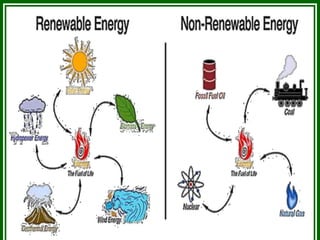
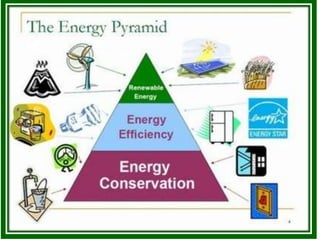
This presentation discusses energy conservation. It defines energy as the ability to do work and outlines different types of energy sources, distinguishing between renewable sources like solar and wind, and non-renewable fossil fuels. The presentation urges conservation efforts, noting that demands are increasing while resources are limited. It suggests individual actions like using efficient light bulbs and unplugging unused devices to save energy and money. India relies heavily on fossil fuel imports, so increased conservation could help address future energy demands and reliance on foreign sources.