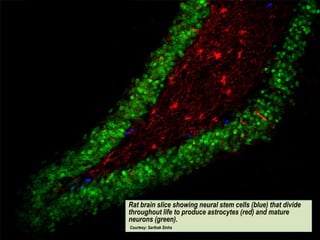
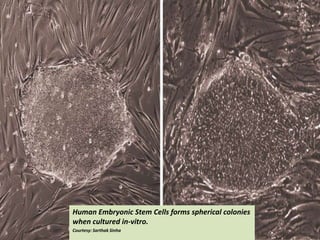
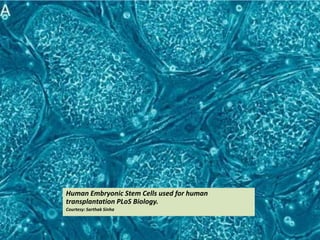
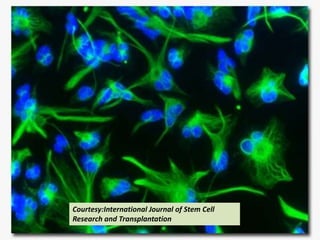
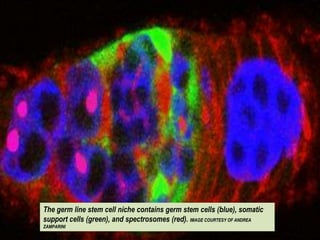
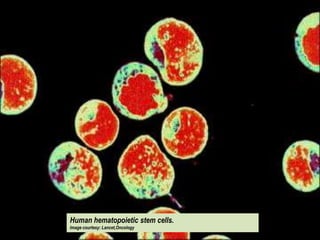
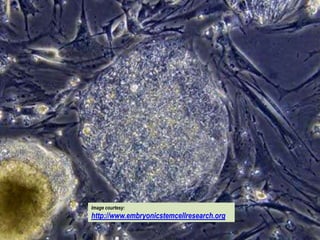
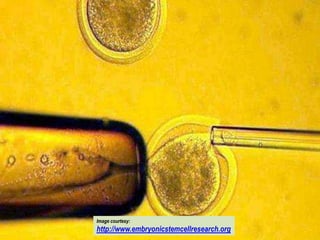
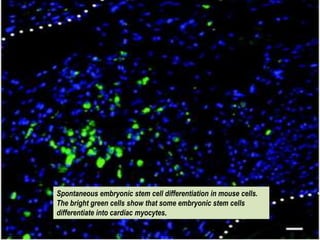
This document presents a picture gallery of stem cells from various published papers and research. It includes images of neural stem cells in rat brain tissue, human embryonic stem cells forming colonies in vitro and for transplantation, germ line stem cells in tissue, and hematopoietic stem cells. Captions describe the stem cell types and sources. The document also lists important milestones in embryonic stem cell research from 1981 onward, such as the first in vitro mouse stem cell line and first primate embryonic stem cell line.