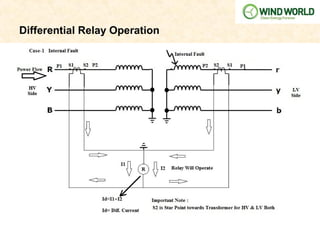
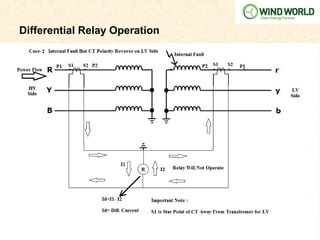
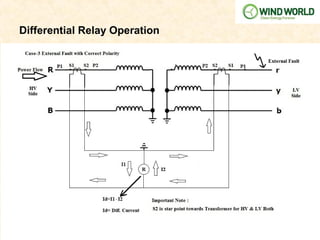
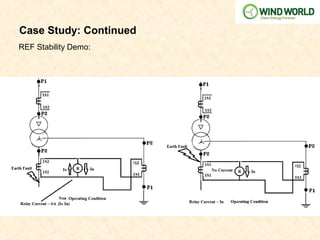
This document discusses power transformer protection. It begins by explaining that transformers are static devices that transform electrical energy between circuits without changing frequency. Power transformers are vital but expensive components that are difficult to repair if damaged. Transformer protection is needed to prevent severe damage from faults and ensure continuous network operation. Common fault types and causes are then outlined, including insulation breakdown, overheating, contamination, and phase/turn faults. The document proceeds to describe the general scheme of differential protection and specific protection functions like bias differential, overfluxing, over/under voltage, and restricted earth fault protection. It provides an example calculation for setting a transformer differential relay and diagrams demonstrating differential relay operation. Finally, it reviews models from various manufacturers and presents a case study




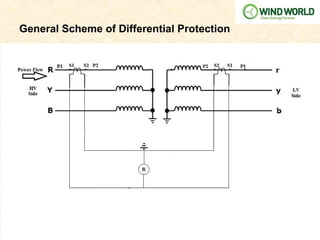

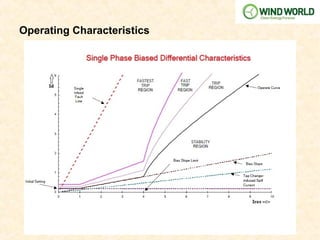

![Calculation for Transformer Differential Protection
HV rated current = 60MVA / (132 * 1.732) = 262.4A.
LV rated current = 60MVA / (33* 1.732) = 1049.76A
Mean Tap value = [(+5) + (-15)] / 2 = -5%
HV current at –5% tap = (60MVA) / (1.732 * 132KV *0.95) = 276.2A
HV Multiplier = 300 / 276.2 = 1.086 = 1.09
LV CT secondary current = 1049.7 / 1200 = 0.87475A
So the LV multiplier = 1200 / 1049.7 = 1.143 = 1.14
Initial Setting = 200mA (20%)
Bias setting = Selectable Slope
Bias Slope Limit = 4 times of full load current
HV ICT multiplier = 1.09
LV ICT multiplier = 1.14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/differentialprotection-160908072328/85/Power-Transformer-Differential-protection-9-320.jpg)