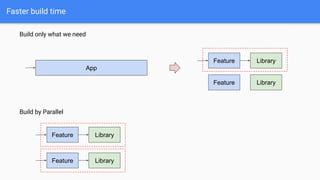
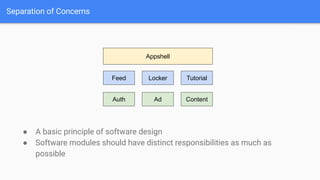
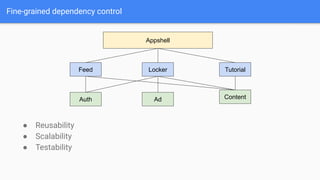
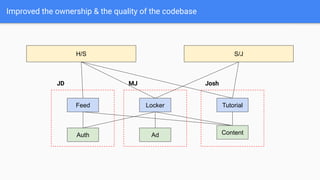
This document discusses strategies for modularizing an Android app. It recommends separating the app into modules based on features or libraries to achieve benefits like faster build times, improved reusability, and better code quality. Key modules include an appshell module to handle dependency injection and navigation between features, feature modules that group related functionality, and library modules to extract shared code. Navigation between modules could use reflection, interfaces, or Jetpack Navigation. Communication may involve callbacks, RxJava, or LiveData. The document also covers source control, branching strategies, versioning, build tools, and continuous integration considerations for a modularized app codebase.