TLC
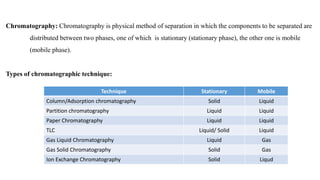
- 1. Chromatography: Chromatography is physical method of separation in which the components to be separated are distributed between two phases, one of which is stationary (stationary phase), the other one is mobile (mobile phase). Types of chromatographic technique: Technique Stationary Mobile Column/Adsorption chromatography Solid Liquid Partition chromatography Liquid Liquid Paper Chromatography Liquid Liquid TLC Liquid/ Solid Liquid Gas Liquid Chromatography Liquid Gas Gas Solid Chromatography Solid Gas Ion Exchange Chromatography Solid Liqud
- 3. Introduction TLC is one of the most simplest, fastest, easiest and least expensive of several chromatographic techniques Used in qualitative and quantitative analysis to separate organic compounds and to test the purity of Compound TLC is the form of liquid chromatography consisting of: • A mobile phase • A stationary phase • Analysis is performed on a flat surface under constant atmospheric pressure
- 4. Definition Thin Layer Chromatography can be defined as a method of separation or identification of a mixture of components into individual components by using finely divided adsorbent solid/liquid spread over a glass plate (or other material) and liquid as mobile phase
- 5. Principle of TLC It is based on the principle of adsorption chromatography or partition chromatography or combination of both, Depending on adsorbent, its treatment and nature of solvents employed The components with more affinity towards stationary phase travels slower, The components with less affinity towards stationary phase travels faster
- 6. • The two most common classes of TLC are: – Normal phase – Reversed phase • Normal phase is the terminology used when the stationary phase is polar; for example silica gel, and the mobile phase is an organic solvent or a mixture of organic solvents which is less polar than the stationary phase. • Reversed phase is the terminology used when the stationary phase is a silica bonded with an organic substrate such as a long chain aliphatic acid like C-18 and the mobile phase is a mixture of water and organic solvent which is more polar than the stationary phase.
- 7. • The following are the important components of a typical TLC system: – Apparatus (developing chamber) – Stationary phase layer and mobile phase – Application of sample – Development of the plate – Detection of analyte Important Steps in TLC process
- 8. 1. Stationary phase Adsorbents mixed with water or other solvents→ slurry Silica gel H ( Silica gel with out binder ) Silica gel G ( Silica gel + CaSO4 ) Silica GF (Silica gel + binder + fluorescent indicator) Alumina, Cellulose powder, Kieselguhr G( Diatomaceous earth + binder) GLASS PLATE Specific dimensions- 20cm Х 20cm, 20cm Х 10cm, 20cm Х 5cm Microscopic slides can also be used Plates should be of good quality & withstand high temperatures
- 9. Pouring ( simplest methods ) Dipping (used for small plates ) Spraying ( difficult to get uniform layers ) Spreading (Best technique ) TLC Spreader Activation: ○ After spreading → Air dry (5 to 10 minutes) ○ Activated by heating at about 100˚C for 30 min. Then plates may be kept in desiccators
- 10. Application of sample: » Using capillary tube or micropipette » Spotting area should not be immersed in the mobile phase Development tank ▫ Better to develop in glass beakers, jars to avoid more wastage of solvents ▫ When standard method is used, use twin trough tanks ▫ Do chamber saturation to avoid “edge effect”
- 11. Mobile phase used depends upon various factors ► Nature of the substance ► Nature of the S.P ►Mode of Chromatography ►Separation to be achieved, Analytical/Preparative e.g. → pyridine, pet. ether, carbon tetrachloride, acetone, water, glycerol, ethanol, benzene….
- 12. Iodine chamber method Sulphuric acid spray reagent UV chamber for fluorescent compounds Using fluorescent stationary phase Detection or visualizing the agent Non specific method : Specific method : 1) Ferric chloride - for phenolic compounds and tannins 2) Ninhydrin in acetone – for amino acids 3) Dragondroff’s reagent – for alkaloids 4) 3,5-dinitro benzoic acid – For cardiac glycoside 5) 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine – For aldehyde and ketones
- 13. Detecting techniques can also categorised as: 1) Destructive technique: eg. Specific spray reagents, sulphuric acid spray reagent, etc. where the samples are destroyed for detection. 2) Non-destructive technique: like uv chamber method, iodine chamber method, densitometric method etc where the sample is not destroyed even after detection. these detection techniques are used in TLC method development and preparative TLC
- 14. • Rf value – Rf value is the ratio of distance travelled by the solute to the distance travelled by the solvent front the range of Rf value from 0 to 1. But ideal values are from 0.3 to 0.8. Rf value is specific and constant for every compound in particular combination of stationary and mobile phase • Rx value – The ratio of distance travelled by the sample & the distance travelled by the standard. Always closer to 0 to 1 Qualitative analysis Rf = D distance travelled by the solute distance travelled by the solvent front
- 15. Application: Purity of sample Examination of reaction Identification of compounds Biochemical analysis In pharmaceutical industry Separation of multicomponent pharmaceutical Formulations In food and cosmetic industry
- 16. High-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC)
- 17. Principle: • Separation my result due to adsorption or partition or by both phenomenon depending upon the nature of adsorbents used on plates and solvents system used for development. • The mobile phase flows through the plate because of capillary action. the components move according to their affinites toward the adsorbent . • The component with more affinity towards stationary phase travels slower. the component lesser affinity towards stationary phase travel faster
- 18. Sample preparation Application of sample Chromatography development Detection of spots Scanning and documentation Selection of chromatography layer Pre washing Preconditioning Steps involving in HPTLC
- 19. Selection Of Chromatography Plates •Hand Made Plates •Pre Coated Plates •Hand Made Plates Cellulose Cellulose with binder starch Silica gel with starch Acetylated cellulose + CaSO4 ½ H2O
- 20. Precoated Layer Of HPTLC •Different support materials are used •Glass •Polyester sheets •Aluminium •Silica gel 60F •Aluminium oxide: Basic substances ,alkaloid and steroids. •RP,RP8,RP18: Nonpolar substances ,fatty acids,carotenoids,cholesterol. •Preservatives,barbiturates,analgesic and phenothiazines-Hybrid plates RP18WF25S
- 21. Sample And Standard Preparation •Sample and standard should dissolved in the same solvent to ensure comparable distribution at stationary zones. •For normal phase chromatography solvent for dissolving the sample should be non polar. •For reverse phase chromatography polar solvents are used.
- 22. Pre Washing Of Pre Coated Plates •To avoid any possible interference due to impurities it is recommended to wash the plates is called pre washing. •Methods used for pre washing are : Dipping Ascending Solvents used for washing are: Chloroform in methanol(1:1) Methylene chloride – methanol(1:1) 1%ammonia or 1% acetic acid
- 23. Activation Of Pre-coated Plates •Freshly open box of plates do not require activation. •Plates exposed to high humidity or kept on hand for long time to be activated •By placing in oven at 110-120ºc for 30 minutes prior to spotting. •Aluminium sheets should be kept in between two glass plates and placing in oven at 110-115ºc for 15 minutes.
- 24. Application Of Standard And Sample •Selection of sample application and devices used depends on •Sample volume •Number of samples to be applied •Samples is applied by use of automatic devices and graduated capillaries. •Volume recommended for HPTLC 0.5-5μl •Sample should not excess or not low •Over loading can be over come by applying sample as band.
- 25. Selection Of Mobile Phase •Normal phase – •Stationary phase is polar •Mobile phase is non polar •Non polar compounds eluted first because of lower affinity with stationary phase . •polar compound retained because of higher affinity with the stationary phase •Reversed phase •Stationary phase is non polar •Mobile phase is polar •polar compound eluted first because of lower affinity with stationary phase non polar compounds retained because of higher affinity with the stationary phase.
- 26. Detection and visualization •Detection under UV light is first choice –non destructive spots of fluorescent compounds can be seen at 254nm(near UV range)
- 27. Quantification •Sample and standard should be chromatographed on sample plate after development chromatogram is scanned •Camag TLC scanner III scan the chromatogram in reflectance or in transmittance mode by absorbance or by fluorescent mode. •Scanning speed is selectable up to 100 mm/s –spectra recording is fast -36 tracks with up to 100 peak windows can be evaluated. •Calibration of single and multiple levels with linear or nonlinear regressions are possible. When target values are to be verified such as stability testing and dissolution profile single level calibration is suitable.
- 28. Application of HPTLC •Pharmaceutical Industry : quality control, content uniformity, identity/purity check. •Food Analysis: quality control, additives, pesticides, stability testing. •Clinical Application :metabolism studies, drug screening, stability testing etc. •Industrial Application: process development and optimization, In-process check, validation etc. •Forensic : poisoning investigation. •Finger print analysis.
- 29. Difference between HPTLC & TLC