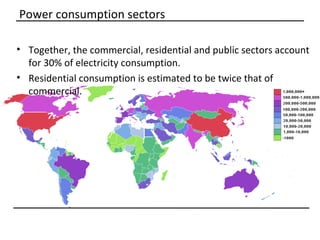
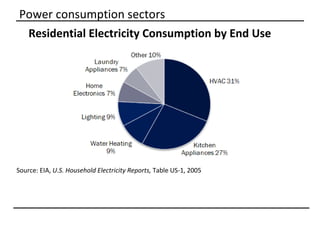
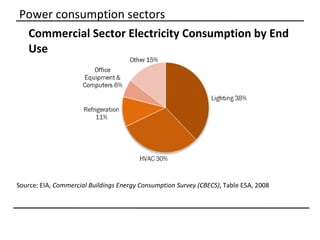
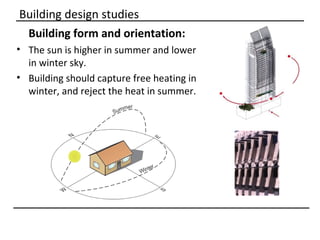
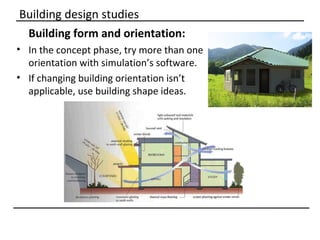
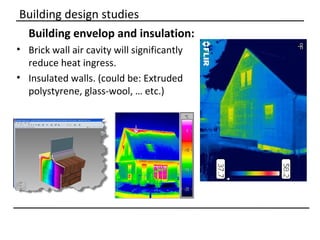
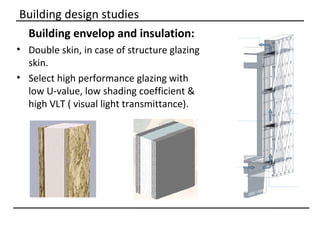
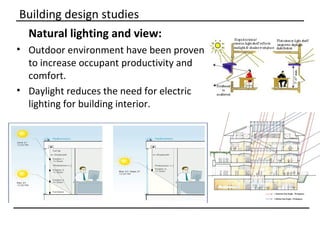
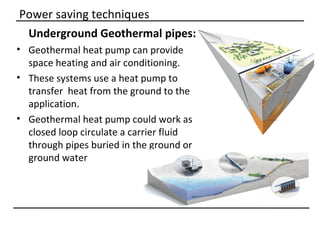
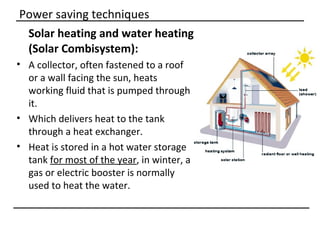
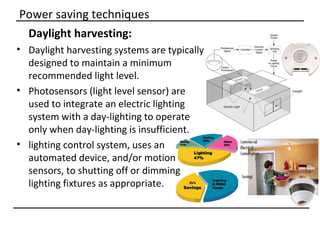
The document discusses why sustainable buildings are important and provides techniques to save power in buildings. It notes that buildings consume a large portion of energy usage annually. Building sustainably can reduce environmental impacts from fossil fuel usage and is more efficient over time due to lower operating costs. The document then outlines major sectors of power consumption in residential and commercial buildings. It also discusses prerequisite studies of building design considerations like orientation, envelopes and insulation to improve energy performance. Finally, it presents various power saving techniques for buildings like geothermal systems, solar heating, efficient lighting and daylight harvesting.