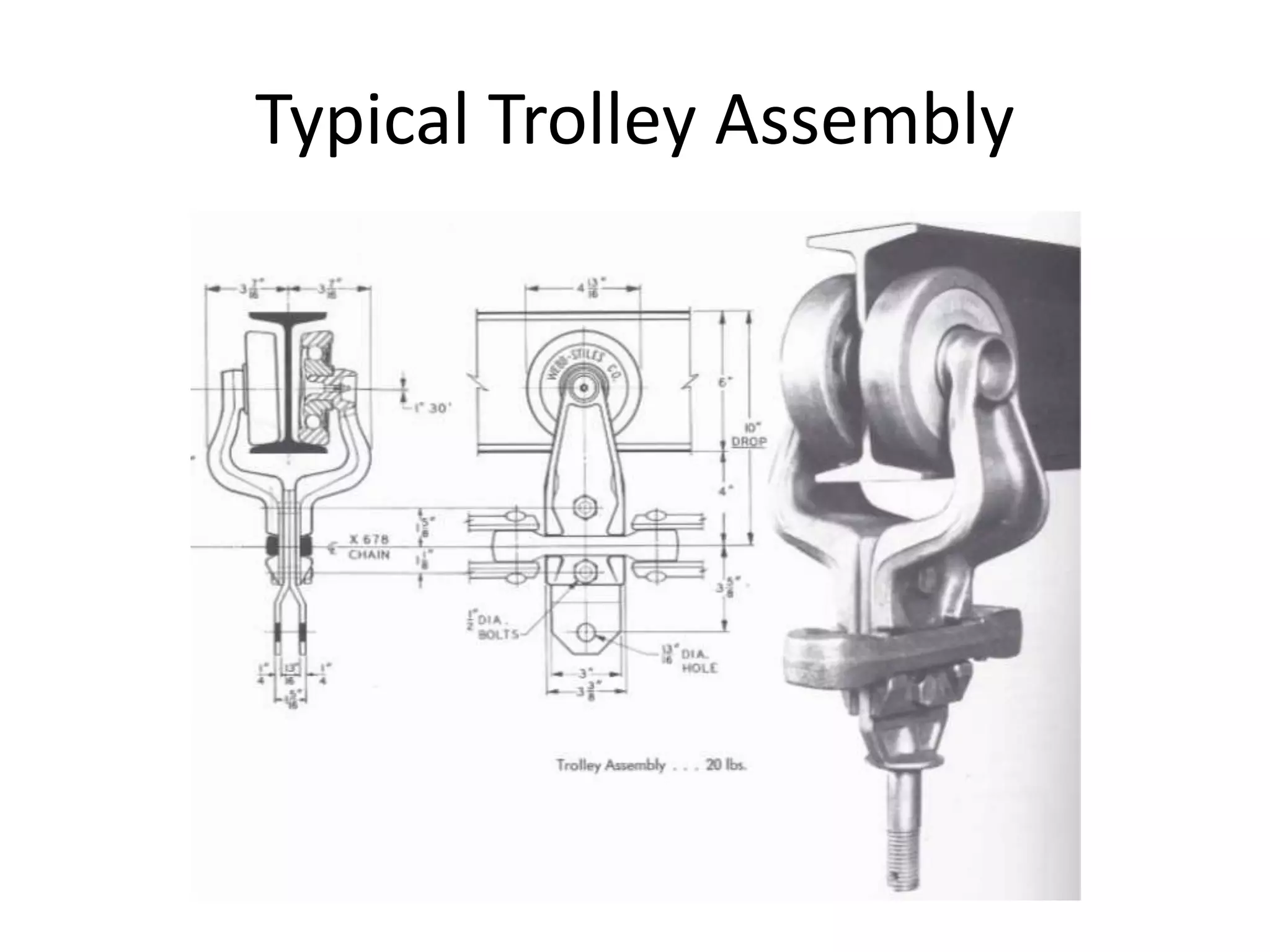
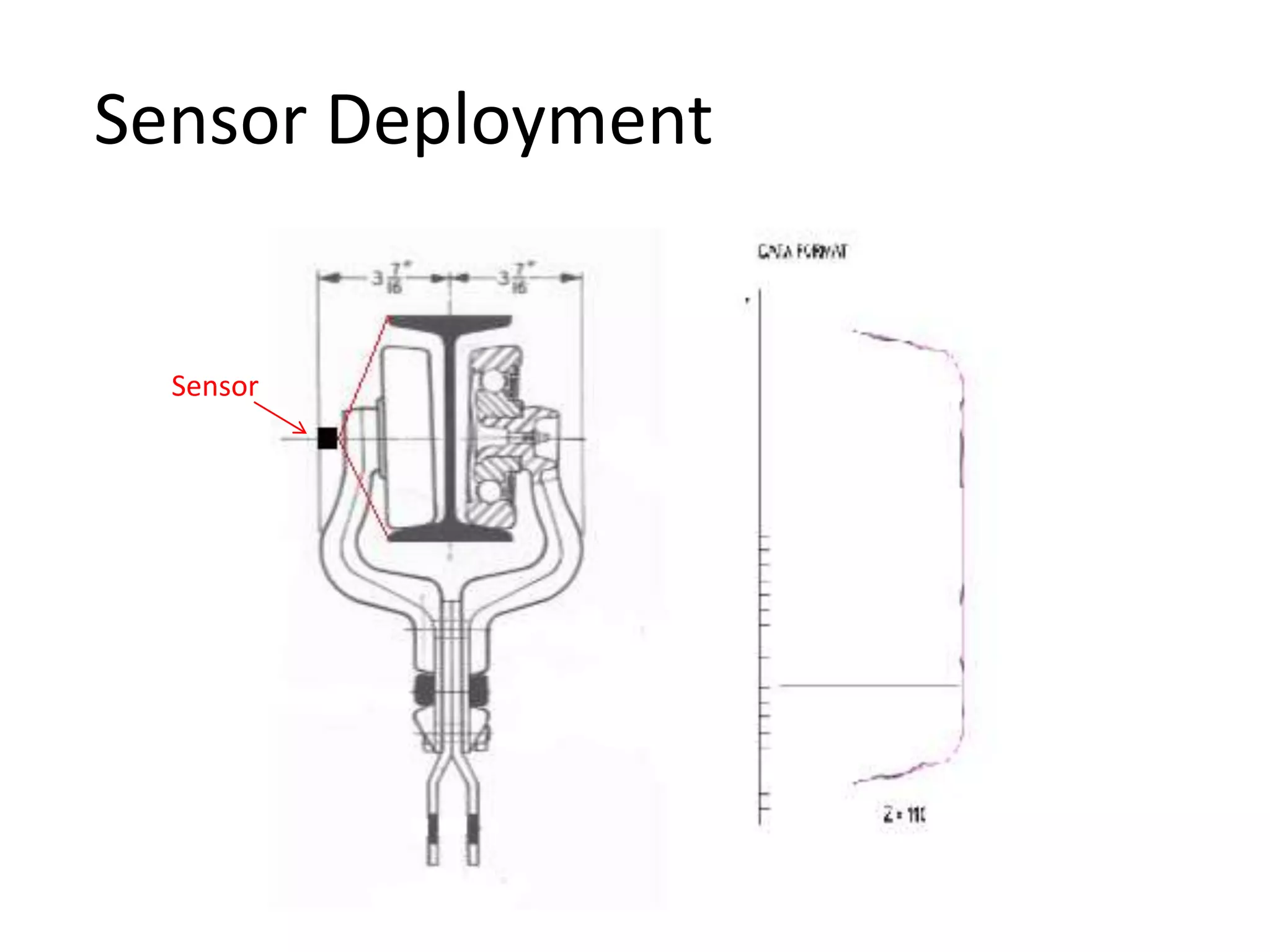
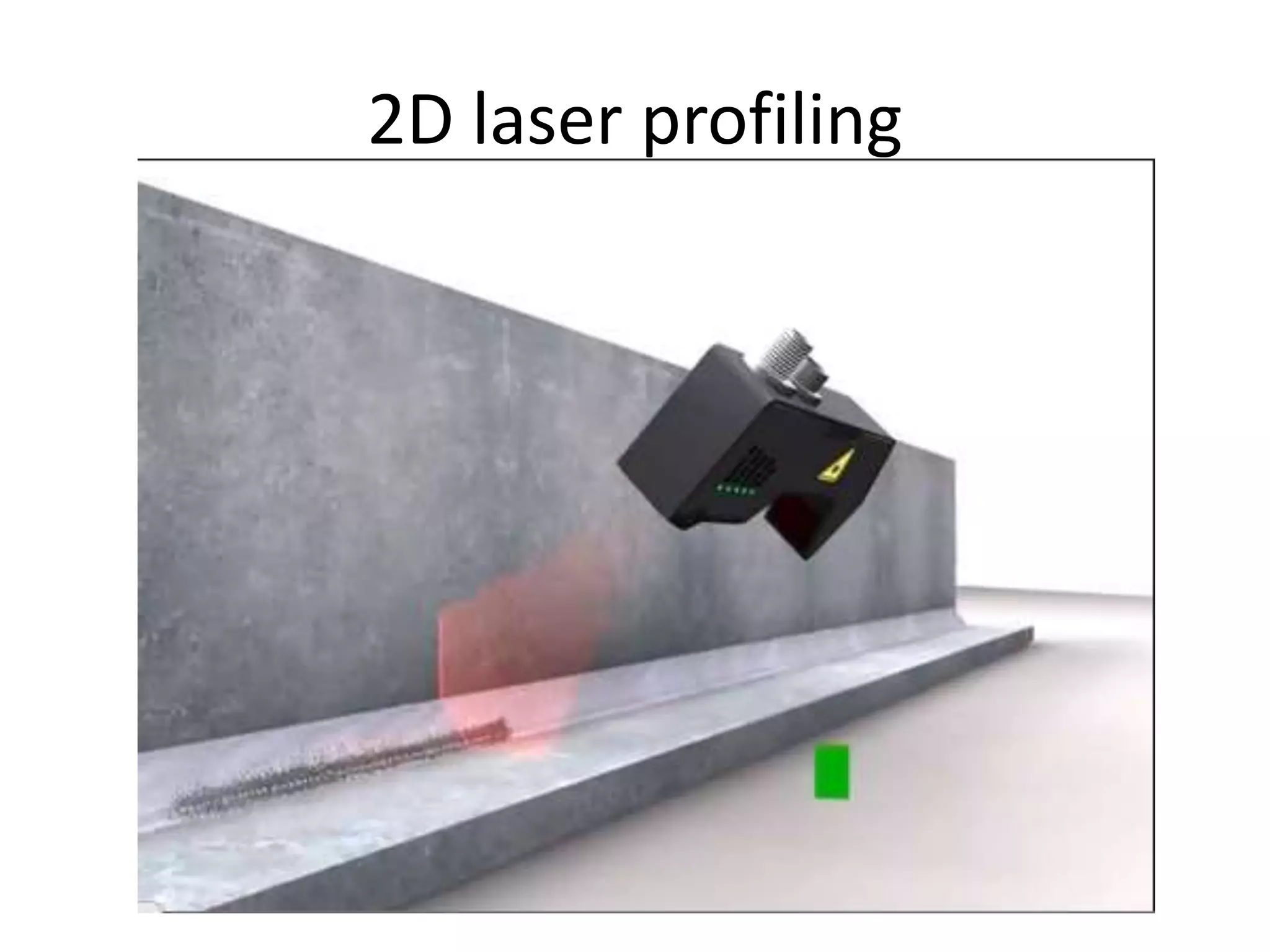
This document compares and contrasts four methods for monitoring conveyor track wear: eddy current, Hall effect sensing, ultrasound, and laser. Eddy current uses electromagnetic induction to detect flaws but has limitations related to material properties and accessibility. Hall effect sensing measures thickness changes by placing a small target on one side of the material and a probe on the other but requires access to both sides. Ultrasound measures time of flight through the material and works from one side but requires calibration for material properties. Laser sensors can measure height, thickness, and profiles at high speeds but deployment of multiple 1D sensors or use of a 2D sensor is needed to monitor an I-beam track for wear.