Chemical Formulas and Compounds Classification
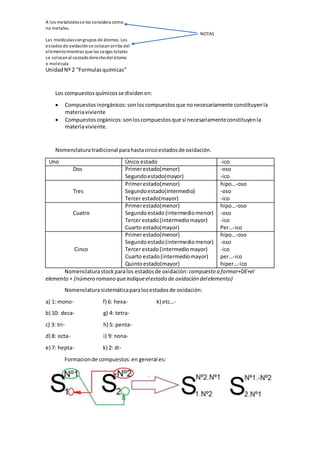
- 1. A los metaloidesse los considera como no metales. NOTAS Las moléculassongrupos de átomos. Los estados de oxidaciónse colocanarriba del elementomientras que las cargas totales se colocanal costadoderechodel átomo o molécula UnidadNº 2 “Formulasquímicas” Los compuestosquímicosse dividenen: Compuestosinorgánicos:sonloscompuestosque nonecesariamente constituyenla materiaviviente Compuestos orgánicos:sonloscompuestosque si necesariamenteconstituyenla materiaviviente. Nomenclaturatradicional parahastacincoestadosde oxidación. Uno Único estado -ico Dos Primerestado(menor) Segundoestado(mayor) -oso -ico Tres Primerestado(menor) Segundoestado(intermedio) Tercer estado(mayor) hipo…-oso -oso -ico Cuatro Primerestado(menor) Segundoestado(intermediomenor) Tercer estado(intermediomayor) Cuarto estado(mayor) hipo…-oso -oso -ico Per…-ico Cinco Primerestado(menor) Segundoestado(intermediomenor) Tercer estado(intermediomayor) Cuarto estado(intermediomayor) Quintoestado(mayor) hipo…-oso -oso -ico per…-ico hiper…-ico Nomenclaturastockparalos estadosde oxidación: compuesto a formar+DE+el elemento + (número romano queindiqueelestado de oxidación delelemento) Nomenclaturasistemáticaparalosestadosde oxidación: a) 1: mono- f) 6: hexa- k) etc…- b) 10: deca- g) 4: tetra- c) 3: tri- h) 5: penta- d) 8: octa- i) 9: nona- e) 7: hepta- k) 2: di- Formacionde compuestos:en general es:
- 2. A los metaloidesse los considera como no metales. NOTAS Las moléculassongrupos de átomos. Los estados de oxidaciónse colocanarriba del elementomientras que las cargas totales se colocanal costadoderechodel átomo o molécula Óxidos:el oxígenoreaccionacontodosloselementosmenosconlosgasesnobles: Básicos:elementometálico+oxigeno;porejemplo,el óxidoferrosoomonóxidode hierrou óxidode hierro(III) Ácidos:elementonometálico+oxigeno;porejemplo:oxidosulfúrico Hidróxidos:oxidobásico+H2O M-1(OH)Nº1; por ejemplo,hidróxidoférricoy hidróxidoaluminicoohidróxidode aluminio. Ácidos:oxidoacido+ H2OH2NMONº1+Nº2; por ejemplo,acidosulfúrico,acido nítrico y acidonitroso. Hidruros:elemento+hidrogeno;el elementosiempre actúaconsu menorvalencia: Metálicos:MNº1 + H-1 𝑀1 𝑁º1 𝐻𝑁º1 𝑁º1.1 ; por ejemplo,hidrurode aluminioy hidrurode hierro No metálicos NM-Nº1 +H+1 N𝑀1 𝑁º1 𝐻𝑁º1 𝑁º1 ; al nombre del elementose le pone prefijouro yen agua sonácidosya que se nombranacido+el nombre del elementoque se le cambia el uro porhídrico; por ejemplo,sulfurode hidrogenoque enaguaes ácidosulfúrico. Sales:se lescambialas terminaciones osoporito e ico por ato: Oxisales:HNMO+M(OH)NMMO+H2O; por ejemplo,sulfatode sodio, sulfitocúprico,nitratoargentosoycarbonitode cadmio. Básicas:las haymonobásicas,tribásicas,etc.: HNM+M(OH)NMOMNM(OH)+H2O; carbonitobásicocobalticoy carbonato monobásicocobaltico. Acidas:lashay monoacidas,triacidas,etc.: HNM+M(OH)NMHM+H20; por ejemplo,carbonatoacidode sodio Neutras(haloideas):hidróxido+hidruronometálico;sunomenclaturaesdiferentealas de otras sales,se nombran:el nometal con uro+de+el metal,ysi esnecesariose usala nomenclaturasistemática;porejemplo,el clorurode sodio,monosulfurode disodioy trisulfurode aluminio;tambiénliberanagua. Nomenclaturade nometalesconnometales:prefijode cantidad-el nombrede unno metal-uro+de+prefijode cantidad-el nombre de otronometal;porejemplo,carburode azufre o sulfurode carbono.
- 3. A los metaloidesse los considera como no metales. NOTAS Las moléculassongrupos de átomos. Los estados de oxidaciónse colocanarriba del elementomientras que las cargas totales se colocanal costadoderechodel átomo o molécula Valenciasconlasque actúan algunosátomosysus diferencias H= ±1 no metal Li=1 metal B= 3 metaloide C= 2, ±4 no metal N= ±3 y 5 no metal O= -2 nometal F= -1 nometal Na= 1 metal Mg= 2 metal Al=3 metal Si= 4 metaloide P= ± 3 y 5 no metal S= (-2),4 y 6 nometal Cl= ±1, 3, 5 y 7 K= 1 metal Ca= 2 metal Cr= 2, 3 y 6 metal Mn= 2, 3, 4 y 7 metal Fe= 2 y 3 metal Co= 2 y 3 metal Ni=2 y 3 metal Cu= 1 y 2 metal Zn= 2 metal As= ±3 y 5 metaloide Br= ±1, 3, 5 y 7 no metal Ag= 1 metal Sn= 2 y 4 metal I= ±1, 3, 5 y 7 no metal Pt= 2 y 4 metal
- 4. A los metaloidesse los considera como no metales. NOTAS Las moléculassongrupos de átomos. Los estados de oxidaciónse colocanarriba del elementomientras que las cargas totales se colocanal costadoderechodel átomo o molécula Au= 1 y 3 metal Hg= 1 y 2 metal Pb= 2 y 4 metal Excepciones: (NH4)+ amoniaco (H3O)+ hidronio (NO2)+ nitronio (AsO4)-3 arseniato (AsO3)-3 arsenito (BO3)-3 borato (CrO4)-2 cromato (Cr2O7)-2 dicromato (PO4)-3 fosfato (HPO4)-2 fosfato acido (H2PO4)-1 fosfato diácido (PO3)-3 fosfito (MnO4)-1 permanganato (OH)-1 oxidrilo o hidróxido (C-4 N)-1 cianuro (C)-1 carburo (He)+2 partícula alfa (H)+ hidrogenión