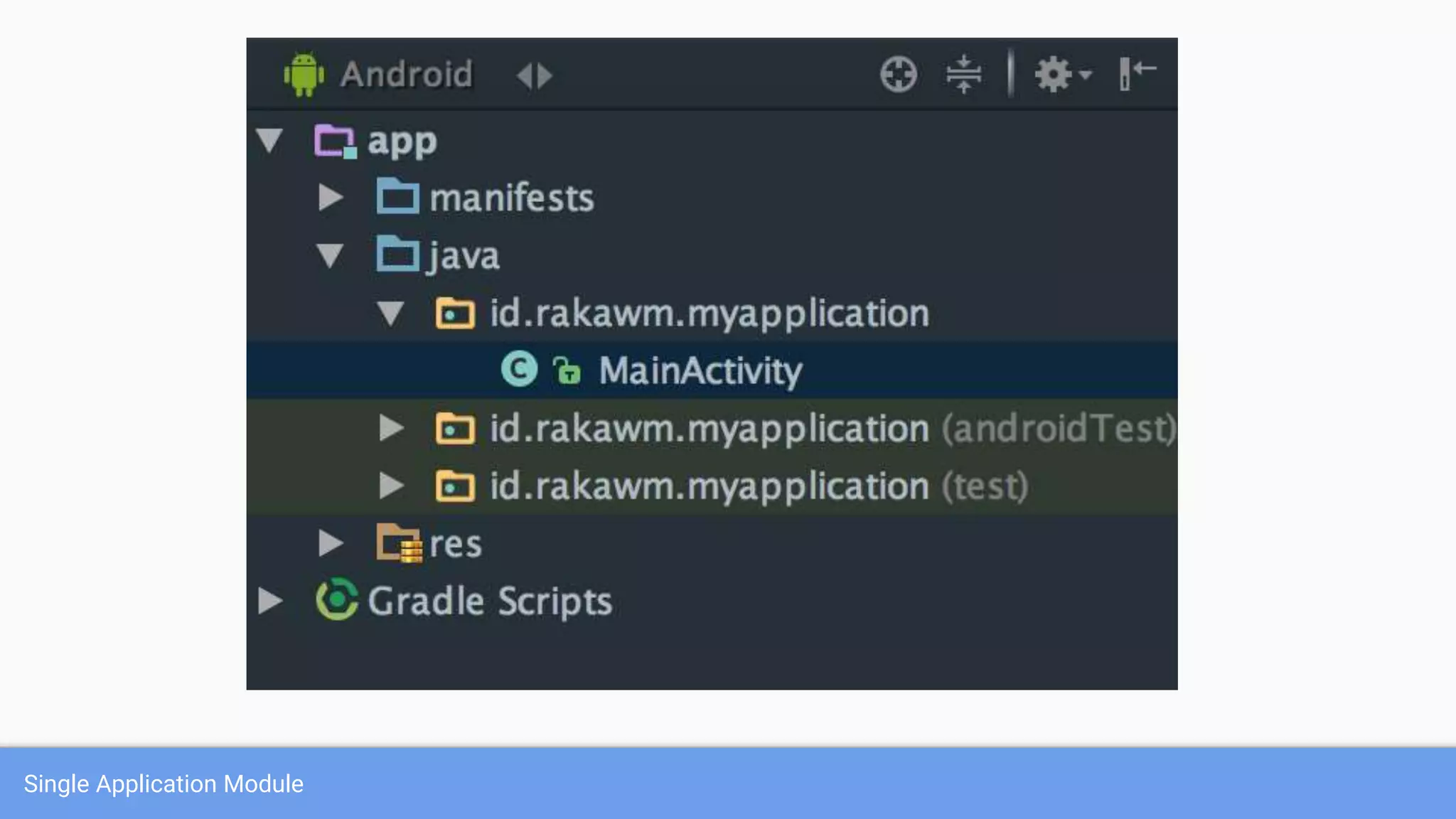
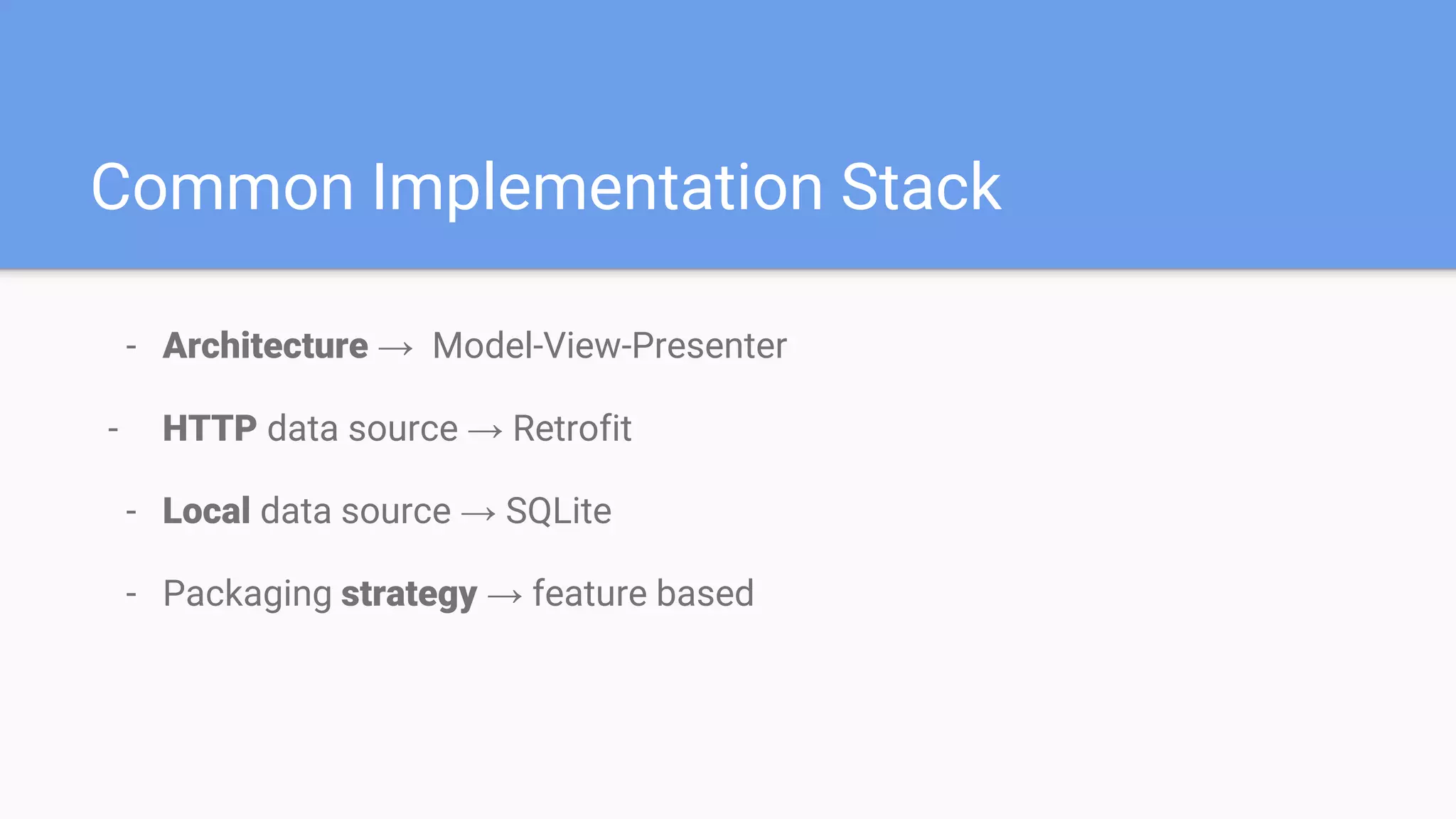
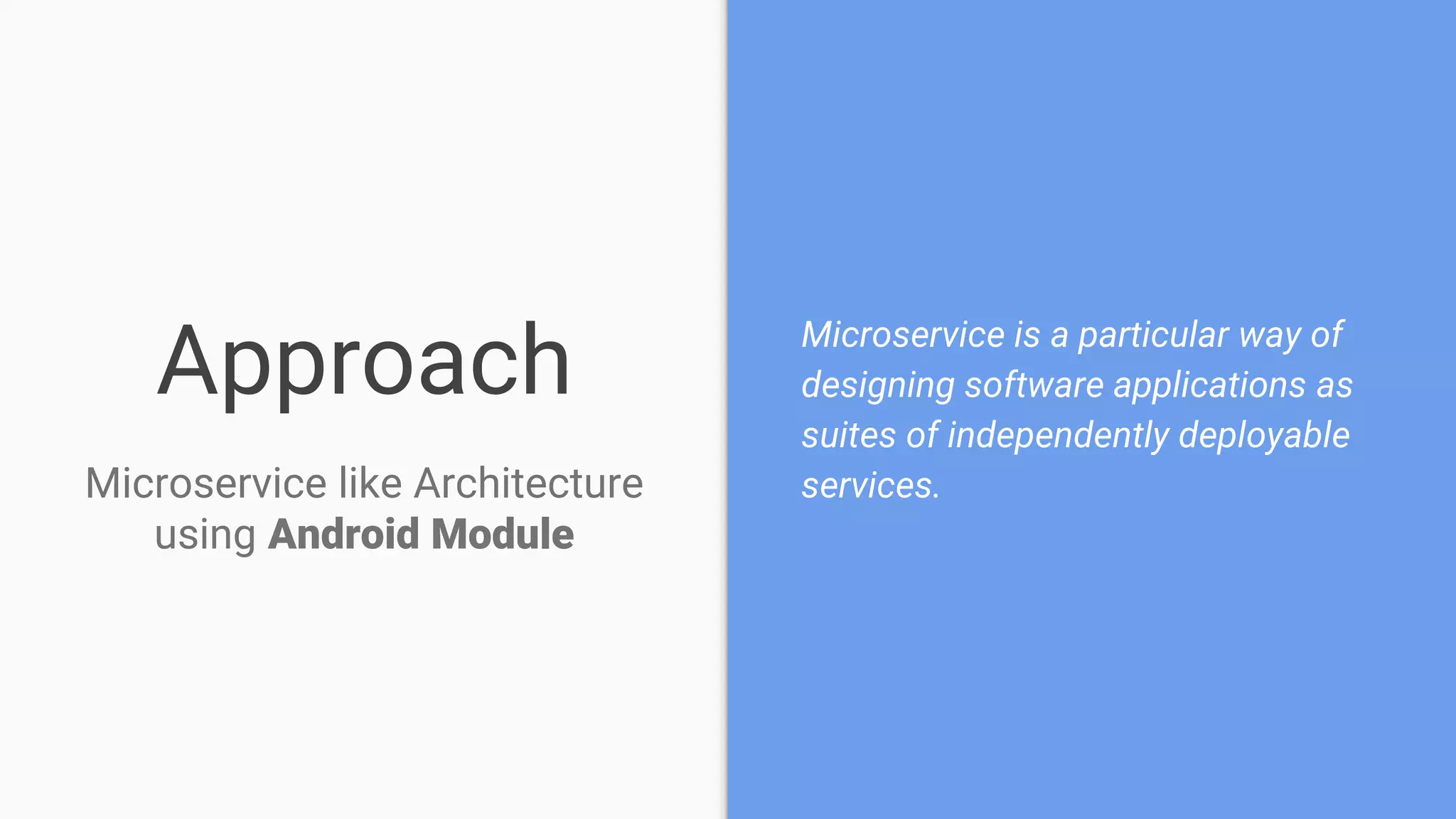
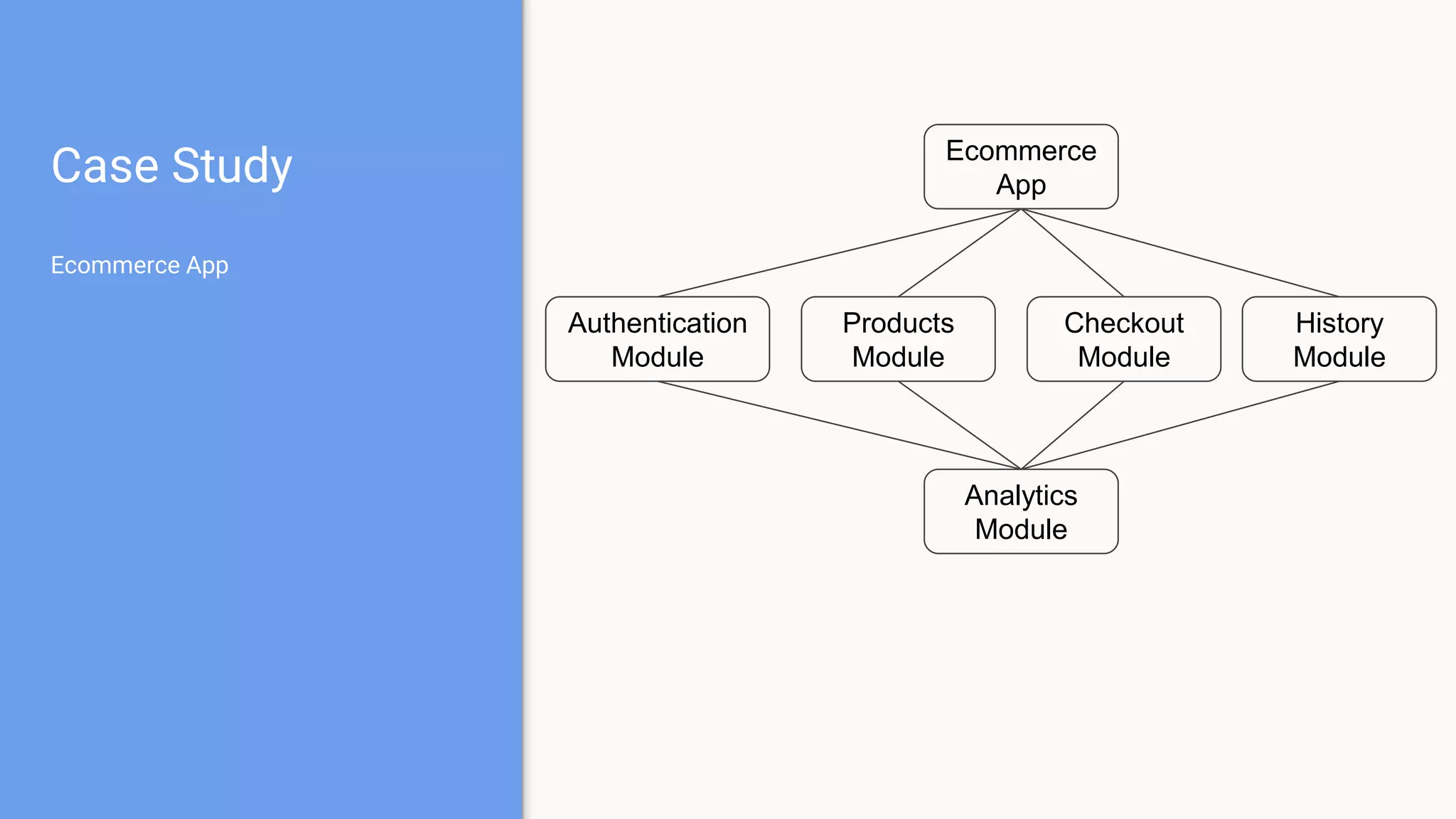
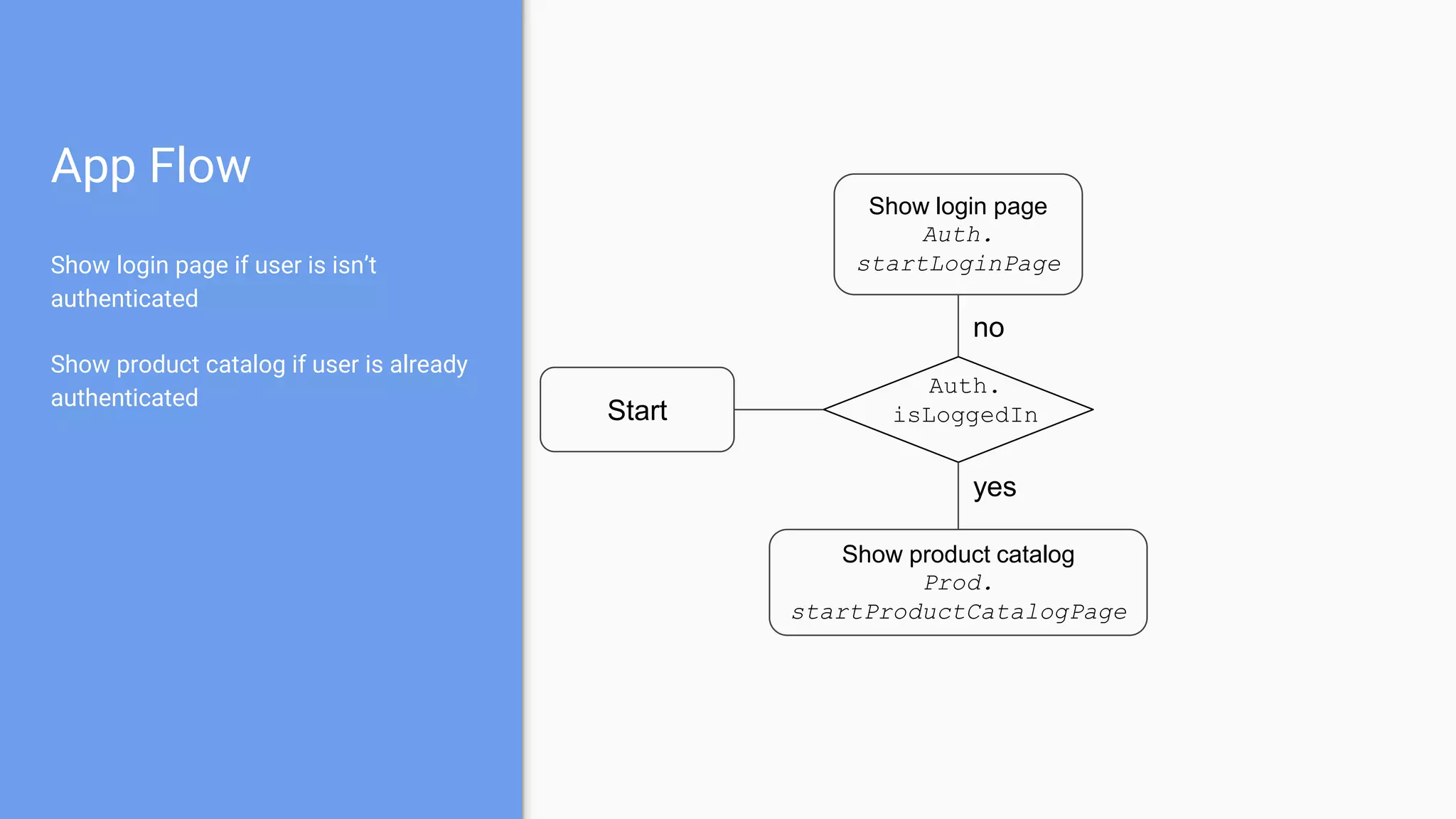
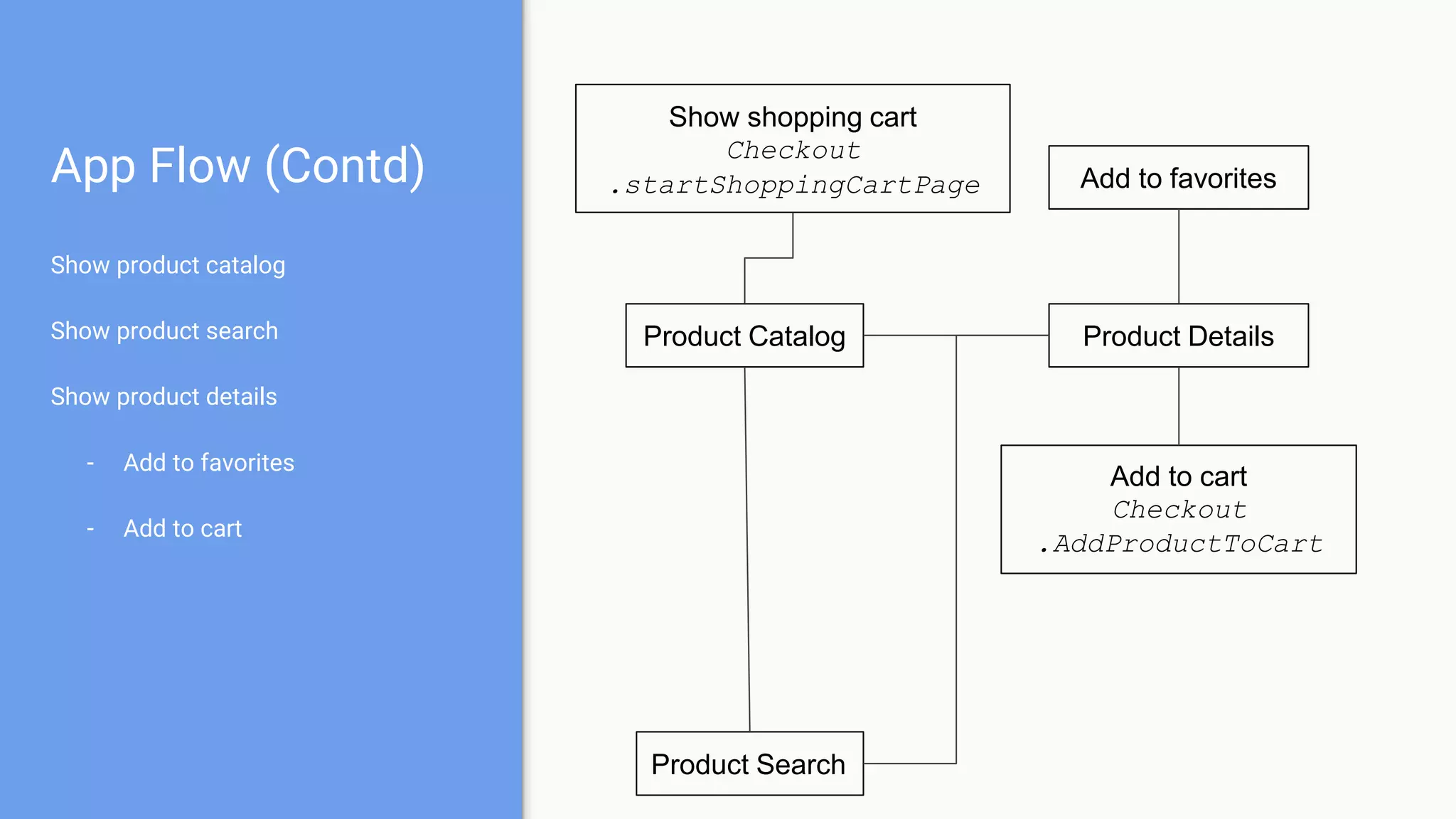
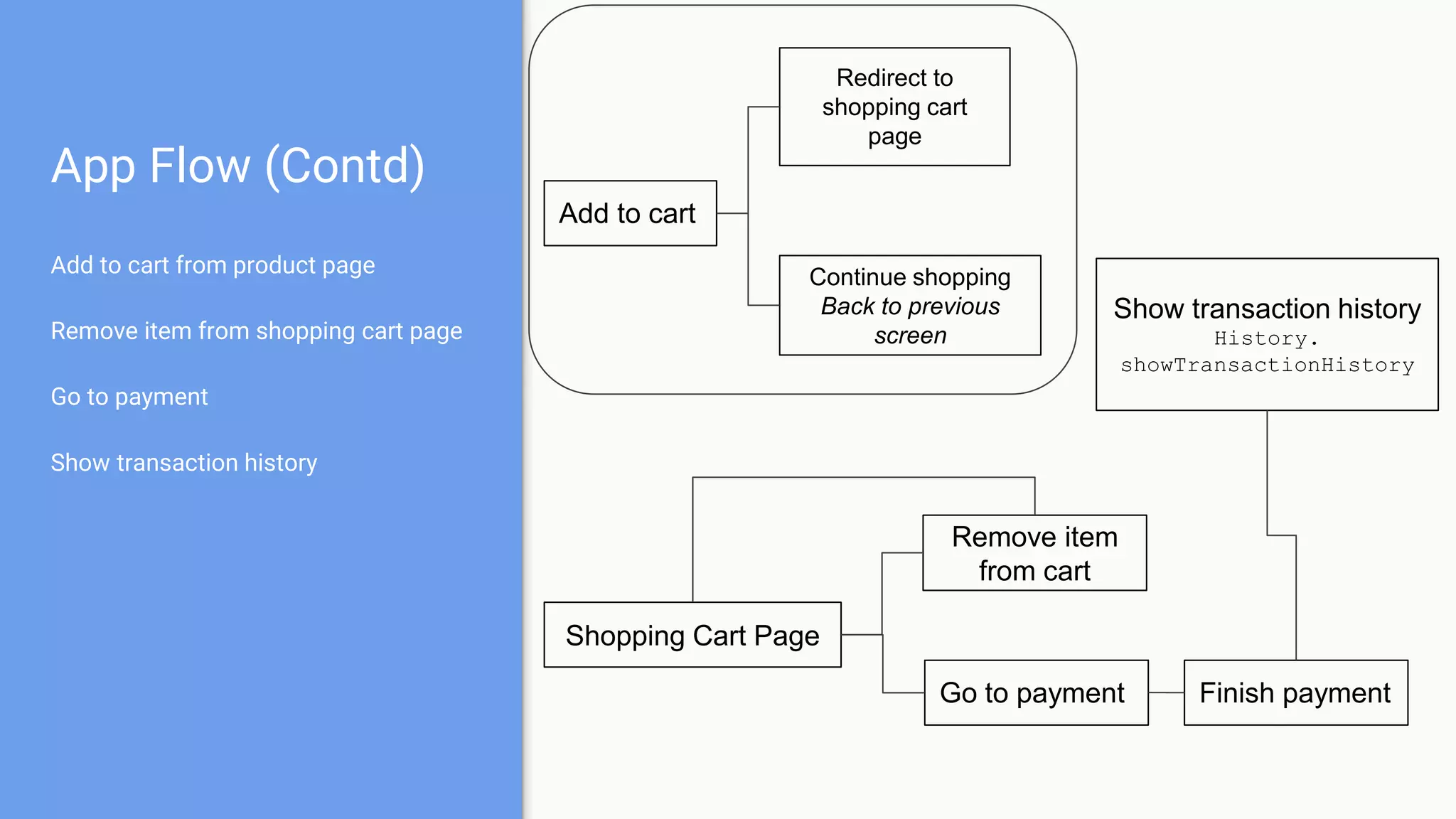
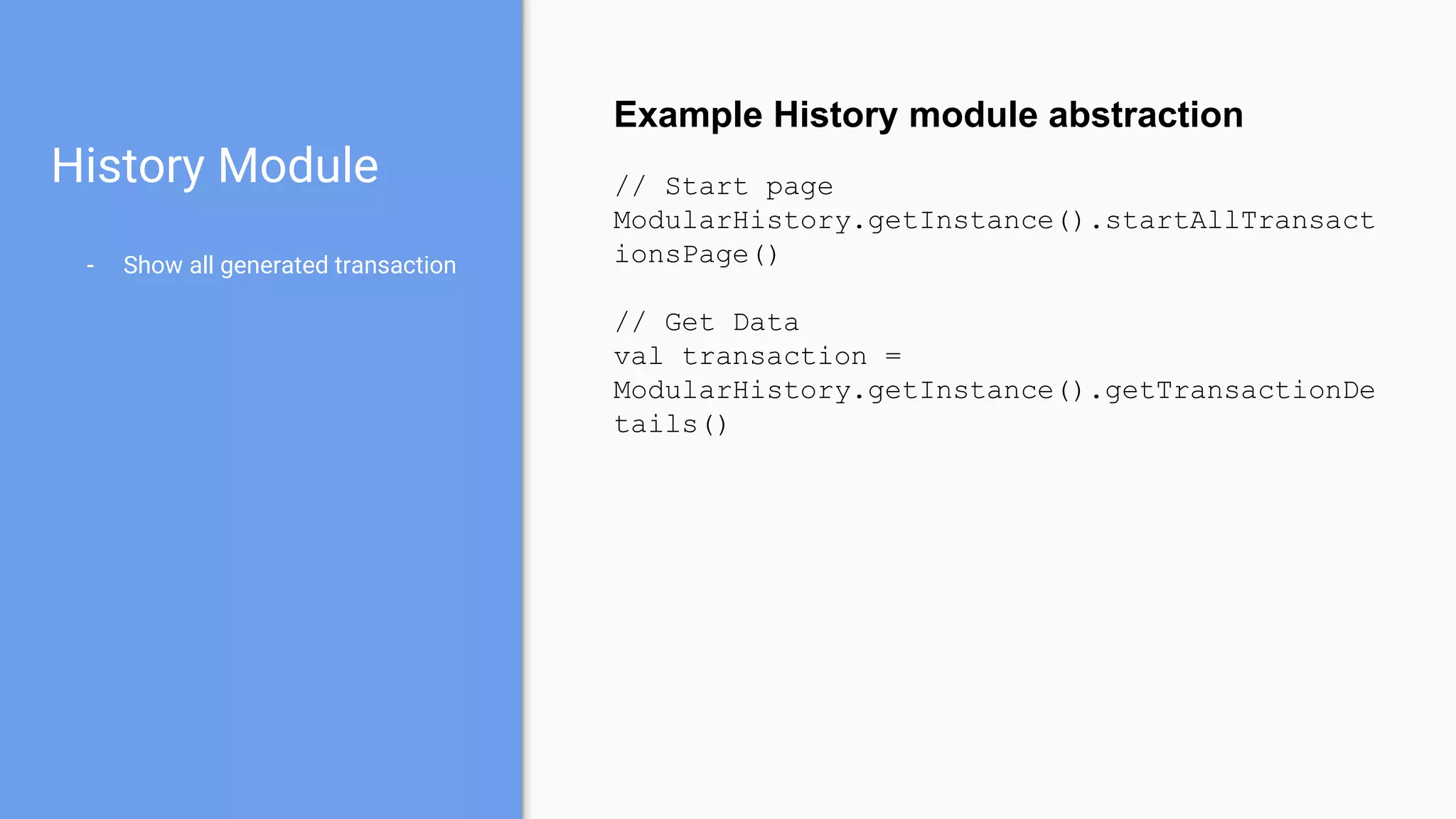
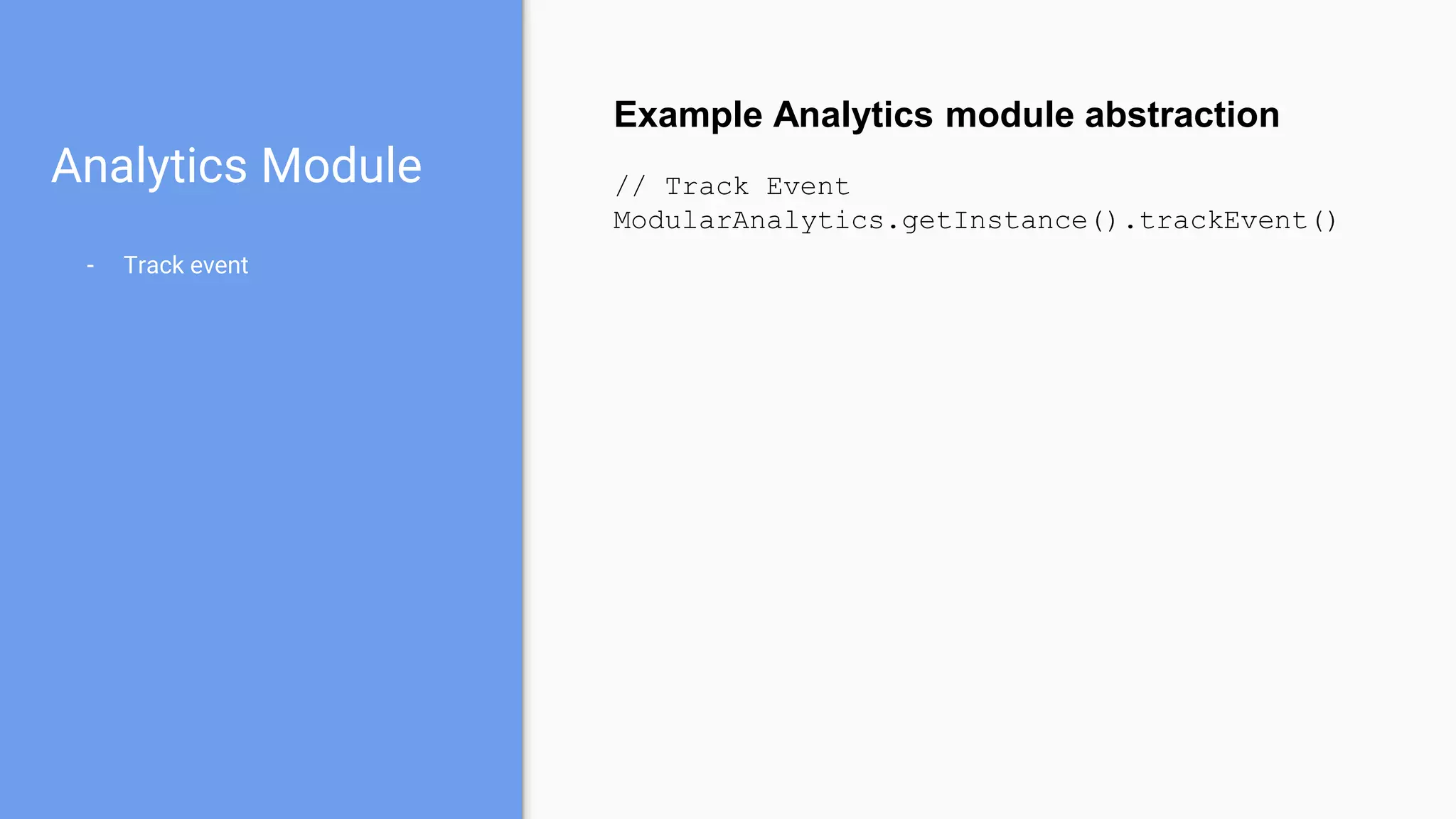
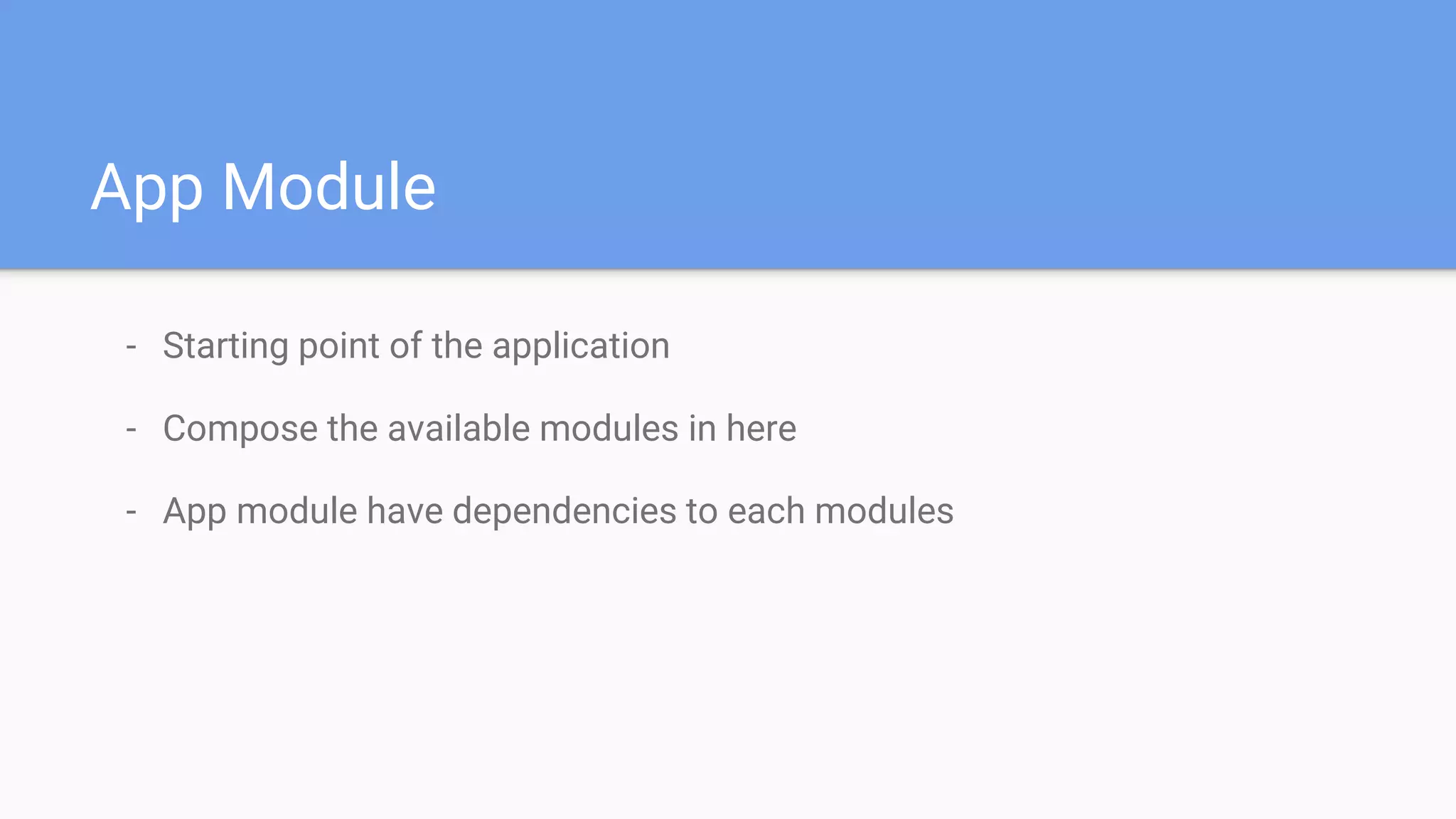
This document discusses using a modular architecture approach for Android projects. It proposes decomposing large apps into independent modules based on features or functions. This allows each module to be developed separately by different teams. The document provides examples of common module types like authentication and checkout. It describes advantages like reusability and easier collaboration. Communicating between modules can be done through interfaces or an event bus. The modular approach is compared to a traditional monolithic architecture.