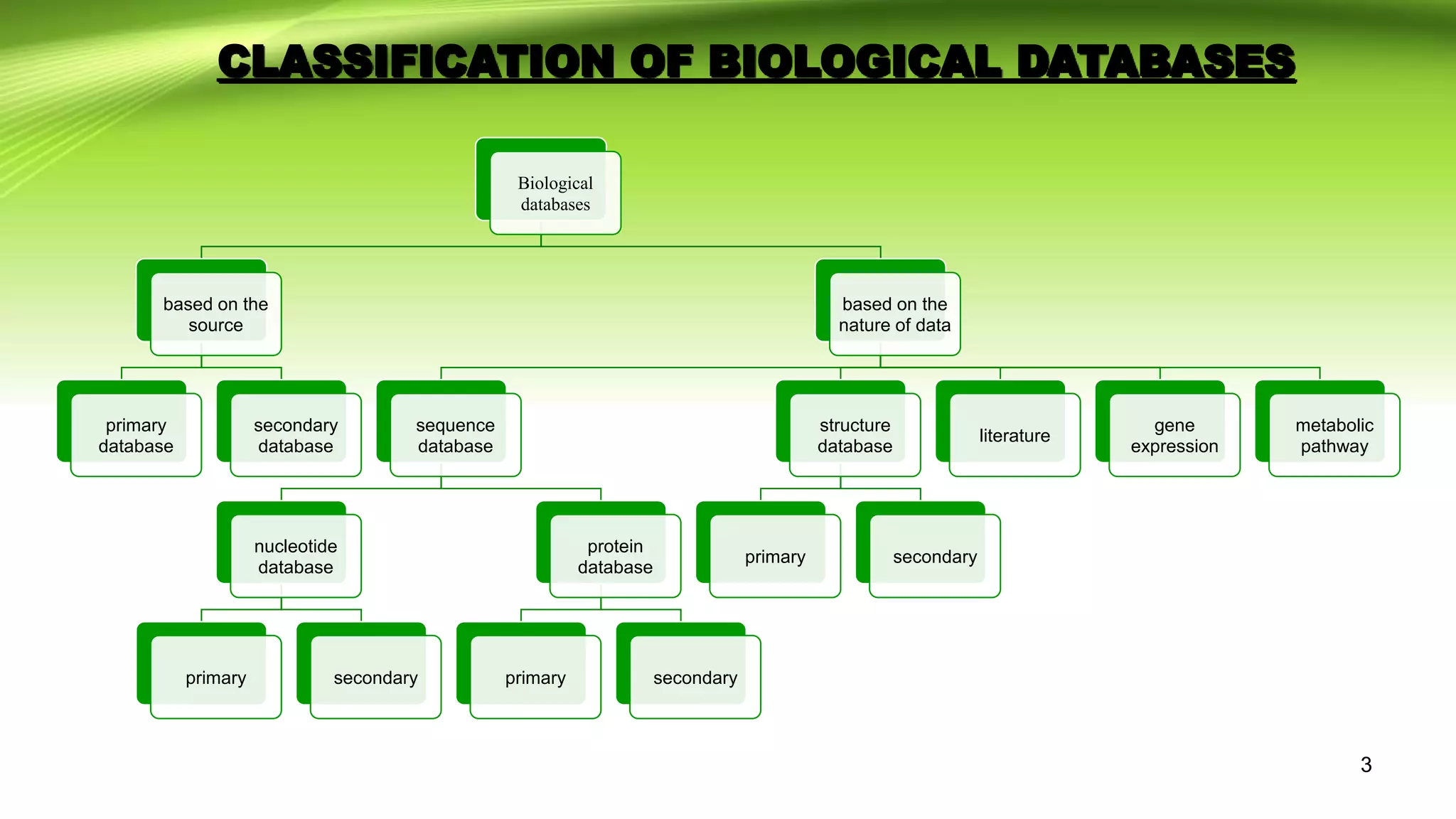
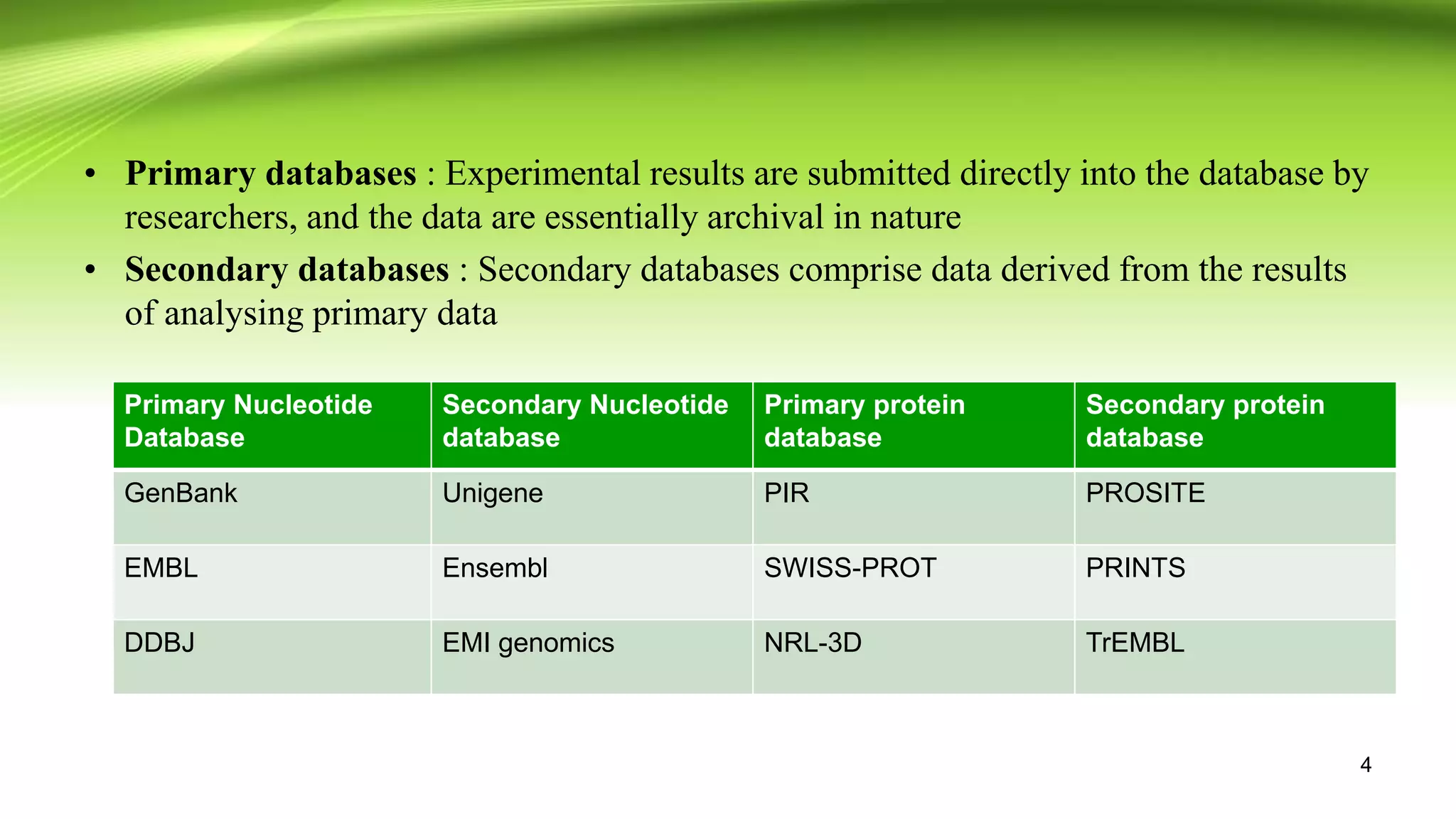
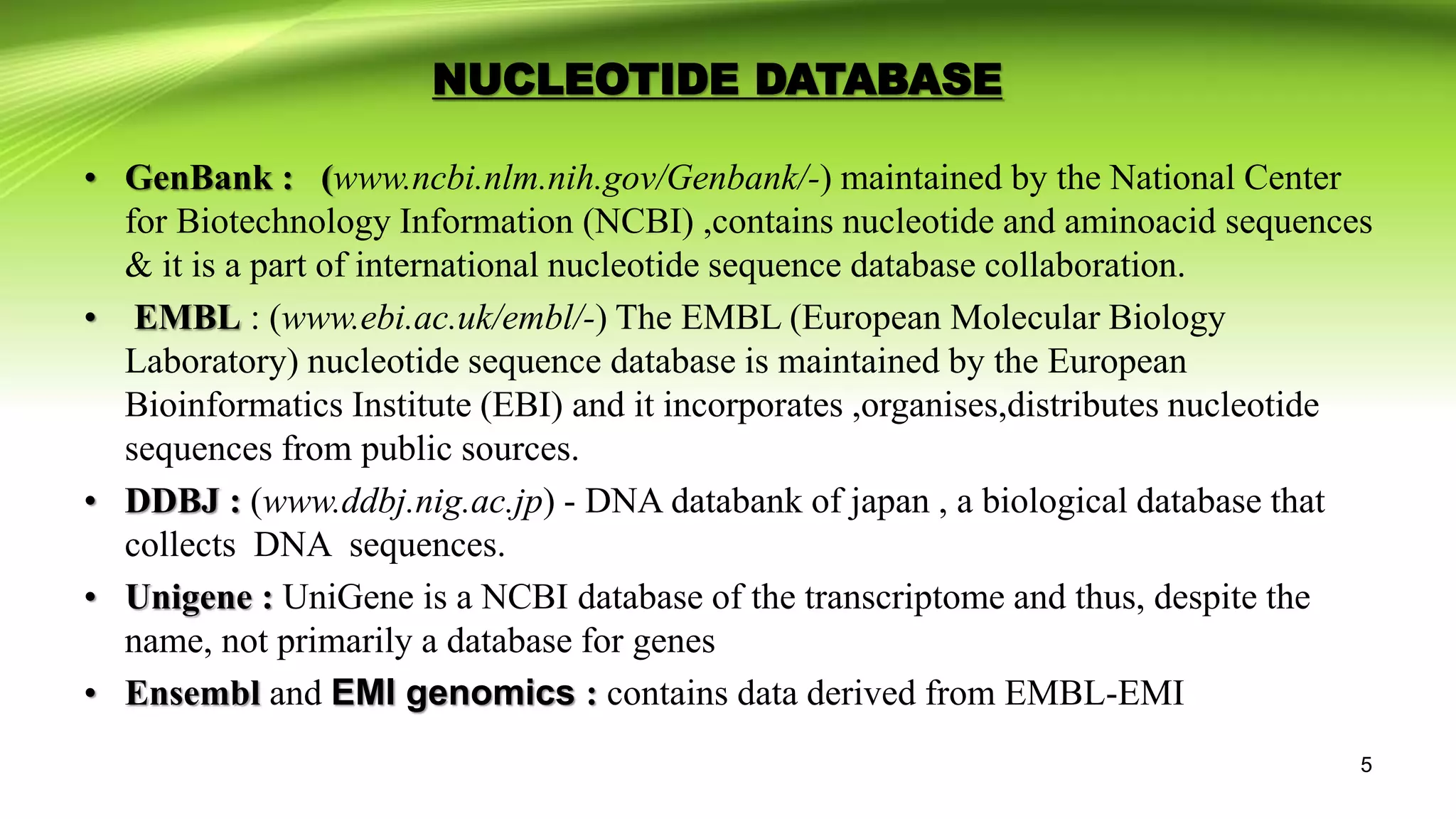
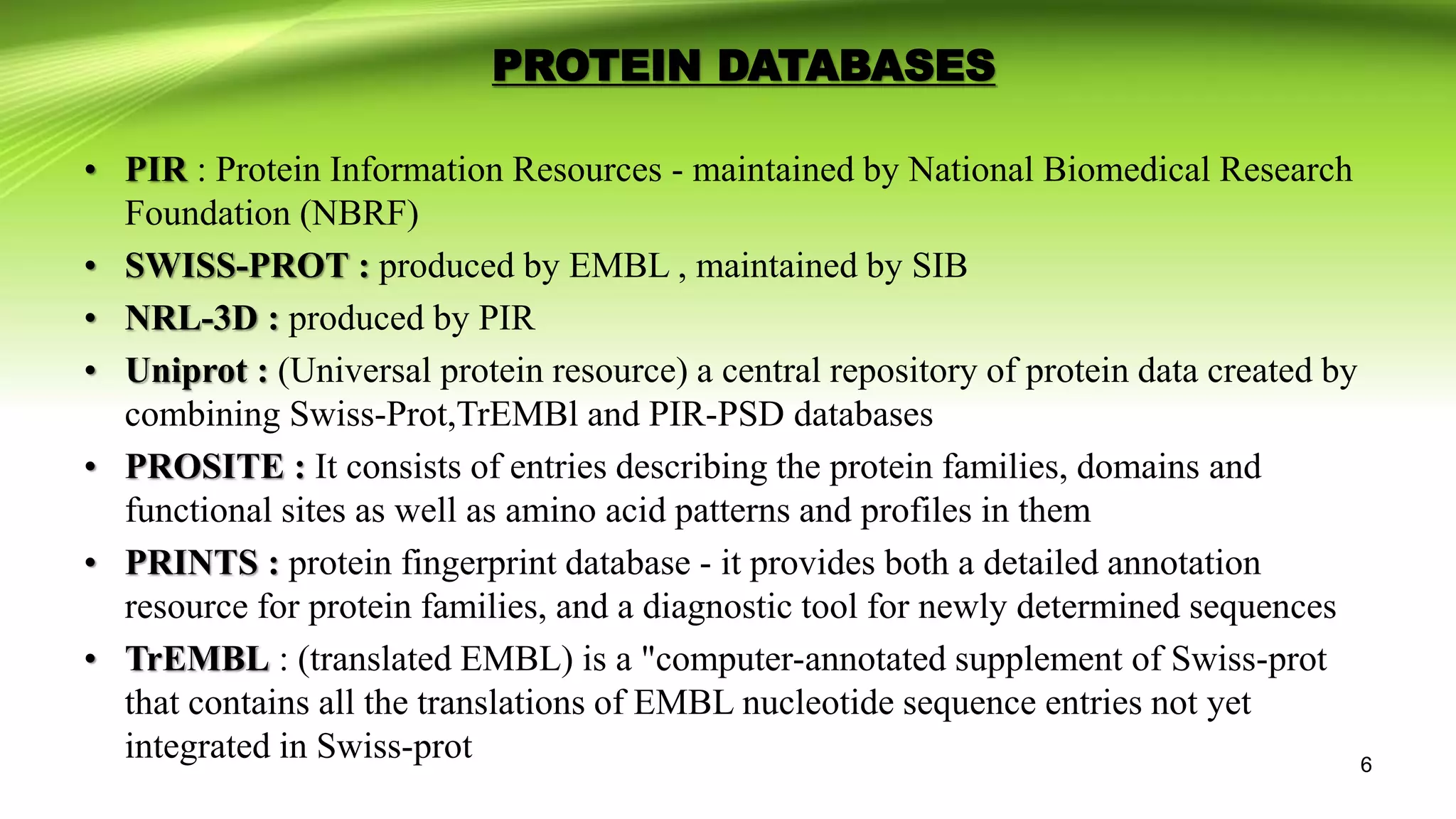
The document discusses biological databases, which are libraries of life sciences information from various research areas such as genomics and proteomics. It categorizes databases into primary and secondary types based on their data sources and provides examples of each, including GenBank, EMBL, and UniProt. Additionally, it addresses structural and pathway databases like PDB, KEGG, and Biocyc, which contain critical information for biological research.